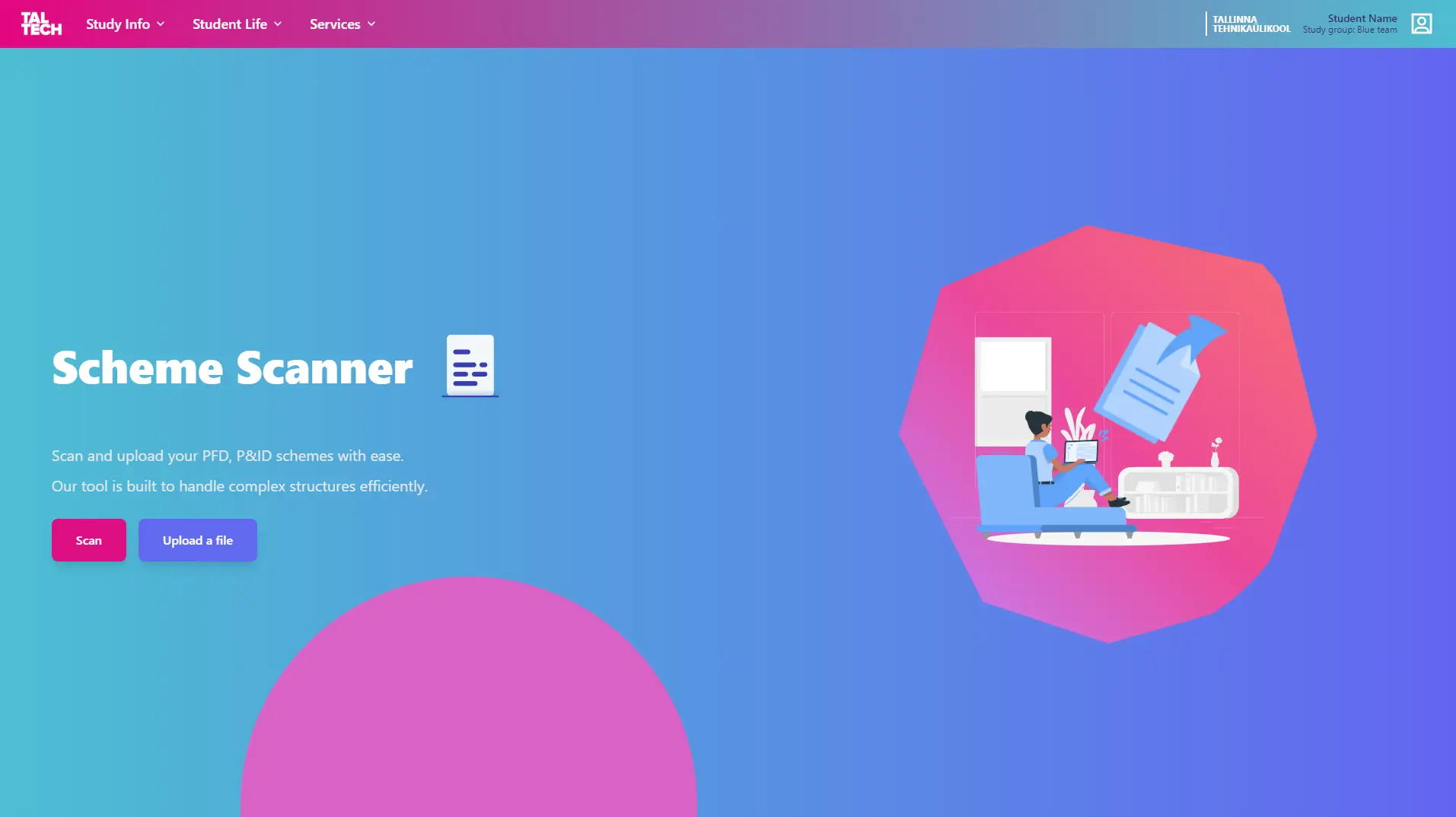
Scheme Scanner is a full-stack web application designed to scan and analyze PFD and P&ID schemes in real-time using your device's camera. You can also upload pre-captured images or files for scanning. The application utilizes a custom machine learning model, trained from scratch on 9,000+ images, ensuring accurate and efficient scheme detection.
- ⭐ Features
- 🛠️ How It Works
- 💻 Installation
- 📱 How To Use
- 📸 Live Scan
- 📤 File Upload
- 🚀 Technology Stack
- 🔧 Technical Implementation
- 💡 Challenges and Solutions
- 🔄 Maintenance and Expansion
- Live Scanning: Scan schemes in real-time using your camera.
- File Upload: Upload files containing schemes for scanning.
- Machine Learning Model: Trained on over 9k images for more precise detection.
- User-Friendly Interface: Simple and intuitive interface for easy use.
Scheme Scanner uses a custom-built machine learning model that has been trained to identify and analyze schemes. You can either scan schemes live via your camera or upload them as files to get instant results. The model processes the images in the background and displays the relevant information to the user.
1. Install Docker Desktop and login. After login minimise the app and do not close it:
https://desktop.docker.com/win/main/amd64/Docker%20Desktop%20Installer.exe?utm_source=docker&utm_medium=webreferral&utm_campaign=docs-driven-download-win-amd64
2. Open an IDE of your choice (Visual Studio Code preferably.) and open your terminal with git bash. Use cd command to move to your desired location where you want to download the project.
3. Download the project:
https://github.com/RemiPR/Erasmus-BIP-Scheme-Scanner/archive/refs/heads/master.zip
4. Navigate to the project directory:
cd Erasmus-BIP-Scheme-Scanner5. Install the dependencies using Docker inside the IDE terminal(Should take about 5 to 10 mins)
docker-compose build --no-cache6. Once the installation is finished, start the local development server:
docker-compose up7. Open a browser of your choice(Google Chrome recommended) and go to localhost:3000
1. if not installed, install git:
https://git-scm.com/download/win
2. if not installed, install Node.js:
https://nodejs.org/dist/v20.18.0/node-v20.18.0-x64.msi
3. Open an IDE of your choice (Visual Studio Code etc.) and open your terminal with git bash. Use cd command to move to your desired location where you want to download the project.
4. Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/RemiPR/Erasmus-BIP-Scheme-Scanner.git5. Navigate to the project directory:
cd Erasmus-BIP-Scheme-Scanner/frontend6. Install dependencies:
npm install7. Start the local development server:
npm run dev8. Open a browser of your choice(Google Chrome recommended) and go to localhost:3000
- Open the application and select the option to scan schemes via your camera.
- Grant camera access when prompted.
- Point your camera at the scheme, and the system will automatically detect it.
- Choose the option to upload a scheme image from your device.
- Upload the file, and the model will analyze it for you.
- Nuxt.js
- HTML5
- Tailwind CSS
- Python
- YOLO (You Only Look Once)
- Roboflow
Components
- svgAnimation.vue: This component is responsible for handling SVG-based animations displayed on the landing page.
Pages
- index.vue (Landing Page): Serves as the main entry point to the application, featuring introductory content and providing navigation to key functionalities such as real-time scanning and image uploaging for object detection.
- scan.vue: Implements real-time object detection through the integration of the user's webcam, allowing for live scanning and recognition of objects.
- upload.vue: Facilitates the upload of images, enabling object detection to be performed on the uploaded files.
Public Folder
- Contains essential assets, including the logo, landing page images, and animations. These are utilized for both documentation purposes and in the user interface.
Layouts
- default.voe: Defines the overall layour structure, incorporating a navigation bar and global design components that are consistent across the application.
The app's logic is modularized into the following core areas:
References
- DOM Elements: Manages references to video and canvas elements for rendering the webcam feed and drawing bounding boxes, alongside state management for detected items.
State Management
- Reactive Maps and Refs: Handle object detection, webcam feed, and canvas rendering.
- Computed Properties: Convert reactive maps into arrays for easier manipulation within the template.
Lifecycle Hooks
- onMounted: Initializes the video feed, loads the YOLO object detection model from Roboflow, and sets up continuous detection.
- onBeforeUnmount: Cleans up by removing event listeners.
Detection Logic
- initializeApp(): Starts the video stream and loads the YOLO model for real-time detection.
- detectFrame(): Captures video frames for object detection.
- updateDetectedItems(predictions): Updates detected items based on predictions from the model.
- renderPredictions(predictions): Draws bounding boxes and labels for detected objects on the canvas.
- resizeCanvas(): Aligns the canvas size with the video for accurate rendering.
Video Stream
- startVideoStream(): Accesses the webcam, sets it as the video source, and adjusts the canvas for rendering object detection results.
Model Loading
- loadModel(): Loads the YOLO object detection model from Roboflow using the provided publishable key.
Object Detection
- detectFrame(): Continuously detects objects in video frames, updating the state with their names and confidence levels.
State and Render Updates
- updateDetectedItems(predictions): Tracks detected objects, updating their names, confidence levels, and visibility based on timestamps.
- renderPredictions(predictions): Draws bounding boxes and labels for each detected object on the canvas.
- getConfidenceClass(confidence): Applies dynamic color classes (green, yellow, red) based on detection confidence levels.
File Upload and Image Processing
- uploadFile(): Manages image uploads to Cloudinary, retrieving the URL for further processing.
- processImage(): Uses the YOLO model to detect objects in the uploaded image and draws bounding boxes around them.
- Landing Page (index.vue)
- Video Animation: Integrates a background animation using the .webm video format.
- Navigation: Buttons provide navigation to the real-time object detection page (scan.vue) and the image upload page (upload.vue).
- Visual Design: Utilizes Tailwind CSS for gradients and blob shapes, giving the page a modern and fluid look.
- Real-time Object Detection (scan.vue)
- Video Feed: Displays the live webcam feed with a canvas overlay for real-time object detection (bounding boxes around detected objects).
- Detection Results: A list of detected objects is shown, including each object's name and confidence score.
- Responsive Layout: Ensures an optimal experience across mobile and desktop devices.
- Image Upload and Detection (upload.vue)
- Image Upload: Allows users to upload images for object detection.
- Image Preview: Displays the uploaded image with bounding boxes overlaid for detected objects.
- Detection List: Shows the detected objects and their confidence levels.
The project utilizes Tailwind CSS for all styling. Key design elements include:
- Background Gradients: Smooth transitions from light blue to purple for a modern, polished look.
- Blob Shapes: Dynamic, organic shapes that break the grid layout, adding a fluid and visually appealing design.
- Responsiveness: The grid layout adjusts seamlessly across various screen sizes, ensuring an optimal user experience on both desktop and mobile devices.
- Nuxt3: Used for server-side rendering and modern Vue 3-based development.
- Tailwind CSS: Utility-first CSS framework for creating a responsive UI.
- Roboflow: Machine learning API for integrating YOLO object detection.
- Cloudinary: Manages image uploads and storage, used in the upload.vue component for object detection.
The development journey of Scheme Scanner came with several problems that significantly shaped the final product:
- Training the Model: Training the YOLO model required considerable effort, taking over 5 hours to process more than 9,000 images. This extensive dataset was necessary to improve accuracy and ensure that the model could reliably recognize diverse scheme types.
Problem: During the development phase, we encountered issues with file uploads, specifically handling large image files, which led to timeouts or application crashes.
Solution: We implemented an image compression technique using the sharp library to reduce the file size before sending it to the server. Additionally, we configured the server to allow larger file sizes and implemented progress tracking to improve user experience.
Problem: Loading the machine learning model asynchronously on the frontend caused delays in the application initialization. Sometimes, the Roboflow model was not ready when the user attempted to scan a scheme.
Solution: We introduced a polling mechanism that checks for the model’s availability and ensures it is loaded before allowing the user to interact with the app.
Problem: The system had conflicts when switching between live camera input and file upload, leading to the webcam feed failing or canvas rendering issues.
Solution: We restructured the application to handle separate input streams more efficiently, ensuring that switching between the two modes would not cause conflicts. We added event listeners to properly terminate the webcam stream when users opt for file uploads.
Problem: Due to security settings on the Roboflow and Cloudinary APIs, we encountered CORS-related issues that blocked requests from the frontend.
Solution: We added appropriate CORS headers and ensured that API keys were configured correctly. Also, we configured nuxt.config.ts to allow nitro to use allow CORS by adding the necessary configuration:
nitro: {
cors: true,
},- Dataset Expansion: Regularly update the dataset with new images, particularly from new industries or sectors using unique schemes. Aim to add at least 1,000 new images every quarter to ensure model robustness.
- Re-Training: Re-train the YOLO model every 6 months or after any significant dataset update. Monitor the model’s accuracy and adjust the training parameters to reduce false positives/negatives.
- Performance Monitoring: Implement automated tests to check model accuracy against a validation set. Use metrics like precision, recall, and F1 score to determine if re-training is required.
- Frontend Libraries: Regularly check for updates to Nuxt.js, Tailwind CSS, and any other frontend libraries. Perform updates every 3 months or in response to critical security patches.
- API Key Management: Review the API key configurations for Roboflow and Cloudinary periodically. Rotate API keys every 6 months and implement environment-specific configurations.
- Security Scans: Conduct vulnerability scans using tools like Snyk or OWASP ZAP to identify and fix potential security flaws.
- User Authentication: If the app handles sensitive data in future versions, integrate user authentication with secure options like OAuth 2.0 or OpenID Connect.
- Use a version control system for tracking bugs and feature requests (e.g., GitHub Issues). Prioritize issues based on user impact and maintain a consistent bug-fixing schedule.
- Implement an automated error-logging system like Sentry to capture frontend and backend errors. This will aid in identifying critical bugs proactively.
- Performance Reviews: Periodically review and refactor code for optimization, especially as new features are added. Focus on reducing the app's load time and memory usage.
- Tech Debt: Address any technical debt by maintaining clear documentation of areas needing refactoring, optimizing data handling, and improving database queries.
- Annotation Tools: Develop annotation tools for users to manually highlight and label areas of interest on detected schemes. This could improve training data accuracy for future models.
- History and Analysis: Introduce a user history feature to store past scans and enable users to view, download, or compare previous analysis results.
- Reporting: Add the ability to generate detailed PDF reports of analyzed schemes, including detected elements, confidence levels, and any extracted data.
- Mobile App: Develop a native mobile application for Android and iOS using a framework like React Native or Flutter. This could allow for smoother real-time scanning with device-specific optimizations.
- Cloud Integration: Integrate with cloud platforms like AWS or Google Cloud for scalable storage and processing, which can handle larger datasets or provide faster model training.
- Third-Party API Integration: Connect with industrial software like AutoCAD or Plant 3D to allow importing/exporting scanned data directly into CAD environments.
- Edge Computing: Explore edge computing solutions for real-time detection on mobile devices without relying heavily on server-side processing. Implement TensorFlow Lite for mobile-optimized models.
- Caching Mechanisms: Implement caching for frequently scanned schemes to reduce server load and improve response time.
- Compression Techniques: Continue refining image compression to handle larger file uploads, focusing on lossless methods that do not compromise the accuracy of scheme detection.
- Model Versioning: Use MLflow or a similar tool to manage different versions of the model and track their performance metrics over time.
- Transfer Learning: Investigate pre-trained models for specialized detection tasks, then fine-tune them using the existing dataset to save on training time and improve accuracy.
- Model Optimization: Use techniques like pruning or quantization to reduce the model size and enhance performance, especially for mobile deployment.
- Theming and Customization: Allow users to customize the UI theme (light/dark mode) and layout to suit their preferences.
- Localization: Implement localization to support multiple languages, starting with the most common languages used by the current user base.
- Feedback System: Add a feedback option in the app for users to report issues or suggest features directly. This will aid in prioritizing future updates.
- User Tutorials: Develop in-app guides or video tutorials, detailing advanced usage scenarios, customization options, and best practices.