English | Português | 简体中文 | Español
A wrapper around InheritedWidget to make them easier to use and more reusable.
By using provider instead of manually writing InheritedWidget, you get:
- simplified allocation/disposal of resources
- lazy-loading
- a vastly reduced boilerplate over making a new class every time
- friendly to devtools
- a common way to consume these InheritedWidgets (See Provider.of/Consumer/Selector)
- increased scalability for classes with a listening mechanism that grows exponentially in complexity (such as ChangeNotifier, which is O(N) for dispatching notifications).
To read more about a provider, see its documentation.
See also:
- The official Flutter state management documentation, which showcases how to use
provider+ ChangeNotifier - flutter architecture sample, which contains an implementation of that app using
provider+ ChangeNotifier - flutter_bloc and Mobx, which uses a
providerin their architecture
-
initialDatafor bothFutureProviderandStreamProvideris now required.To migrate, what used to be:
FutureProvider<int>( create: (context) => Future.value(42), child: MyApp(), ) Widget build(BuildContext context) { final value = context.watch<int>(); return Text('$value'); }
is now:
FutureProvider<int?>( initialValue: null, create: (context) => Future.value(42), child: MyApp(), ) Widget build(BuildContext context) { // be sure to specify the ? in watch<int?> final value = context.watch<int?>(); return Text('$value'); }
-
ValueListenableProvideris removedTo migrate, you can instead use
Providercombined withValueListenableBuilder:ValueListenableBuilder<int>( valueListenable: myValueListenable, builder: (context, value, _) { return Provider<int>.value( value: value, child: MyApp(), ); } )
Providers allow you to not only expose a value, but also create, listen, and dispose of it.
To expose a newly created object, use the default constructor of a provider.
Do not use the .value constructor if you want to create an object, or you
may otherwise have undesired side effects.
See this StackOverflow answer
which explains why using the .value constructor to create values is undesired.
- DO create a new object inside
create.
Provider(
create: (_) => MyModel(),
child: ...
)- DON'T use
Provider.valueto create your object.
ChangeNotifierProvider.value(
value: MyModel(),
child: ...
)-
DON'T create your object from variables that can change over time.
In such a situation, your object would never update when the value changes.
int count;
Provider(
create: (_) => MyModel(count),
child: ...
)If you want to pass variables that can change over time to your object,
consider using ProxyProvider:
int count;
ProxyProvider0(
update: (_, __) => MyModel(count),
child: ...
)NOTE:
When using the create/update callback of a provider, it is worth noting that this callback
is called lazily by default.
This means that until the value is requested at least once, the create/update callbacks won't be called.
This behavior can be disabled if you want to pre-compute some logic, using the lazy parameter:
MyProvider(
create: (_) => Something(),
lazy: false,
)If you already have an object instance and want to expose it, it would be best to use the .value constructor of a provider.
Failing to do so may call your object dispose method when it is still in use.
- DO use
ChangeNotifierProvider.valueto provide an existing ChangeNotifier.
MyChangeNotifier variable;
ChangeNotifierProvider.value(
value: variable,
child: ...
)- DON'T reuse an existing ChangeNotifier using the default constructor
MyChangeNotifier variable;
ChangeNotifierProvider(
create: (_) => variable,
child: ...
)The easiest way to read a value is by using the extension methods on [BuildContext]:
context.watch<T>(), which makes the widget listen to changes onTcontext.read<T>(), which returnsTwithout listening to itcontext.select<T, R>(R cb(T value)), which allows a widget to listen to only a small part ofT.
One can also use the static method Provider.of<T>(context), which will behave similarly
to watch and when the listen parameter is set to false like Provider.of<T>(context, listen: false), then
it will behave similarly to read.
It's worth noting that context.read<T>() won't make a widget rebuild when the value
changes and it cannot be called inside StatelessWidget.build/State.build.
On the other hand, it can be freely called outside of these methods.
These methods will look up in the widget tree starting from the widget associated
with the BuildContext passed and will return the nearest variable of type T
found (or throw if nothing is found).
This operation is O(1). It doesn't involve walking in the widget tree.
Combined with the first example of exposing a value, this
the widget will read the exposed String and render "Hello World."
class Home extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Text(
// Don't forget to pass the type of the object you want to obtain to `watch`!
context.watch<String>(),
);
}
}Alternatively, instead of using these methods, we can use Consumer and Selector.
These can be useful for performance optimizations or when it is difficult to
obtain a BuildContext descendant of the provider.
See the FAQ or the documentation of Consumer and Selector for more information.
Sometimes, we may want to support cases where a provider does not exist. An example would be for reusable widgets that could be used in various locations, including outside of a provider.
To do so, when calling context.watch/context.read, make the generic type
nullable. Such that instead of:
context.watch<Model>()which will throw a ProviderNotFoundException if no matching providers
are found, do:
context.watch<Model?>()which will try to obtain a matching provider. But if none are found,
null will be returned instead of throwing.
When injecting many values in big applications, Provider can rapidly become
pretty nested:
Provider<Something>(
create: (_) => Something(),
child: Provider<SomethingElse>(
create: (_) => SomethingElse(),
child: Provider<AnotherThing>(
create: (_) => AnotherThing(),
child: someWidget,
),
),
),To:
MultiProvider(
providers: [
Provider<Something>(create: (_) => Something()),
Provider<SomethingElse>(create: (_) => SomethingElse()),
Provider<AnotherThing>(create: (_) => AnotherThing()),
],
child: someWidget,
)The behavior of both examples is strictly the same. MultiProvider only changes
the appearance of the code.
Since the 3.0.0, there is a new kind of provider: ProxyProvider.
ProxyProvider is a provider that combines multiple values from other providers into a new object and sends the result to Provider.
That new object will then be updated whenever one of the provider we depend on gets updated.
The following example uses ProxyProvider to build translations based on a counter coming from another provider.
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MultiProvider(
providers: [
ChangeNotifierProvider(create: (_) => Counter()),
ProxyProvider<Counter, Translations>(
update: (_, counter, __) => Translations(counter.value),
),
],
child: Foo(),
);
}
class Translations {
const Translations(this._value);
final int _value;
String get title => 'You clicked $_value times';
}It comes under multiple variations, such as:
-
ProxyProvidervsProxyProvider2vsProxyProvider3, ...That digit after the class name is the number of other providers that
ProxyProviderdepends on. -
ProxyProvidervsChangeNotifierProxyProvidervsListenableProxyProvider, ...They all work similarly, but instead of sending the result into a
Provider, aChangeNotifierProxyProviderwill send its value to aChangeNotifierProvider.
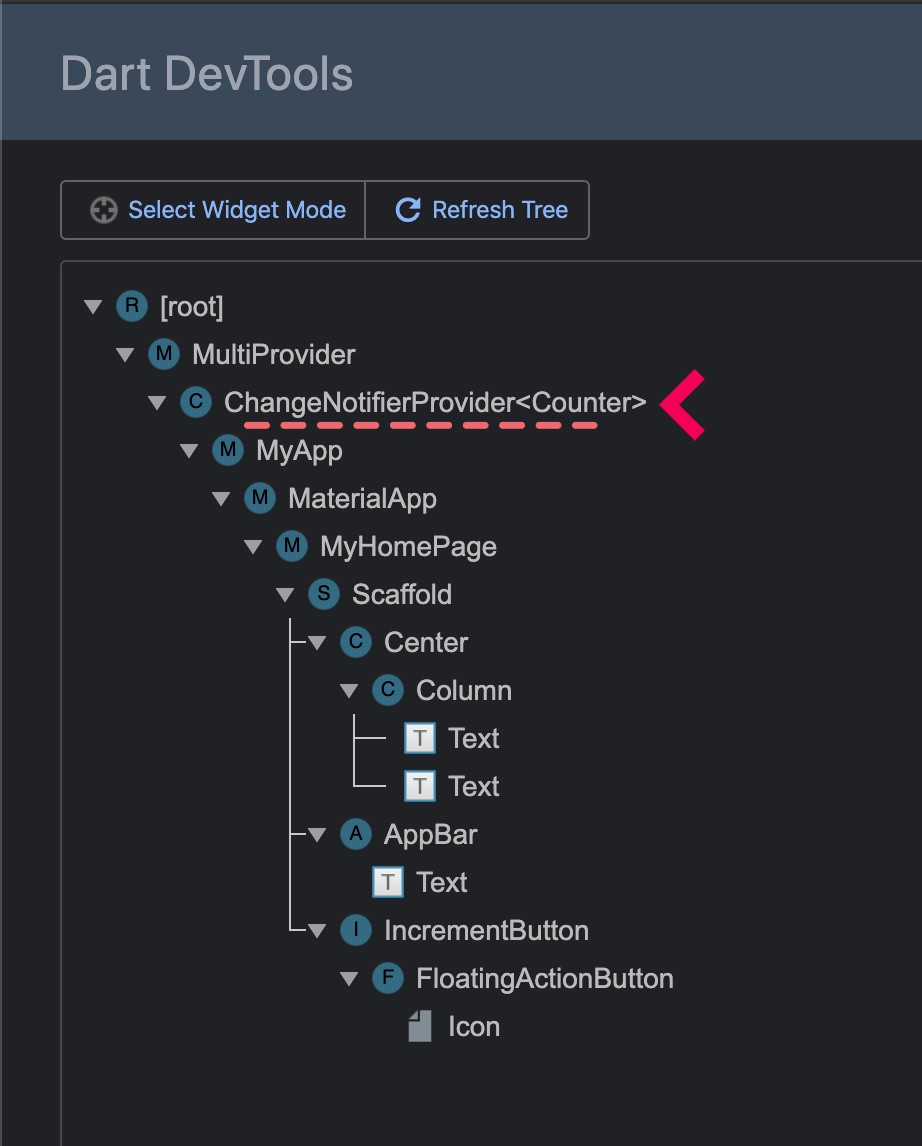
Flutter comes with a devtool that shows what the widget tree is at a given moment.
Since providers are widgets, they are also visible in that devtool:
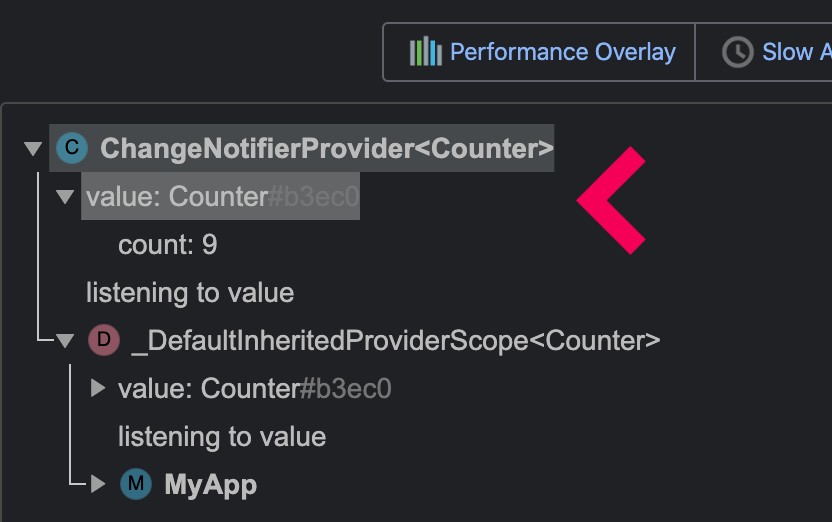
From there, if you click on one provider, you will be able to see the value it exposes:
(screenshot of the devtools using the example folder)
By default, the devtool relies on toString, which defaults to "Instance of MyClass".
To have something more useful, you have two solutions:
-
use the Diagnosticable API from Flutter.
For most cases, I will use DiagnosticableTreeMixin on your objects, followed by a custom implementation of debugFillProperties.
class MyClass with DiagnosticableTreeMixin { MyClass({this.a, this.b}); final int a; final String b; @override void debugFillProperties(DiagnosticPropertiesBuilder properties) { super.debugFillProperties(properties); // list all the properties of your class here. // See the documentation of debugFillProperties for more information. properties.add(IntProperty('a', a)); properties.add(StringProperty('b', b)); } }
-
Override
toString.If you cannot use DiagnosticableTreeMixin (like if your class is in a package that does not depend on Flutter), then you can override
toString.This is easier than using DiagnosticableTreeMixin but is less powerful: You will not be able to expand/collapse the details of your object.
class MyClass with DiagnosticableTreeMixin { MyClass({this.a, this.b}); final int a; final String b; @override String toString() { return '$runtimeType(a: $a, b: $b)'; } }
This exception happens because you're trying to listen to a provider from a life-cycle that will never ever be called again.
It means that you either should use another life-cycle (build), or explicitly
specify that you do not care about updates.
As such, instead of:
initState() {
super.initState();
print(context.watch<Foo>().value);
}you can do:
Value value;
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final value = context.watch<Foo>.value;
if (value != this.value) {
this.value = value;
print(value);
}
}which will print value whenever it changes (and only when it changes).
Alternatively, you can do:
initState() {
super.initState();
print(context.read<Foo>().value);
}Which will print value once and ignore updates.
You can make your provided object implement ReassembleHandler:
class Example extends ChangeNotifier implements ReassembleHandler {
@override
void reassemble() {
print('Did hot-reload');
}
}Then used typically with provider:
ChangeNotifierProvider(create: (_) => Example()),I use ChangeNotifier, and I have an exception when I update it. What happens?
This likely happens because you are modifying the ChangeNotifier from one of its descendants while the widget tree is building.
A typical situation where this happens is when starting an http request, where the future is stored inside the notifier:
initState() {
super.initState();
context.read<MyNotifier>().fetchSomething();
}This is not allowed because the state update is synchronous.
This means that some widgets may build before the mutation happens (getting an old value), while other widgets will build after the mutation is complete (getting a new value). This could cause inconsistencies in your UI and is therefore not allowed.
Instead, you should perform that mutation in a place that would affect the entire tree equally:
-
directly inside the
createof your provider/constructor of your model:class MyNotifier with ChangeNotifier { MyNotifier() { _fetchSomething(); } Future<void> _fetchSomething() async {} }
This is useful when there's no "external parameter".
-
asynchronously at the end of the frame:
initState() { super.initState(); Future.microtask(() => context.read<MyNotifier>().fetchSomething(someValue); ); }
It is slightly less ideal, but allows passing parameters to the mutation.
Do I have to use ChangeNotifier for complex states?
No.
You can use any object to represent your state. For example, an alternate
architecture is to use Provider.value() combined with a StatefulWidget.
Here's a counter example using such architecture:
class Example extends StatefulWidget {
const Example({Key key, this.child}) : super(key: key);
final Widget child;
@override
ExampleState createState() => ExampleState();
}
class ExampleState extends State<Example> {
int _count;
void increment() {
setState(() {
_count++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Provider.value(
value: _count,
child: Provider.value(
value: this,
child: widget.child,
),
);
}
}where we can read the state by doing:
return Text(context.watch<int>().toString());and modify the state with:
return FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () => context.read<ExampleState>().increment(),
child: Icon(Icons.plus_one),
);Alternatively, you can create your own provider.
Yes. provider exposes all the small components that make a fully-fledged provider.
This includes:
-
SingleChildStatelessWidget, to make any widget works withMultiProvider.
This interface is exposed as part ofpackage:provider/single_child_widget -
InheritedProvider, the generic
InheritedWidgetobtained when doingcontext.watch.
Here's an example of a custom provider to use ValueNotifier as the state:
https://gist.github.com/rrousselGit/4910f3125e41600df3c2577e26967c91
Instead of context.watch, you can use context.select to listen only to the specific set of properties on the obtained object.
For example, while you can write:
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final person = context.watch<Person>();
return Text(person.name);
}It may cause the widget to rebuild if something other than name changes.
Instead, you can use context.select to listen only to the name property:
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final name = context.select((Person p) => p.name);
return Text(name);
}This way, the widget won't unnecessarily rebuild if something other than name changes.
Similarly, you can use Consumer/Selector. Their optional child argument allows rebuilding only a particular part of the widget tree:
Foo(
child: Consumer<A>(
builder: (_, a, child) {
return Bar(a: a, child: child);
},
child: Baz(),
),
)In this example, only Bar will rebuild when A updates. Foo and Baz won't
unnecessarily rebuild.
No. While you can have multiple providers sharing the same type, a widget will be able to obtain only one of them: the closest ancestor.
Instead, it would help if you explicitly gave both providers a different type.
Instead of:
Provider<String>(
create: (_) => 'England',
child: Provider<String>(
create: (_) => 'London',
child: ...,
),
),Prefer:
Provider<Country>(
create: (_) => Country('England'),
child: Provider<City>(
create: (_) => City('London'),
child: ...,
),
),Yes, a type hint must be given to the compiler to indicate the interface will be consumed, with the implementation provided in create.
abstract class ProviderInterface with ChangeNotifier {
...
}
class ProviderImplementation with ChangeNotifier implements ProviderInterface {
...
}
class Foo extends StatelessWidget {
@override
build(context) {
final provider = Provider.of<ProviderInterface>(context);
return ...
}
}
ChangeNotifierProvider<ProviderInterface>(
create: (_) => ProviderImplementation(),
child: Foo(),
),provider exposes a few different kinds of "provider" for different types of objects.
The complete list of all the objects available is here
| name | description |
|---|---|
| Provider | The most basic form of provider. It takes a value and exposes it, whatever the value is. |
| ListenableProvider | A specific provider for Listenable object. ListenableProvider will listen to the object and ask widgets which depend on it to rebuild whenever the listener is called. |
| ChangeNotifierProvider | A specification of ListenableProvider for ChangeNotifier. It will automatically call ChangeNotifier.dispose when needed. |
| ValueListenableProvider | Listen to a ValueListenable and only expose ValueListenable.value. |
| StreamProvider | Listen to a Stream and expose the latest value emitted. |
| FutureProvider | Takes a Future and updates dependents when the future completes. |