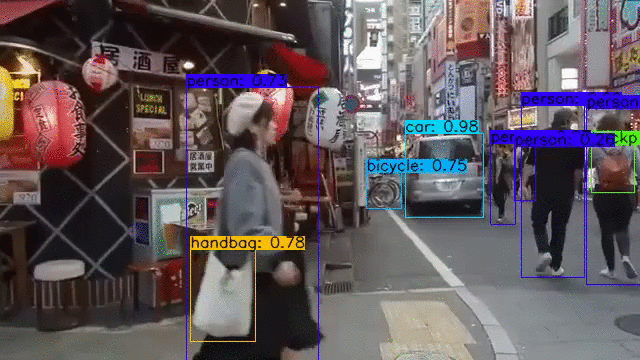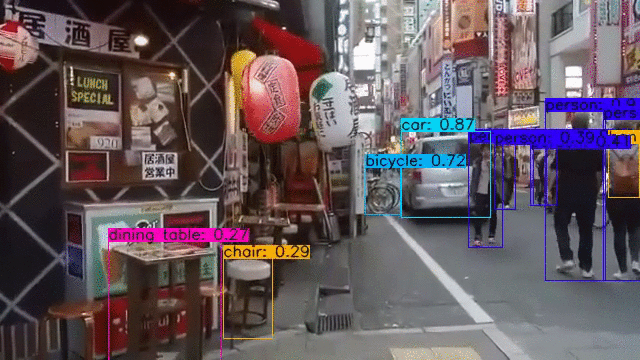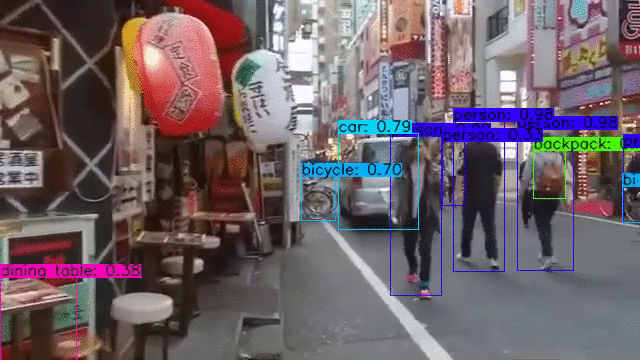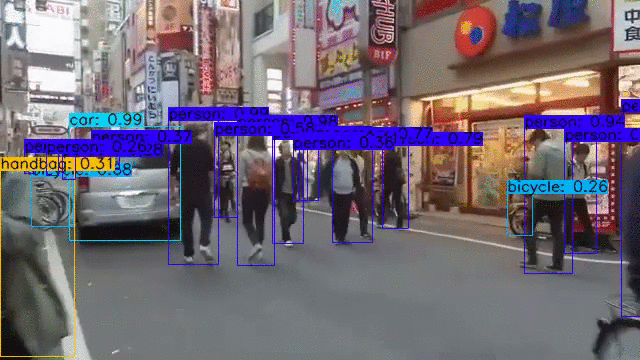
YOLOv4, YOLOv4-tiny Implemented in Tensorflow 2.0. Convert YOLO v4, YOLOv3, YOLO tiny .weights to .pb, .tflite and trt format for tensorflow, tensorflow lite, tensorRT.
# Tensorflow CPU
conda env create -f conda-cpu.yml
conda activate yolov4-cpu
# Tensorflow GPU
conda env create -f conda-gpu.yml
conda activate yolov4-gpu# TensorFlow CPU
pip install -r requirements.txt
# TensorFlow GPU
pip install -r requirements-gpu.txtMake sure to use CUDA Toolkit version 10.1 as it is the proper version for the TensorFlow version used in this repository. https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-10.1-download-archive-update2
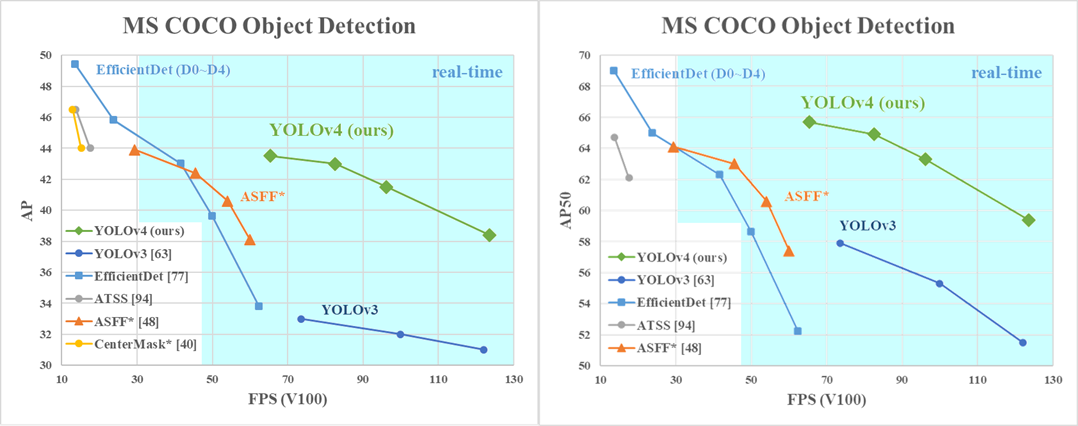
Check out how YOLOv4 compares to other object detection systems.
YOLOv4 comes pre-trained and able to detect 80 classes. For easy demo purposes we will use the pre-trained weights. Download pre-trained yolov4.weights file: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1cewMfusmPjYWbrnuJRuKhPMwRe_b9PaT
Copy and paste yolov4.weights from your downloads folder into the 'data' folder of this repository.
If you want to use yolov4-tiny.weights, a smaller model that is faster at running detections but less accurate, download file here: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/releases/download/darknet_yolo_v4_pre/yolov4-tiny.weights
Learn How To Train Custom YOLOv4 Weights here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mmj3nxGT2YQ
Copy and paste your custom .weights file into the 'data' folder and copy and paste your custom .names into the 'data/classes/' folder.
The only change within the code you need to make in order for your custom model to work is on line 14 of 'core/config.py' file. Update the code to point at your custom .names file as seen below. (my custom .names file is called custom.names but yours might be named differently)
Note: If you are using the pre-trained yolov4 then make sure that line 14 remains coco.names.
To implement YOLOv4 using TensorFlow, first we convert the .weights into the corresponding TensorFlow model files and then run the model.
# Convert darknet weights to tensorflow
## yolov4
python save_model.py --weights ./data/yolov4.weights --output ./checkpoints/yolov4-416 --input_size 416 --model yolov4
# yolov4-tiny
python save_model.py --weights ./data/yolov4-tiny.weights --output ./checkpoints/yolov4-tiny-416 --input_size 416 --model yolov4 --tiny
# custom yolov4
python save_model.py --weights ./data/custom.weights --output ./checkpoints/custom-416 --input_size 416 --model yolov4
# Run yolov4 tensorflow model
python detect.py --weights ./checkpoints/yolov4-416 --size 416 --model yolov4 --images ./data/images/kite.jpg
# Run yolov4-tiny tensorflow model
python detect.py --weights ./checkpoints/yolov4-tiny-416 --size 416 --model yolov4 --images ./data/images/kite.jpg --tiny
# Run custom yolov4 tensorflow model
python detect.py --weights ./checkpoints/custom-416 --size 416 --model yolov4 --images ./data/images/car.jpg
# Run yolov4 on video
python detect_video.py --weights ./checkpoints/yolov4-416 --size 416 --model yolov4 --video ./data/video/video.mp4 --output ./detections/results.avi
# Run yolov4 on webcam
python detect_video.py --weights ./checkpoints/yolov4-416 --size 416 --model yolov4 --video 0 --output ./detections/results.aviIf you want to run yolov3 or yolov3-tiny change --model yolov3 and .weights file in above commands.
Note: You can also run the detector on multiple images at once by changing the --images flag like such --images "./data/images/kite.jpg, ./data/images/dog.jpg"
You can find the outputted image(s) showing the detections saved within the 'detections' folder.
Video saves wherever you point --output flag to. If you don't set the flag then your video will not be saved with detections on it.
Can also implement YOLOv4 using TensorFlow Lite. TensorFlow Lite is a much smaller model and perfect for mobile or edge devices (raspberry pi, etc).
# Save tf model for tflite converting
python save_model.py --weights ./data/yolov4.weights --output ./checkpoints/yolov4-416 --input_size 416 --model yolov4 --framework tflite
# yolov4
python convert_tflite.py --weights ./checkpoints/yolov4-416 --output ./checkpoints/yolov4-416.tflite
# yolov4 quantize float16
python convert_tflite.py --weights ./checkpoints/yolov4-416 --output ./checkpoints/yolov4-416-fp16.tflite --quantize_mode float16
# yolov4 quantize int8
python convert_tflite.py --weights ./checkpoints/yolov4-416 --output ./checkpoints/yolov4-416-int8.tflite --quantize_mode int8 --dataset ./coco_dataset/coco/val207.txt
# Run tflite model
python detect.py --weights ./checkpoints/yolov4-416.tflite --size 416 --model yolov4 --images ./data/images/kite.jpg --framework tfliteYou can find the outputted image(s) showing the detections saved within the 'detections' folder.
Yolov4 and Yolov4-tiny int8 quantization have some issues. I will try to fix that. You can try Yolov3 and Yolov3-tiny int8 quantization
Can also implement YOLOv4 using TensorFlow's TensorRT. TensorRT is a high-performance inference optimizer and runtime that can be used to perform inference in lower precision (FP16 and INT8) on GPUs. TensorRT can allow up to 8x higher performance than regular TensorFlow.
python save_model.py --weights ./data/yolov3.weights --output ./checkpoints/yolov3.tf --input_size 416 --model yolov3
python convert_trt.py --weights ./checkpoints/yolov3.tf --quantize_mode float16 --output ./checkpoints/yolov3-trt-fp16-416
# yolov3-tiny
python save_model.py --weights ./data/yolov3-tiny.weights --output ./checkpoints/yolov3-tiny.tf --input_size 416 --tiny
python convert_trt.py --weights ./checkpoints/yolov3-tiny.tf --quantize_mode float16 --output ./checkpoints/yolov3-tiny-trt-fp16-416
# yolov4
python save_model.py --weights ./data/yolov4.weights --output ./checkpoints/yolov4.tf --input_size 416 --model yolov4
python convert_trt.py --weights ./checkpoints/yolov4.tf --quantize_mode float16 --output ./checkpoints/yolov4-trt-fp16-416
python detect.py --weights ./checkpoints/yolov4-trt-fp16-416 --model yolov4 --images ./data/images/kite.jpg --framework trt
save_model.py:
--weights: path to weights file
(default: './data/yolov4.weights')
--output: path to output
(default: './checkpoints/yolov4-416')
--[no]tiny: yolov4 or yolov4-tiny
(default: 'False')
--input_size: define input size of export model
(default: 416)
--framework: what framework to use (tf, trt, tflite)
(default: tf)
--model: yolov3 or yolov4
(default: yolov4)
detect.py:
--images: path to input images as a string with images separated by ","
(default: './data/images/kite.jpg')
--output: path to output folder
(default: './detections/')
--[no]tiny: yolov4 or yolov4-tiny
(default: 'False')
--weights: path to weights file
(default: './checkpoints/yolov4-416')
--framework: what framework to use (tf, trt, tflite)
(default: tf)
--model: yolov3 or yolov4
(default: yolov4)
--size: resize images to
(default: 416)
--iou: iou threshold
(default: 0.45)
--score: confidence threshold
(default: 0.25)
detect_video.py:
--video: path to input video (use 0 for webcam)
(default: './data/video/video.mp4')
--output: path to output video (remember to set right codec for given format. e.g. XVID for .avi)
(default: None)
--output_format: codec used in VideoWriter when saving video to file
(default: 'XVID)
--[no]tiny: yolov4 or yolov4-tiny
(default: 'false')
--weights: path to weights file
(default: './checkpoints/yolov4-416')
--framework: what framework to use (tf, trt, tflite)
(default: tf)
--model: yolov3 or yolov4
(default: yolov4)
--size: resize images to
(default: 416)
--iou: iou threshold
(default: 0.45)
--score: confidence threshold
(default: 0.25)# run script in /script/get_coco_dataset_2017.sh to download COCO 2017 Dataset
# preprocess coco dataset
cd data
mkdir dataset
cd ..
cd scripts
python coco_convert.py --input ./coco/annotations/instances_val2017.json --output val2017.pkl
python coco_annotation.py --coco_path ./coco
cd ..
# evaluate yolov4 model
python evaluate.py --weights ./data/yolov4.weights
cd mAP/extra
python remove_space.py
cd ..
python main.py --output results_yolov4_tf| Detection | 512x512 | 416x416 | 320x320 |
|---|---|---|---|
| YoloV3 | 55.43 | 52.32 | |
| YoloV4 | 61.96 | 57.33 |
python benchmarks.py --size 416 --model yolov4 --weights ./data/yolov4.weights| YoloV4 416 images/s | FP32 | FP16 | INT8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch size 1 | 55 | 116 | |
| Batch size 8 | 70 | 152 |
| Detection | 512x512 | 416x416 | 320x320 |
|---|---|---|---|
| YoloV3 FPS | 40.6 | 49.4 | 61.3 |
| YoloV4 FPS | 33.4 | 41.7 | 50.0 |
| Detection | 512x512 | 416x416 | 320x320 |
|---|---|---|---|
| YoloV3 FPS | 10.8 | 12.9 | 17.6 |
| YoloV4 FPS | 9.6 | 11.7 | 16.0 |
| Detection | 512x512 | 416x416 | 320x320 |
|---|---|---|---|
| YoloV3 FPS | 27.6 | 32.3 | 45.1 |
| YoloV4 FPS | 24.0 | 30.3 | 40.1 |
| Detection | 512x512 | 416x416 | 320x320 |
|---|---|---|---|
| YoloV3 FPS | 20.2 | 24.2 | 31.2 |
| YoloV4 FPS | 16.2 | 20.2 | 26.5 |
| Detection | 512x512 | 416x416 | 320x320 |
|---|---|---|---|
| YoloV3 FPS | |||
| YoloV4 FPS |
# Prepare your dataset
# If you want to train from scratch:
In config.py set FISRT_STAGE_EPOCHS=0
# Run script:
python train.py
# Transfer learning:
python train.py --weights ./data/yolov4.weightsThe training performance is not fully reproduced yet, so I recommended to use Alex's Darknet to train your own data, then convert the .weights to tensorflow or tflite.
Use this video to train your own model easily in Google Colab: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mmj3nxGT2YQ
- Convert YOLOv4 to TensorRT
- YOLOv4 tflite on android
- YOLOv4 tflite on ios
- Training code
- Update scale xy
- ciou
- Mosaic data augmentation
- Mish activation
- yolov4 tflite version
- yolov4 in8 tflite version for mobile
My project is inspired by these previous fantastic YOLOv3 implementations: