Version 0.1.5, August 10 2023
This repository includes scripts, tooling and documentation to provision an instance of CML on Amazon Web Services (AWS).
IMPORTANT The AWS CML deployment and the toolchain / code provided in this repository are considered "experimental". If you encounter any errors or problems that might be related to the code in this repository then please open an issue on the Github issue tracker for this repository.
The tooling uses Terraform to deploy CML instances on AWS. It's therefore required to have a functional Terraform installation on the computer where this tool chain should be used.
Furthermore, the user needs to have access to AWS console to create or modify an automation account with the required permissions and policies applied.
In addition, the upload-images-to-aws.sh script requires the AWS CLI and the dialogutility to upload images to S3. It is a Bash shell script that requires Linux to run.
The AWS CLI and Terraform can be installed on the on-prem CML controller or, when this is undesirable due to support concerns, on a separate Linux instance.
That said, it should be possible to run the tooling also on macOS with tools installed via Homebrew. Or on Windows with WSL. However, this hasn't been tested by us.
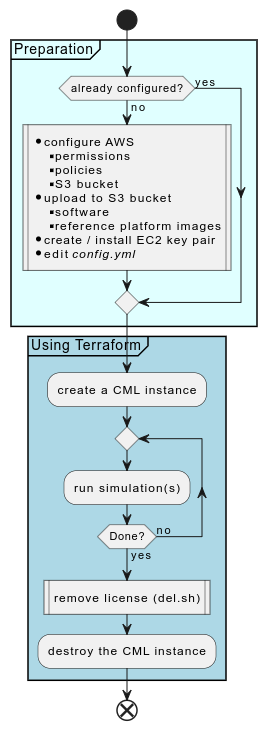
Some of the steps and procedures outlined below are preparation steps and only need to be done once. Those are
- cloning of the repository
- installation of software (Terraform, AWS CLI)
- creating and configuring the AWS automation account, including the creation of associated access credentials
- creating the AWS S3 bucket and uploading images and software into it
- creation of an SSH key pair and installing it into AWS EC2
- editing the
config.ymlconfiguration file including the selection of an instance flavor, region and other parameters
Terraform can be downloaded for free from here. This site has also instructions how to install it on various supported platforms.
Deployments of CML using Terraform were tested using version 1.4.6 on Ubuntu Linux.
$ terraform version
Terraform v1.4.6
on linux_amd64
+ provider registry.terraform.io/ciscodevnet/cml2 v0.6.2
+ provider registry.terraform.io/hashicorp/aws v4.67.0
+ provider registry.terraform.io/hashicorp/random v3.5.1
$
It is assumed that the CML cloud repository was cloned to the computer where Terraform was installed. The following command are all executed within the directory that has the cloned repositories. In particular, this README.md, the main.tf and the config.yml files, amongst other files.
When installed, run terraform init to initialize Terraform. This will download the required providers and create the state files.
The AWS CLI can be downloaded from here. This was tested using the following AWS CLI version:
$ aws --version
aws-cli/2.10.4 Python/3.9.11 Linux/5.19.0-40-generic exe/x86_64.ubuntu.22 prompt/off
$
If you need to use a proxy to access AWS then define it using environment variables. E.g. export HTTPS_PROXY=http://my.proxy.corp:80/ when using bash.
This section describes the resources required by the provisioning scripts to successfully deploy CML on AWS. These configurations and policies need to be created prior to using the tooling. This can be done on the AWS console or via the preferred deployment method (e.g. also via Terraform).
Note: There's also a video on YouTube which shows all the steps outlined below.
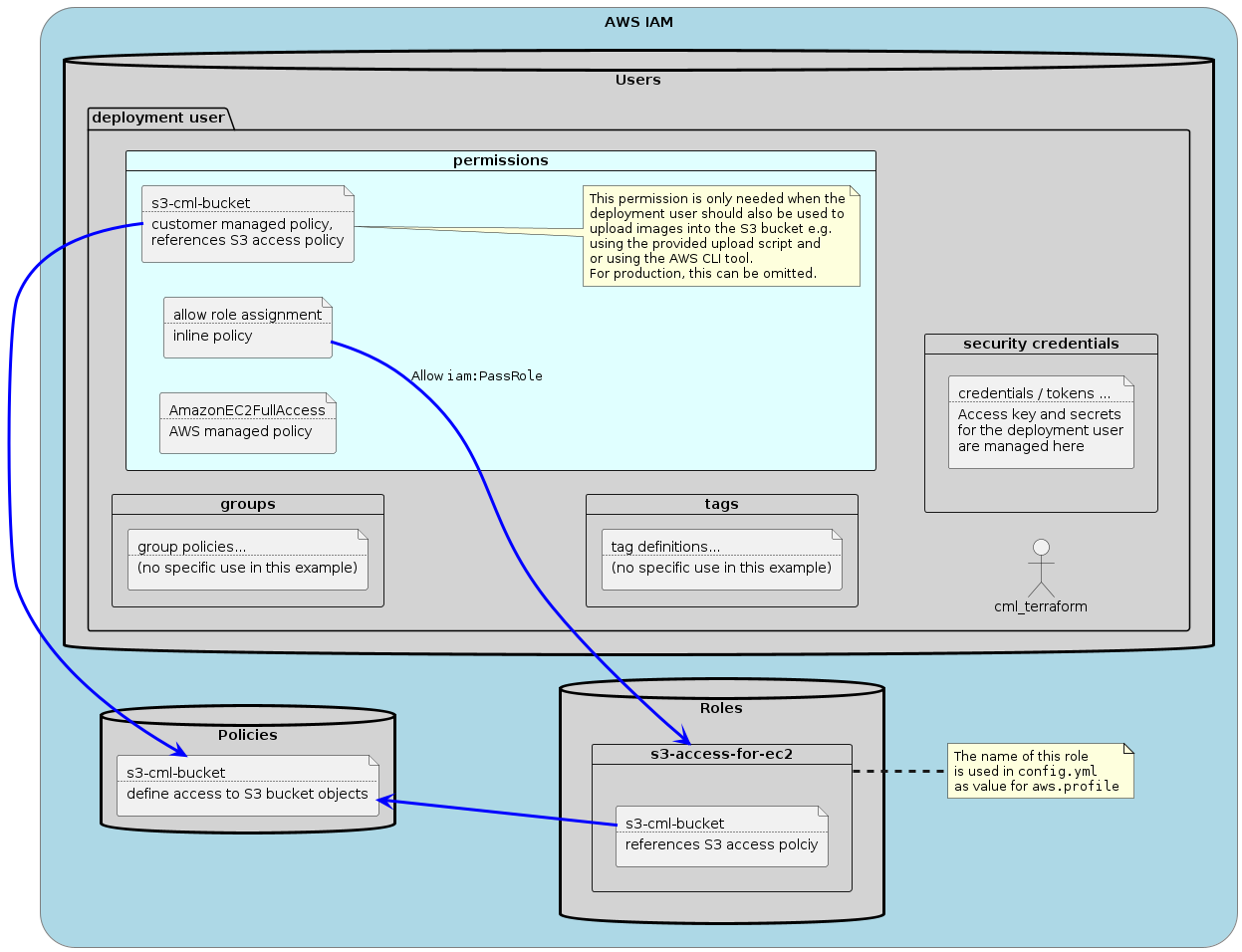
A user is needed which can be used by Terraform to deploy the CML instance. It is recommended to also create a group and attach the required policies to the group. A user is then created and assigned to this group in the final step below. This user inherits the policies from the group.
- click "User groups"
- click "Create group"
- enter a name ("terraform")
- click "Create group"
Next, we will create an S3 access policy which is reused to manage the bucket containing the reference platform as well as during CML deployment to allow copying the reference platform images to the EC2 instance.
To create the policy, go to "Policies", then click "Create policy". There select "JSON" instead of "Visual" at the top right and paste the following JSON:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::bucket-name",
"arn:aws:s3:::bucket-name/*"
]
}
]
}Replace "bucket-name" to the bucket name of your S3 bucket. This permits Read/Write and List access to the specified bucket and all objects within that bucket.
Note: This could be further tightened by removing the "PutObject" action from the policy as the EC2 instance / the CML controller only needs read access ("GetObject") and not write access access ("PutObject"). However, to upload images into the bucket, the write access is required at least initially.
Click "Next" and provide a policy name, "cml-s3-access" for example. Finally, click "Create policy".
Now that we have the S3 access policy, we can create a role that uses this policy.
-
go to "Roles"
-
click "Create role"
-
select "AWS service" for the "Trusted entity type" (the default)
-
select "EC2" for the "Use case"
-
click "Next"
-
select the S3 access policy that was created in the previous section ("cml-s3-access") from the permission policy list
-
scroll to the bottom and click "Next"
-
provide a role name, use "s3-access-for-ec2" (this is important to note as this is the policy name that is also referenced in the Terraform configuration to deploy CML and in the inline role assignment). See here, search for
iam_instance_profile, it saysIAM Instance Profile to launch the instance with. Specified as the name of the Instance Profile. Ensure your credentials have the correct permission to assign the instance profile according to the EC2 documentation, notably
iam:PassRole. -
click "Create role" at the bottom right
In the third step we attach permission policies to the group created in the step above. The policies in question are
- AmazonEC2FullAccess, a pre-defined policy that allows to control EC2 instances
- cml-s3-access, the S3 access policies allowing users in this group to read/write/list objects in the bucket specified by the policy
- the "pass role" policy which passes the permission allowing access to the S3 bucket to EC2 instances the users in this group create
To add these permission follow these steps:
- click on "Add permissions"
- select "Add permissions" from the drop down
- select "Attach policies directly"
- search for "EC2Full" which will result in the "AmazonEC2FullAccess" policy
- select this policy
- click "Next"
- click "Add permissions"
- click on "Add permissions"
- select "Add permissions" from the drop down
- select "Attach policies directly"
- select "Customer managed" in the "Filter by type" drop down
- select the "cml-s3-access" customer managed policy (the one we created above)
- click "Next"
- click "Add permissions"
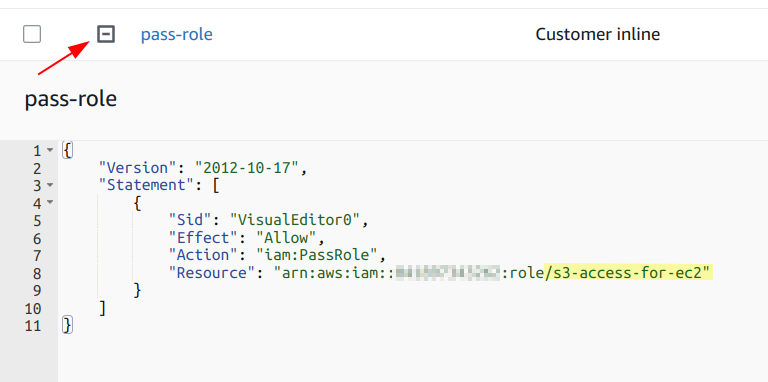
- click on "Add permissions"
- select "Create inline policy" from the drop down
- click on "IAM" from the "Select a service" section
- click on the "Write" Access level section
- select the "PassRole" write action
- in the "Resources" section click "Add arn"
- in the dialog "Specify ARNs"
- click "This account"
- in the last field, add the "s3-access-for-ec2" policy to the end of the arn. It will look like "arn:aws:iam::111111111111111:role/s3-access-for-ec2" (where the numbers represent your account ID, which is already inserted for you by the UI)
- click "Add ARN"
- click "Next"
- provide a Policy name, "pass role" works
- click "Create policy"
The final step is to create a user and associate it with the group
- click on "Users"
- click "Add users"
- provide a user name
- click "Next"
- select "Add user to group" (the default)
- select the group previously created ("terraform")
- click "Next"
- click "Create user"
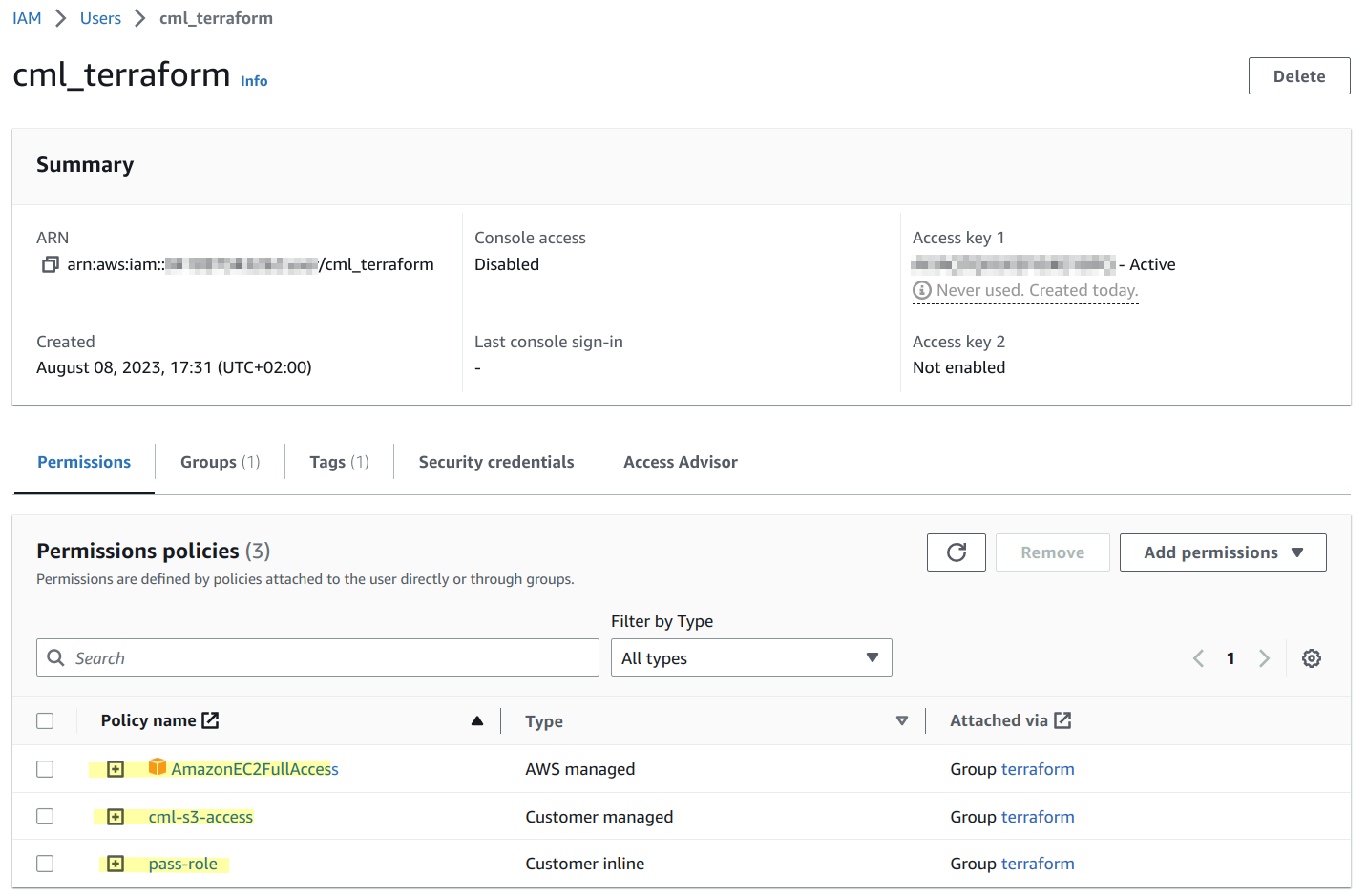
The final step is about creating access credentials that can be used with Terraform. We need an access key and a secret key.
- click on "Users"
- select the "cml_terraform" user
- click on the "Security credentials" tab
- scroll down to the "Access keys" section
- click on "Create access key"
- make a note of the access key and the secret key (copy them into an editor so that they can be later used when editing the
config.ymlof the deployment tool)
This access key and the associated secret key must be provided to the AWS Terraform provider via the the variables access_key and secret_key, ideally via environment variables or a vault. See the Variables section below.
The below screen shot shows an example of such a user with the required permission policies highlighted where the name of the user is "cml_terraform". Note that the required permission policies are listed. They are inherited from the "terraform" group. There's also an access key that has been created for this user.
This role that is passed ("s3-access-for-ec2") is then configured in the config.yml attribute 'aws.profile'.
The following diagram outlines the relation between the various IAM elements:
In addition to the user and group policies set in the previous steps, the following resources for a successful deployment are required.
The key name specifies the name of the SSH key that exists for the EC2 service. A valid SSH key private key must be imported into EC2 and the given name must be referenced within the provisioning HCL.
Key pairs are created locally and the public key is uploaded to EC2
EC2 → Key pairs → Create key pair (choose ED25519 key pair type)
Alternatively, it's also possible to import a public key without exposing the private key via
EC2 → Key pairs → Actions → Import key pair.
Another alternative is to manage keys via the aws_key_pair Terraform resource. See the official documentation.
The instance type defines the "hardware" of the created CML instance. For full functionality on AWS, a "metal" flavor is required as only metal flavors allow the use of nested virtualization. Please refer to the instance type explorer.
Limited usability can be achieved by using compute optimized C5 instances (link to the documentation). However, this is considered experimental and not supported as a lot of CML node types will not work when using on a non-metal flavor. This was tested using 'c5.2xlarge' instances and the following node types have been working OK:
- External connector and unmanaged switch
- All Linux node types
- IOSv and IOSv-L2
To enable this experimental "feature", the 00-patch_vmx.sh script must be uncommented in the app.customize list of the configuration file. See below.
Now that the deployment user has been defined, we can use the access credentials obtained in one of the previous steps to configure the AWS CLI tool. Ensure that you use the correct region and keys.
$ aws configure
AWS Access Key ID []: ********************
AWS Secret Access Key []: ********************
Default region name []: us-east-1
Default output format []: json
$
AWS CLI configurations are stored in $HOME/.aws.
If everything was configured correct then you should be able to list instances (remember that we permitted EC2 access for the deployment users):
$ aws ec2 describe-instances
{
"Reservations": []
}
$
As there are no instances running in this case, the output is empty. The important thing here is that there's no error and the communication with AWS worked!
CML specific settings are specified in the configuration file config.yml.
This holds the various configurations for the EC2 instance and S3 bucket to be used. The bucket and region values are also required on the actual instance to be able to copy the software onto the instance.
aws.bucket. This is the name of the bucket where the software and the reference platform files are stored. Must be accessible per the policy / role defined aboveaws.region. This defines the region of the bucket and typically matches the region of the AWS CLI as configured above. It also defines the region where the EC2 instances are createdaws.flavor. The flavor / instance type to be used for the AWS CML instance. Typically a metal instanceaws.profile. The name of the permission profile to be used for the instance. This needs to permit access to the S3 bucket with the software and reference platforms. In the example given above, this was named "s3-access-for-ec2"aws.keyname. SSH key name which needs to be installed on AWS EC2. This key will be injected into the instance using cloud-init.aws.disk_size. The size of the disk in gigabytes. 64 is a good starting value but this truly depends on the kind of nodes and the planned instance lifetime.
In theory, the EC2 instance can be run in a different region than the region of the bucket where the software is stored. The tooling, however, assumes that both are in the same region.
Key name hostname. Name of the instance, standard hostname rules apply.
Within the app section, the following keys must be set with the correct values:
app.userusername of the admin user (typically "admin") for UI accessapp.passpassword of the admin userapp.debthe filename of the Debian .deb package with the software, stored in the specified S3 bucket at the top levelapp.customizea list of scripts, located in thescriptsfolder which will be run as part of the instance creation to customize the install
There are currently two scripts provided for CML instance customization.
- Patch VMX. The
00-patch_vmx.shscript disables/bypasses the VMX CPU flag check. This allows to run some reference platforms on non-metal AWS instance flavors. This limits the list of nodes that actually work quite significantly and is not supported. Use at your own risk. - PATty. The
01-patty.shscript installs the PATty package. The package must be present in the bucket at the top level. It is experimental at this point in time. The name of the Debian package is hard-coded into the script (this package is currently not available publicly).
There's also a dummy entry in that list as the list must have at least one element. So, when not doing any of the predefined entries, at least the dummy must be present.
Note: PATty is currently not available as a standalone .deb file. We will include it with 2.6.1 as part of the controller distribution (in addition to installing it).
In this section, the OS user and password are defined.
sys.userusername of the OS user (typically "sysadmin") for Cockpit and OS level maintenance accesssys.passthe associated password
This holds the license that should be applied to the instance. It consists of three keys:
license.flavor: eitherCML_Enterprise,CML_Education,CML_PersonalorCML_Personal40are acceptablelicense.token: the Smart Licensing tokenlicense.nodes: the number of additional nodes, not applicable for the personal flavors.
Here, the reference platforms are listed which should be copied from the S3 bucket to the instance. There are two lists:
refplat.definitionslists the node definition IDsrefplat.imageslists the associated image definition IDs
It's mandatory that for each definition at least one matching image definition must be listed and that the name of these node and image definitions match with the names in the specified S3 bucket.
Note: The external connector and unmanaged switch are baked into the software, there's no need to have them listed here again.
The software and reference platform definition and images must be uploaded to the S3 bucket to be used by the provisioning script. This includes:
- the Debian package with the CML2 software
- the reference platform node definitions, image definitions and disk images of the reference platforms which should be available on the CML cloud instance
The reference platform files are taken from the reference platform ISO and can be copied using the provided upload-images-to-aws.sh script or using the AWS CLI script or the Web UI directly into the bucket resulting in a folder hierarchy that looks similar to this:
$ aws s3 ls --recursive s3://aws-bucket-name/
2023-03-02 07:43:56 82189664 cml2_2.5.0-5_amd64.deb
2023-03-02 14:38:10 2136 refplat/node-definitions/alpine.yaml
2023-03-03 11:29:24 1652 refplat/node-definitions/iosv.yaml
2023-03-03 11:29:23 1690 refplat/node-definitions/iosvl2.yaml
2023-03-02 14:38:11 2331 refplat/node-definitions/server.yaml
2023-03-02 14:38:09 51314688 refplat/virl-base-images/alpine-3-13-2-base/alpine-3-13-2-base.qcow2
2023-03-02 14:38:10 263 refplat/virl-base-images/alpine-3-13-2-base/alpine-3-13-2-base.yaml
2023-03-03 11:29:22 258 refplat/virl-base-images/iosv-159-3-m3/iosv-159-3-m3.yaml
2023-03-03 11:29:22 57296384 refplat/virl-base-images/iosv-159-3-m3/vios-adventerprisek9-m.spa.159-3.m3.qcow2
2023-03-03 11:29:23 267 refplat/virl-base-images/iosvl2-2020/iosvl2-2020.yaml
2023-03-03 11:29:22 90409984 refplat/virl-base-images/iosvl2-2020/vios_l2-adventerprisek9-m.ssa.high_iron_20200929.qcow2
2023-03-02 14:38:10 242 refplat/virl-base-images/server-tcl-11-1/server-tcl-11-1.yaml
2023-03-02 14:38:09 23134208 refplat/virl-base-images/server-tcl-11-1/tcl-11-1.qcow2
Note: The Debian package is in the top folder of the bucket and the platform files are in the refplat folder. Within that folder, the structure is identical to the structure of the reference platform ISO image.
Uploading the files into the S3 bucket is only required for the first time or when updating software. Even when CML instances are stopped / destroyed, the software in the S3 bucket is typically not removed.
The upload tool makes it easy to quickly select and upload the software package and images to a defined S3 bucket (the bucket must exist already).
Note: The required CML software is the "pkg" file that is available for download from the Cisco software download page. Example:
cml2_2.6.0-5_amd64-5.pkg. Also note the .pkg suffix.Placing the .pkg file into the directory with the upload tool will automatically extract the needed Debian package and offer the user to upload that package to the S3 bucket.
Start the tool by providing the bucket name as an argument and the location of the reference platform images. The defaults for both are aws-cml-images for the bucket name and /var/lib/libvirt/images for the reference platform image location.
The tool will then display a simple dialog where the images which should be copied to the bucket can be selected:
After selecting OK the upload process will be started immediately. To abort the process, Ctrl-C can be used.
Note: If a CML2 .pkg file is present in the directory where the tool is started, then the tool will offer to upload the software to the bucket.
Help can be obtained via ./upload-images-to-aws.sh --help.
The variable.tf defines the authentication secrets needed by the Terraform AWS provider.
Here's an example using a bash script that can be sourced and which defines those variables. To automate things further, a tool like direnv can be used to load this environment when changing into the directory which has this file.
Content of file .envrc:
export TF_VAR_access_key="your-access-key-string-from-iam"
export TF_VAR_secret_key="your-secret-key-string-from-iam"Alternatively, it's also possible to provide values for variables via a file called terraform.tfvars file. There are various ways how to define / set variables with Terraform. See the Terraform documentation for additional details.
When all requirements are met, an instance can be deployed using Terraform.
- Terraform CLI installed
- policies and users configured in AWS IAM
- software and reference platforms uploaded into a bucket on AWS S3
- configuration files prepared with correct values
- variables defined in environment or in
terraform.tfvars
All configurations and variables relate to the relevant sections defined above.
Starting an instance is done via terraform plan and terraform apply. The instance will be deployed and fully configured based on the provided configuration. Terraform will wait until CML is up and running, this will take approximately 5-10 minutes and depends a bit on the flavor used.
At the end, the Terraform output shows the relevant information about the instance:
- The URL to access it
- The public IP address
- The CML software version running
- The command to automatically remove the license from the instance prior to destroying it (see below).
Before destroying an instance using terraform destroy it is important to remove the CML license either by using the provided script or by unregistering the instance (UI → Tools → Licensing → Actions → Deregister). Otherwise, the license is not freed up on the Smart Licensing servers and subsequent deployments might not succeed due to insufficient licenses available in the smart account.
To remove the license using automation, a script is provided in /provision/del.sh. The output from the deployment can be used, it looks like this:
ssh -p1122 sysadmin@IP_ADDRESS_OF_CONTROLLER /provision/del.sh
This requires all labs to be stopped (no running VMs allowed) prior to removing the license. It will only work as long as the provisioned usernames and passwords have not changed between deployment and destruction of the instance.
To deploy a CML instance on AWS and after configuring the required variables and editing the config.yaml file, a terraform plan will show all the planned changes. After reviewing those, a terraform apply will start and configure a CML instance on AWS.
$ terraform apply -auto-approve
module.deploy.data.aws_ami.ubuntu: Reading...
module.deploy.data.aws_ami.ubuntu: Read complete after 1s [id=ami-0d497a49e7d359666]
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
<= read (data resources)
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# module.deploy.aws_instance.cml will be created
+ resource "aws_instance" "cml" {
+ ami = "ami-0d497a49e7d359666"
+ arn = (known after apply)
+ associate_public_ip_address = (known after apply)
+ availability_zone = (known after apply)
+ cpu_core_count = (known after apply)
[...]
Plan: 3 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Changes to Outputs:
+ cml2info = {}
module.deploy.random_id.id: Creating...
module.deploy.random_id.id: Creation complete after 0s [id=x1hR1Q]
module.deploy.aws_security_group.sg-tf: Creating...
module.deploy.aws_security_group.sg-tf: Creation complete after 2s [id=sg-04865f65e43aa917f]
module.deploy.aws_instance.cml: Creating...
module.deploy.aws_instance.cml: Still creating... [10s elapsed]
module.deploy.aws_instance.cml: Creation complete after 13s [id=i-0e7697766ca6c18e1]
module.ready.data.cml2_system.state: Reading...
module.ready.data.cml2_system.state: Still reading... [10s elapsed]
module.ready.data.cml2_system.state: Still reading... [20s elapsed]
[...]
module.ready.data.cml2_system.state: Still reading... [3m50s elapsed]
module.ready.data.cml2_system.state: Still reading... [4m0s elapsed]
module.ready.data.cml2_system.state: Read complete after 4m2s [id=dd68b604-8930-45c6-8d58-a1da578e02b4]
Apply complete! Resources: 3 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
cml2info = {
"address" = "18.194.38.215"
"del" = "ssh -p1122 [email protected] /provision/del.sh"
"url" = "https://18.194.38.215"
"version" = "2.5.1+build.10"
}
$
As can be seen above, a public IPv4 address has been assigned to the instance which can be used to access it via SSH and the provided SSH key pair (if this does not connect right away then the system isn't ready, yet and more wait is needed):
$ ssh -p1122 [email protected]
The authenticity of host '[18.194.38.215]:1122 ([18.194.38.215]:1122)' can't be established.
ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:dz7GcRGzcWiyHbPb++NyQykP9r7UoG0rNiACi5ft1lQ.
This key is not known by any other names
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added '[18.194.38.215]:1122' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts.
Welcome to Ubuntu 20.04.6 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.15.0-1033-aws x86_64)
[...]
sysadmin@rschmied-aws-2023042001:~$
At this point, the status of the system can be checked:
sysadmin@rschmied-aws-2023042001:~$ systemctl status | head
● rschmied-aws-2023042001
State: running
Jobs: 0 queued
Failed: 0 units
Since: Fri 2023-04-21 14:45:00 UTC; 4min 34s ago
CGroup: /
├─23120 bpfilter_umh
├─user.slice
│ └─user-1001.slice
│ ├─[email protected]
sysadmin@rschmied-aws-2023042001:~$ systemctl status virl2.target
● virl2.target - CML2 Network Simulation System
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/virl2.target; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active since Fri 2023-04-21 14:47:58 UTC; 2min 13s ago
Warning: some journal files were not opened due to insufficient permissions.
sysadmin@rschmied-aws-2023042001:~$
The system is running and the VIRL2 target (CML) is active!
Prior to stopping the instance, the licensing token must be removed via the UI. Otherwise it's still considered "in use" in Smart Licensing. This is done via the UI or using the del.sh script / SSH command which is provided as part of the deploy output (see above). Then run the destroy command.
Note: The
del.shhas no output if the command is successful.
$ ssh -p1122 [email protected] /provision/del.sh
The authenticity of host '[18.194.38.215]:1122 ([18.194.38.215]:1122)' can't be established.
ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:4QxgLv9zzKR5gJP4rWE41STdnAHufBYkTKBpp/VA+k8.
This key is not known by any other names
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added '[18.194.38.215]:1122' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts.
$ terraform destroy -auto-approve
module.deploy.random_id.id: Refreshing state... [id=x1hR1Q]
module.deploy.data.aws_ami.ubuntu: Reading...
module.deploy.aws_security_group.sg-tf: Refreshing state... [id=sg-04865f65e43aa917f]
module.deploy.data.aws_ami.ubuntu: Read complete after 1s [id=ami-0d497a49e7d359666]
module.deploy.aws_instance.cml: Refreshing state... [id=i-0e7697766ca6c18e1]
module.ready.data.cml2_system.state: Reading...
module.ready.data.cml2_system.state: Read complete after 0s [id=cf22e2e6-7ef2-420b-8191-404f3f7f3600]
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
- destroy
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# module.deploy.aws_instance.cml will be destroyed
- resource "aws_instance" "cml" {
- ami = "ami-0d497a49e7d359666" -> null
[...]
Plan: 0 to add, 0 to change, 3 to destroy.
Changes to Outputs:
- cml2info = {
- address = "18.194.38.215"
- del = "ssh -p1122 [email protected] /provision/del.sh"
- url = "https://18.194.38.215"
- version = "2.5.1+build.10"
} -> null
module.deploy.aws_instance.cml: Destroying... [id=i-0e7697766ca6c18e1]
module.deploy.aws_instance.cml: Still destroying... [id=i-0e7697766ca6c18e1, 10s elapsed]
module.deploy.aws_instance.cml: Still destroying... [id=i-0e7697766ca6c18e1, 20s elapsed]
module.deploy.aws_instance.cml: Still destroying... [id=i-0e7697766ca6c18e1, 30s elapsed]
module.deploy.aws_instance.cml: Destruction complete after 30s
module.deploy.aws_security_group.sg-tf: Destroying... [id=sg-04865f65e43aa917f]
module.deploy.aws_security_group.sg-tf: Destruction complete after 0s
module.deploy.random_id.id: Destroying... [id=x1hR1Q]
module.deploy.random_id.id: Destruction complete after 0s
Destroy complete! Resources: 3 destroyed.
$
At this point, the compute resources have been released / destroyed. Images in the S3 bucket are still available for bringing up new instances.
Note: Metal instances take significantly longer to bring up and to destroy. The
m5zn.metalinstance type takes about 5-10 minutes for both. Deployment times also depend on the number and size of reference platform images that should be copied to the instance.
In case of errors during deployment or when the CML instance won't become ready, the some troubleshooting guidance is provided below.
- add a password to the root user in the
cml.shscript within themodule-cml2-deply-aws/scriptsfolder. Search for "troubleshooting", the line is commented out. Replace the "secret-password-here" with a proper password and uncomment the line by removing the leading hash character. - use the EC2 instance connect / serial console to gain access to the CML2 instance. When doing so soon after creating the instance, some log messages may already reveal what's going wrong
- log in as the root user using the provided password on the serial console
- check for errors in the log files in the
/var/log/cloud/directory - check output of
cloud-init status
Note: Not all instance flavors have a serial console but metal flavors do!
This section lists a couple of caveats and limitations when running CML in AWS.
At this point in time, the tooling only supports AWS. Support for other platforms like Azure and Google Cloud Platform is planned for future releases.
As pointed out above, full functionality requires a metal instance flavor because only the AWS metal flavors provide support for the VMX CPU flag to run accelerated nested VMs.
Software upgrade or migration is not supported for cloud instances. We advise to download topologies or configurations prior to destroying the instance.
At this point in time, CML AWS instances are "all-in-one" instances. No problems are expected running a cluster in AWS but this will require additional network plumbing and orchestration / configuration which hasn't been implemented and tested, yet.
CML cloud instances with the default networking have only one external IP address allocated. In addition, it's mandatory that no L2 frames leak into the outside network as this could disable access to the management IP address.
For this reason, CML cloud instances by default only have the NAT network available. Ensure that all external connectors use the NAT (virbr0) network and not the bridge network (bridge0).
In case of advanced VPC configuration with additional networks and NICs inside of the CML controller, bridging could be set up manually. This is out of scope for this documentation / tooling.
If everything goes well (e.g. the license was successfully removed) then no additional output is shown when running the ssh ... /provision/del.sh command. Errors will be reported otherwise.
The license can't be removed using the script when nodes are running. You will get this message:
{
"description": "Licensing issue: Cannot de-register when nodes are running.",
"code": 400
}If the license has already been removed, then this message is shown:
{
"description": "Licensing issue: The product has already been de-registered.",
"code": 400
}EOF