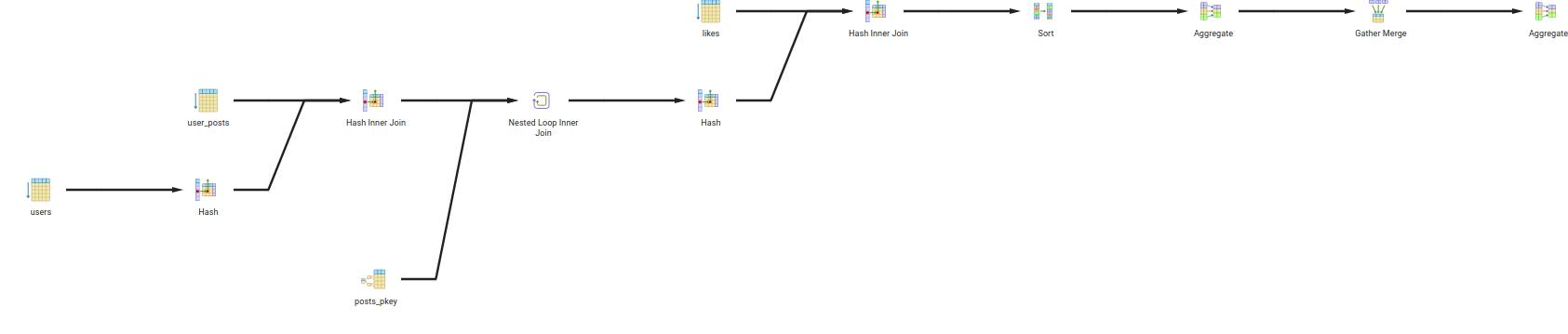
- Query 1:
- Description: Find posts of users in city 1 with more than 20 likes.
- Query:
SELECT p.body FROM posts p JOIN user_posts up ON up.post_id = p.id JOIN users u ON u.id = up.user_id JOIN likes l ON l.post_id = p.id WHERE u.city = 'city 1' GROUP BY p.id HAVING COUNT(l.id) > 20;
- Explain:
- The query will first join the
poststable withuser_poststable onpost_idcolumn. - Then it will join the result with
userstable onuser_idcolumn. - Then it will join the result with
likestable onpost_idcolumn. - Then it will filter the result by
citycolumn. - Then it will group the result by
idcolumn. - Then it will filter the result by
COUNT(l.id) > 20.
- The query will first join the
- Query Tree:
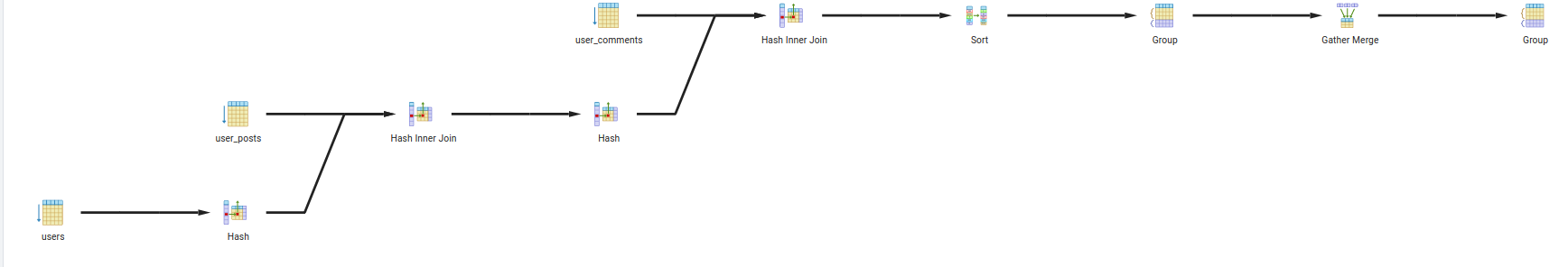
- Query 2:
- Description: Find all the comments and posts of a user that is older than 25 and lives in city 1
- Query:
SELECT uc.comment_id, up.post_id FROM users u INNER JOIN user_posts up ON u.id = up.user_id INNER JOIN user_comments uc ON u.id = uc.user_id WHERE u.age > 25 and u.city = 'city 1' GROUP BY up.post_id , uc.comment_id;
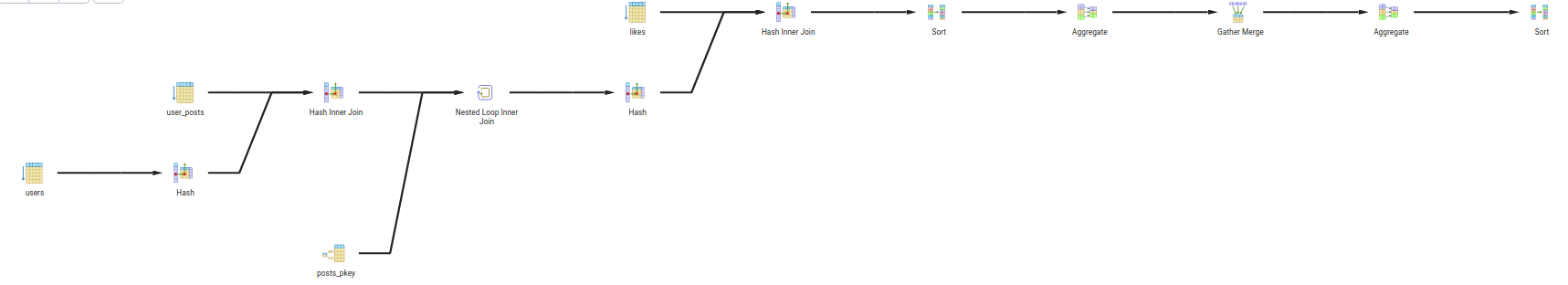
- Query 3:
- Description: Find the posts with most likes in city 1.
- Query:
SELECT p.body, u.city, COUNT(l.id) AS likes_count FROM posts p JOIN user_posts up ON up.post_id = p.id JOIN users u ON u.id = up.user_id JOIN likes l ON l.post_id = p.id WHERE u.city = 'city 1' GROUP BY u.city, p.body ORDER BY likes_count DESC;
- Explain:
- The query will first join the
poststable withuser_poststable onpost_idcolumn. - Then it will join the result with
userstable onuser_idcolumn. - Then it will join the result with
likestable onpost_idcolumn. - Then it will filter the result by
city = 'city 1'. - Then it will group the result by
cityandbody. - Then it will order the result by
likes_countin descending order.
- The query will first join the
- Query Tree:
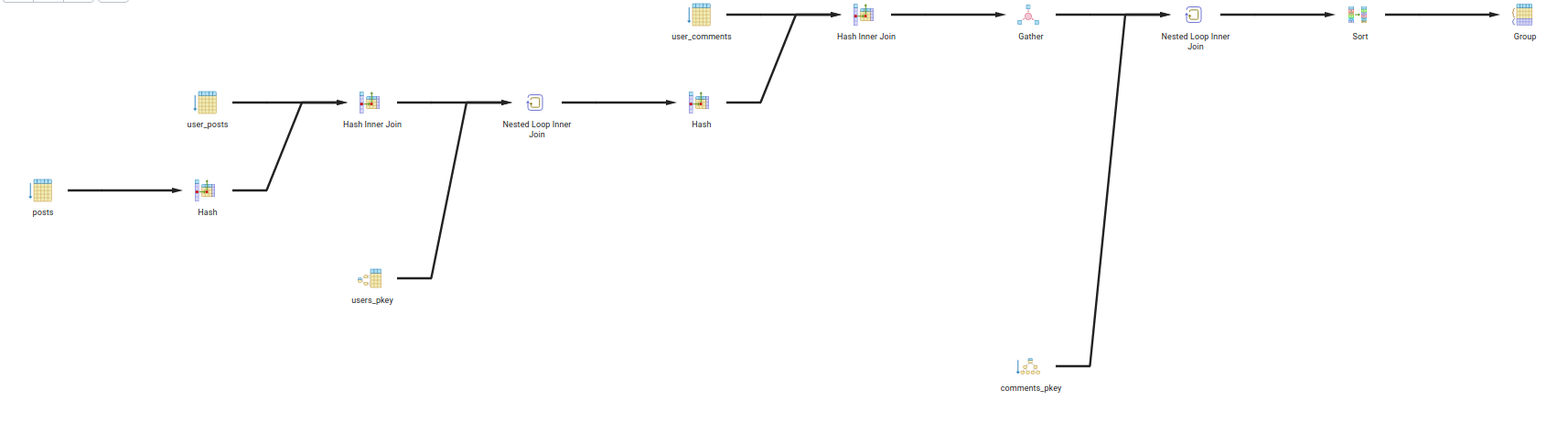
- Query 4:
- Description: Get the full details of all the posts that has 1 in the title and 2 in the body from users that are older than 28 and live in city 1
- Query:
SELECT up.post_id , p.body , p.title FROM users u INNER JOIN user_posts up ON u.id = up.user_id INNER JOIN user_comments uc ON u.id = uc.user_id INNER JOIN posts p ON p.id = up.post_id INNER JOIN comments c ON c.id = uc.comment_id WHERE u.age > 28 and u.City = 'city 1' and p.title LIKE '%title 1%' and p.body LIKE '%body 2%' GROUP BY up.post_id, p.body, p.title;
- Explain:
- The query will first join the
userstable withuser_poststable onidcolumn. - Then it will join the result with
user_commentstable onuser_idcolumn. - Then it will join the result with
poststable onpost_idcolumn. - Then it will join the result with
commentstable oncomment_idcolumn. - Then it will filter the result by
age > 28andcity = 'city 1'andtitle LIKE '%title 1%'andbody LIKE '%body 2%'. - Then it will group the result by
post_id,body,title.
- The query will first join the
- Query Tree:
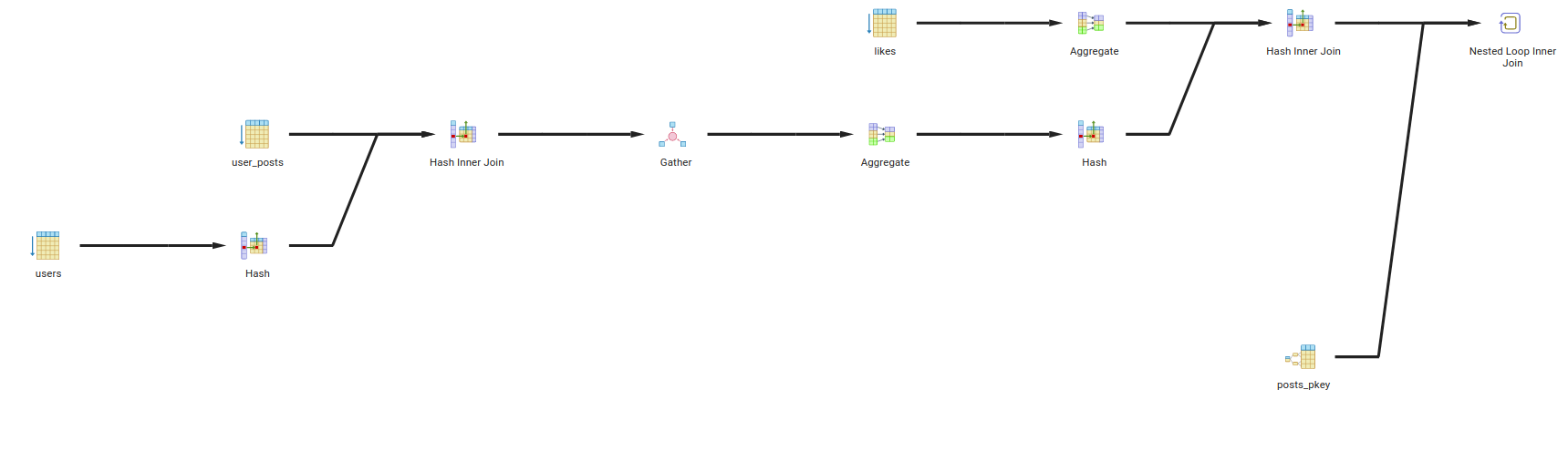
- Query 1:
- Description: Find posts of users in city 1 with more than 20 likes.
- Query:
SELECT p.body FROM posts p where p.id in (SELECT up.post_id FROM user_posts up JOIN users u ON u.id = up.user_id WHERE u.city = 'city 1') And p.id in (SELECT l.post_id FROM likes l GROUP BY l.post_id HAVING COUNT(l.id) > 20);
- Explain:
- The query will first join the
user_poststable withuserstable onidcolumn. - Then it will filter the result by
city = 'city 1'. - Then it will join the result with
likestable onpost_idcolumn. - Then it will group the result by
post_id. - Then it will filter the result by
COUNT(l.id) > 20. - Then it will select the
bodycolumn from the result.
- The query will first join the
- Query Tree:
- Query 2:
- Description: Find all the comments and posts of a user that is older than 25 and lives in city 1
- Query:
with CTE as (SELECT * FROM users WHERE age > 25 and city = 'city 1') SELECT uc.comment_id, up.post_id FROM CTE AS u INNER JOIN user_posts up ON u.id = up.user_id INNER JOIN user_comments uc ON u.id = uc.user_id GROUP BY up.post_id , uc.comment_id;
- Explain:
- The query will first filter the
userstable byage > 25andcity = 'city 1'using a CTE. - Then it will join the result with
user_poststable onuser_idcolumn. - Then it will join the result with
user_commentstable onuser_idcolumn. - Then it will group the result by
post_idandcomment_id.
- The query will first filter the
- Query Tree:
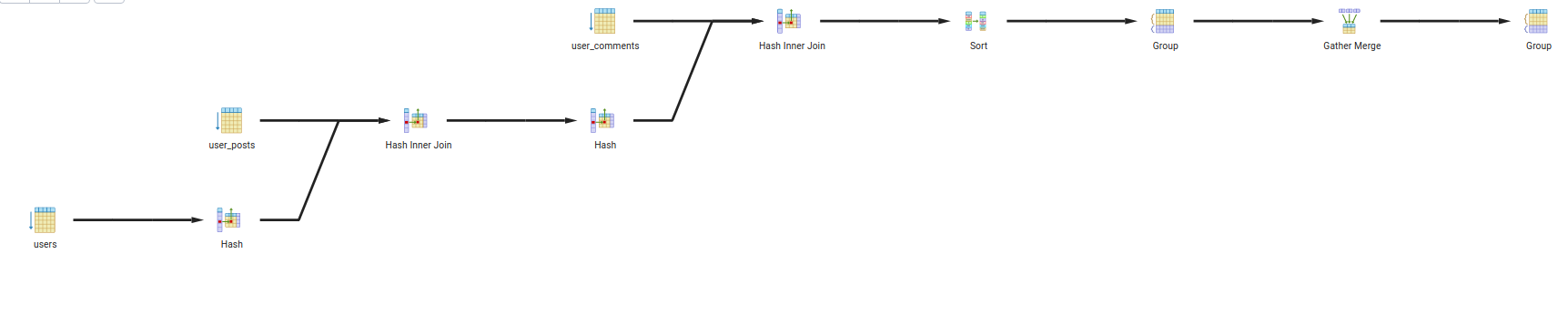
- Query 3:
- Description: Find the posts with most likes in city 1.
- Query:
SELECT p.body, u.city, COUNT(l.id) AS likes_count FROM posts p INNER JOIN user_posts up ON up.post_id = p.id INNER JOIN users u ON u.id = up.user_id INNER JOIN likes l ON l.post_id = p.id WHERE u.city = 'city 1' GROUP BY u.city, p.body ORDER BY likes_count DESC;
- Explain:
- The query will first join the
poststable withuser_poststable onpost_idcolumn. - Then it will join the result with
userstable onuser_idcolumn. - Then it will join the result with
likestable onpost_idcolumn. - Then it will filter the result by
city = 'city 1'. - Then it will group the result by
city,body. - Then it will order the result by
likes_countin descending order. - Then it will select the
body,city,likes_countcolumns.
- The query will first join the
- Query Tree:
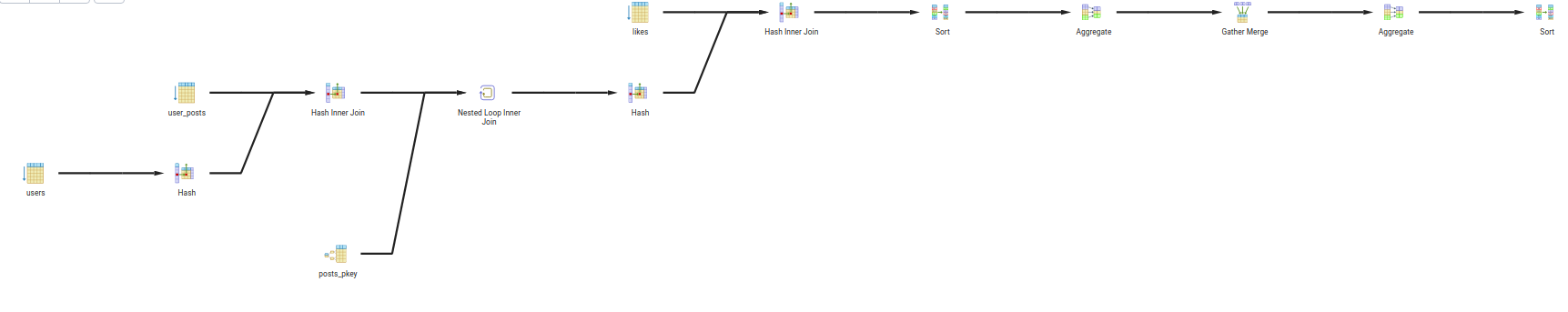
- Query 4:
- Description: Get the full details of all the posts that has 1 in the title and 2 in the body from users that are older than 28 and live in city 1
- Query:
with CTE as (SELECT * FROM users WHERE age > 25 and city = 'city 1') SELECT up.post_id FROM CTE AS u INNER JOIN user_posts up ON u.id = up.user_id inner join posts p on p.id = up.post_id where p.title LIKE '%title 1%' and p.body LIKE '%body 2%' GROUP BY up.post_id;
- Explain:
- The query will first filter the
userstable byage > 25andcity = 'city 1'using a CTE. - Then it will join the result with
user_poststable onuser_idcolumn. - Then it will join the result with
poststable onpost_idcolumn. - Then it will filter the result by
title LIKE '%title 1%'andbody LIKE '%body 2%'. - Then it will group the result by
post_id. - Then it will select the
post_idcolumn.
- The query will first filter the
- Query Tree:
- Query 1:
- Description: Find posts of users in city 1 with more than 20 likes.
- Query:
-- add index for post_id in user_posts table if not exists CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS user_posts_post_id_idx ON user_posts (post_id); -- add index for post_id in likes table if not exists CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS likes_post_id_idx ON likes (post_id); -- add index for city in users table if not exists CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS users_city_idx ON users (city); -- add index for user_id in user_posts table if not exists CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS user_posts_user_id_idx ON user_posts (user_id); -- use explain analyze to see the difference in execution time SELECT p.body FROM posts p JOIN user_posts up ON up.post_id = p.id JOIN users u ON u.id = up.user_id JOIN likes l ON l.post_id = p.id WHERE u.city = 'city 1' GROUP BY p.id HAVING COUNT(l.id) > 20;
- Explain:
- We have added indexes for
post_idinuser_poststable,post_idinlikestable,cityinuserstable, anduser_idinuser_poststable. - We have added those indexes to make the query more computationally efficient.
- For instance, we have added an index for
cityinuserstable to make the filtering bycity = 'city 1'more efficient. - We have added an index for
post_idinuser_poststable to make the join betweenpoststable anduser_poststable more efficient. - We have added an index for
post_idinlikestable to make the join betweenpoststable andlikestable more efficient. - We have added an index for
user_idinuser_poststable to make the join betweenuserstable anduser_poststable more efficient.
- We have added indexes for
- Query Tree:

- Query 2:
- Description: Find all the comments and posts of a user that is older than 25 and lives in city 1
- Query:
-- add composite index for users table if not exists CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS users_age_city_idx ON users (city, age); -- add index for user_id in user_posts table if not exists CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS user_posts_user_id_idx ON user_posts (user_id); -- we changed the order of the conditions in the where clause to make indexing more efficient SELECT uc.comment_id, up.post_id FROM users u INNER JOIN user_posts up ON u.id = up.user_id INNER JOIN user_comments uc ON u.id = uc.user_id WHERE u.city = 'city 1' and u.age > 25 GROUP BY up.post_id , uc.comment_id;
- Explain:
- We have added a composite index for
cityandageinuserstable, and an index foruser_idinuser_poststable. - We have added those indexes to make the query more computationally efficient.
- We have added a composite index for
cityandageinuserstable to make the filtering bycity = 'city 1'andage > 25more efficient. - We changed the order of the conditions in the
whereclause to make indexing more efficient. - We have added an index for
user_idinuser_poststable to make the join betweenuserstable anduser_poststable more efficient.
- We have added a composite index for
- Query Tree:
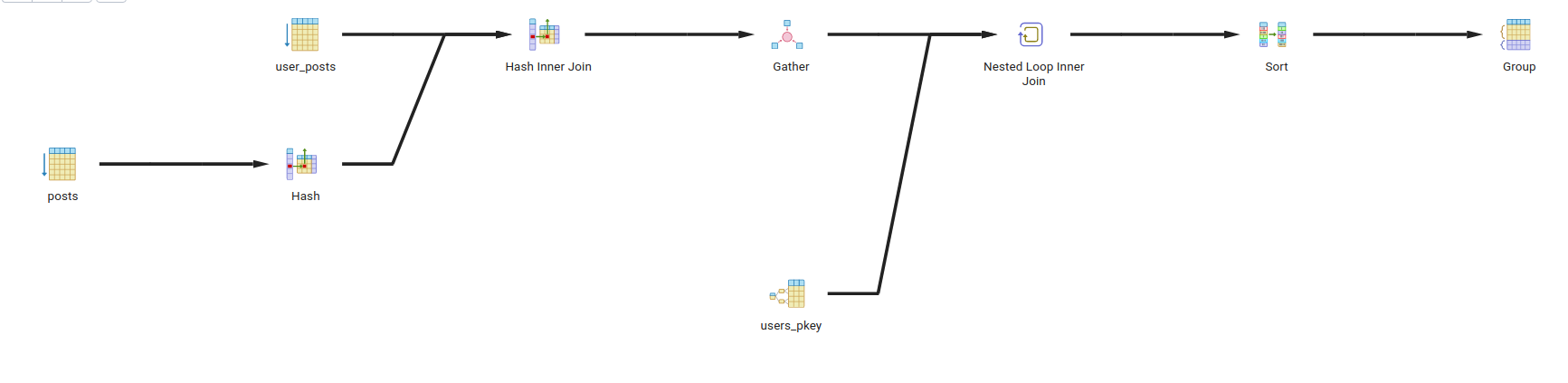
- Query 3:
- Description: Find the posts with most likes in city 1.
- Query:
-- add index for city in users table if not exists CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS users_city_idx ON users (city); -- add index for user_id in user_posts table if not exists CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS user_posts_user_id_idx ON user_posts (user_id); -- get the posts with max likes in every city SELECT p.body, u.city, COUNT(l.id) AS likes_count FROM posts p JOIN user_posts up ON up.post_id = p.id JOIN users u ON u.id = up.user_id JOIN likes l ON l.post_id = p.id WHERE u.city = 'city 1' GROUP BY u.city, p.body ORDER BY likes_count DESC;
- Explain:
- We have added an index for
cityinuserstable, and an index foruser_idinuser_poststable. - We have added those indexes to make the query more computationally efficient.
- We have added an index for
cityinuserstable to make the filtering bycity = 'city 1'more efficient. - We have added an index for
user_idinuser_poststable to make the join betweenuserstable anduser_poststable more efficient.
- We have added an index for
- Query Tree:

- Query 4:
- Description: Get the full details of all the posts that has 1 in the title and 2 in the body from users that are older than 28 and live in city 1
- Query:
-- add composite index for users table if not exists CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS users_age_city_idx ON users (city, age); -- we changed the order of the conditions in the where clause to make indexing more efficient -- indexing won't be efficient due to the use of LIKE operator SELECT up.post_id , p.body , p.title FROM users u INNER JOIN user_posts up ON u.id = up.user_id INNER JOIN user_comments uc ON u.id = uc.user_id INNER JOIN posts p ON p.id = up.post_id INNER JOIN comments c ON c.id = uc.comment_id WHERE u.City = 'city 1' and u.age > 28 and p.title LIKE '%title 12%' and p.body LIKE '%body 22%' GROUP BY up.post_id, p.body, p.title;
- Explain:
- We have added a composite index for
cityandageinuserstable. - We have added those indexes to make the query more computationally efficient.
- We have added a composite index for
cityandageinuserstable to make the filtering bycity = 'city 1'andage > 28more efficient. - We changed the order of the conditions in the
whereclause to make indexing more efficient.
- We have added a composite index for
- Query Tree:

| Table Name | Row Count | Main Key | Indexes | FK | Identity Column | Max Row Size(Bytes) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| users | 50k | Yes | No | No | Yes | 87 |
| posts | 50k | Yes | No | No | Yes | 50 |
| user_posts | 48734 | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | 35 |
| comments | 50k | Yes | No | No | Yes | 38 |
| user_comments | 48734 | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | 39 |
| replies | 9920 | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | 46 |
| likes | 48734 | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | 35 |
| follows | 39302 | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | 35 |
| messages | 50k | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | 46 |
Comparison of the plan and execution times for the queries with different optimization techniques.
Comparison of the plan and execution times for the queries with different sizes.
Comparison of the plan and execution times for the queries with different disks(HDD VS. SSD).
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| OS | Ubuntu 22.04 LTS |
| CPU1 | Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-1087H CPU @ 2.20GHz |
| CPU2 | AMD Ryzen™ 7 5800 @ 2.20GHz |
| Disk1 | HDD 1 TB |
| Disk2 | SSD 1 TB |
| RAM | 16 GB |
- Run
docker-compose up. - You will see a message whether the creation was
OkayorNot Okay. - Exec into the container.
- Populate the data by running with the required size
./mnt/scripts/populate_data.sh 10k. - Run the query using
./mnt/scripts/run_queries.sh query1. - Don't forget to stop the container after you are done.
- Run
docker-compose down --volumesto delete the volumes.
how to copy and paste file in bash script?
cp /mnt/scripts/queries/query1.js /mnt/scripts/queries/query1.js.bak- Run
docker-compose up mongodb - Container will create collections upon startup also it will insert dummy data into them
- Use connect_db.sh to exec into container
- Run the following commands
mongosh
use admin
db.auth("root","pass12345")
use social
- The container starts initially with 10k data for each collection , to change this
- Open a shell in the container using connect_db.sh
- change the number fo dummy data using
export DUMMY_SIZE=1000000 - run
mongosh - Authenticate yourself using step 4 commands
- load the script again using
load("./insert_dummy.js")
- Create queries in the
queriesfolder. - Add the queries to the
run_queries.shfile.
- Add a new script in the
dummyDatafolder. - Add the new size of the data in the
populate_data.shfile.
You can find the schema of the database in the
DDLfolder.
- Note that mongo command should be installed on the computer. On Linux this should be install
mongodb-org-shellpackage. - Connect to MongoDB server
mongo admin -u root -p pass12345It will connect to localhost port 27017. - Show databases:
show dbs - Create new non-existent database:
use mydatabase - Show collections:
show collections - Show contents/documents of a collection:
db.your_collection_name.find() - Save a data to a collection:
db.your_collection_name.save({"name":"Sony AK"}) - Show database version:
db.version() - Show database status:
db.stats()

.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)