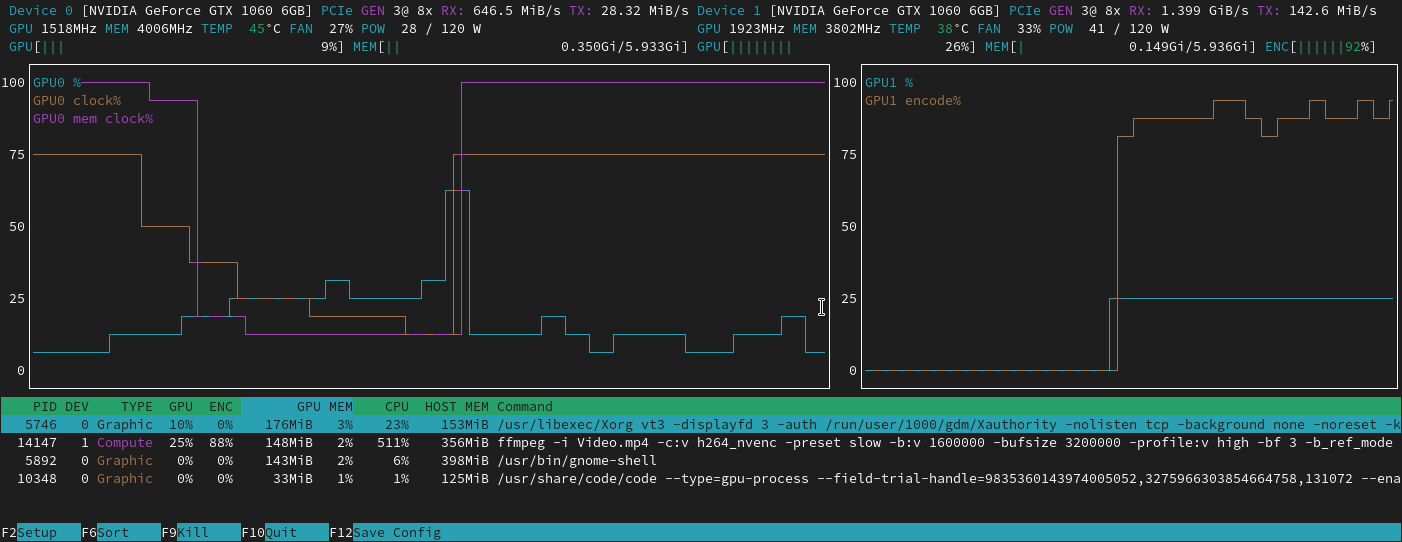
Nvtop stands for Neat Videocard TOP, a (h)top like task monitor for AMD, Intel and NVIDIA GPUs. It can handle multiple GPUs and print information about them in a htop familiar way.
Because a picture is worth a thousand words:
- NVTOP Options and Interactive Commands
- GPU Support
- Build
- Distribution Specific Installation Process
- NVTOP Build
- Troubleshoot
- License
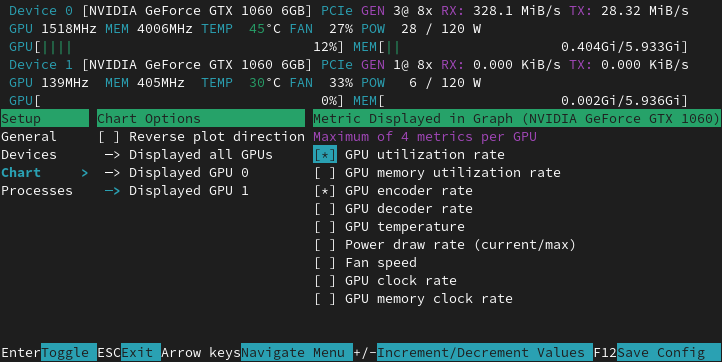
NVTOP has a builtin setup utility that provides a way to specialize the interface to your needs.
Simply press F2 and select the options that are the best for you.
You can save the preferences set in the setup window by pressing F12.
The preferences will be loaded the next time you run nvtop.
NVTOP comes with a manpage!
man nvtopFor quick command line arguments help
nvtop -h
nvtop --helpNVTOP supports AMD GPUs using the amdgpu driver through the exposed DRM and
sysfs interface.
AMD introduced the fdinfo interface in kernel 5.14 (browse kernel source). Hence, you will need a kernel with a version greater or equal to 5.14 to see the processes using AMD GPUs.
Support for recent GPUs are regularly mainlined into the linux kernel, so please use a recent-enough kernel for your GPU.
NVTOP supports Intel GPUs using the i915 linux driver.
Intel introduced the fdinfo interface in kernel 5.19 (browse kernel source). Hence, you will need a kernel with a version greater or equal to 5.19 to see the processes using Intel GPUs.
INTEL SUPPORT STATUS
- Intel is working on exposing more hardware information through an
HWMONinterface. The patches are still a work in progress: see patch series. - The fdinfo interface does not expose the memory allocated by the process. The field in the process list is therefore empty.
The NVML library does not support some of the queries for GPUs coming before the Kepler microarchitecture. Anything starting at GeForce 600, GeForce 800M and successor should work fine. For more information about supported GPUs please take a look at the NVML documentation.
Several libraries are required in order for NVTOP to display GPU information:
- The ncurses library driving the user interface.
- This makes the screen look beautiful.
- For NVIDIA: the NVIDIA Management Library (NVML) which comes with the GPU driver.
- This queries the GPU for information.
- For AMD: the libdrm library used to query AMD GPUs through the kernel driver.
If your distribution provides the snap utility, follow the snap installation process to obtain an up-to-date version of nvtop.
A standalone application is available as AppImage.
-
sudo apt install nvtop
A PPA supporting Ubuntu 20.04, 22.04 and newer is provided by
Martin Wimpress that offers an up-to-date
version of nvtop, enabled for NVIDIA, AMD and Intel.
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:flexiondotorg/nvtop
sudo apt install nvtop-
AMD and Intel Dependencies
sudo apt install libdrm-dev libsystemd-dev # Ubuntu 18.04 sudo apt install libudev-dev -
NVIDIA Depenency
- NVIDIA drivers (see Ubuntu Wiki or Ubuntu PPA or Debian Wiki)
-
NVTOP Dependencies
-
CMake, ncurses and git
sudo apt install cmake libncurses5-dev libncursesw5-dev git- NVTOP
- Follow the NVTOP Build
A standalone application is available as AppImage.
-
AMD and Intel Dependencies
sudo dnf install libdrm-devel systemd-devel
-
NVIDIA Depenency
- NVIDIA drivers, CUDA required for nvml libraries (see RPM Fusion)
-
NVTOP Dependencies
-
CMake, ncurses, c++ and git
sudo dnf install cmake ncurses-devel git gcc-c++- NVTOP
- Follow the NVTOP Build
A standalone application is available as AppImage.
Build process for OpenSUSE:
-
AMD Dependecy
sudo zypper install libdrm-devel
-
NVIDIA Depenency
- NVIDIA drivers (see SUSE Support Database)
-
NVTOP Dependencies
- CMake, ncurses and git
sudo zypper install cmake ncurses-devel git
- CMake, ncurses and git
-
NVTOP
- Follow the NVTOP Build
-
sudo pacman -S nvtop
-
sudo layman -a guru && sudo emerge -av nvtop
An AppImage is a standalone application. Just download the AppImage, make it executable and run it!
-
Go to the release page and download
nvtop-x86_64.AppImage -
# Go to the download location ** The path may differ on your system ** cd $HOME/Downloads # Make the AppImage executable chmod u+x nvtop-x86_64.AppImage # Enjoy nvtop ./nvtop-x86_64.AppImage
If you are curious how that works, please visit the AppImage website.
-
snap install nvtop # Add the capability to kill processes inside nvtop snap connect nvtop:process-control # Add the capability to inspect GPU info (Fan, PCIe, Power, etc) snap connect nvtop:hardware-observe # AMDGPU process list support (read /proc/<pid>) snap connect nvtop:system-observe # Temporary workaround to get per-process GPU usage (read /proc/<pid>/fdinfo) snap connect nvtop:kubernetes-support
Notice: The connect commands allow
-
NVIDIA drivers (same as above)
-
git clone https://github.com/Syllo/nvtop.git && cd nvtop sudo docker build --tag nvtop . sudo docker run -it --rm --runtime=nvidia --gpus=all --pid=host nvtop
git clone https://github.com/Syllo/nvtop.git
mkdir -p nvtop/build && cd nvtop/build
cmake .. -DNVIDIA_SUPPORT=ON -DAMDGPU_SUPPORT=ON -DINTEL_SUPPORT=ON
make
# Install globally on the system
sudo make install
# Alternatively, install without privileges at a location of your choosing
# make DESTDIR="/your/install/path" installIf you use conda as environment manager and encounter an error while building nvtop, try conda deactivate before invoking cmake.
The build system supports multiple build type (e.g. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RelWithDebInfo):
- Release: Binary without debug information
- RelWithDebInfo: Binary with debug information
- Debug: Compile with warning flags and address/undefined sanitizers enabled (for development purposes)
- The plot looks bad:
- Verify that you installed the wide character version of the NCurses library (libncursesw5-dev for Debian / Ubuntu), clean the build directory and restart the build process.
- Putty: Tell putty not to lie about its capabilities (
$TERM) by setting the fieldTerminal-type stringtoputtyin the menuConnection > Data > Terminal Details.
Nvtop is licensed under the GPLV3 license or any later version. You will find a copy of the license inside the COPYING file of the repository or at the gnu website <www.gnu.org/licenses/>.