- Introduction
- Dataset Information
- GitHub Repository
- Project Scope
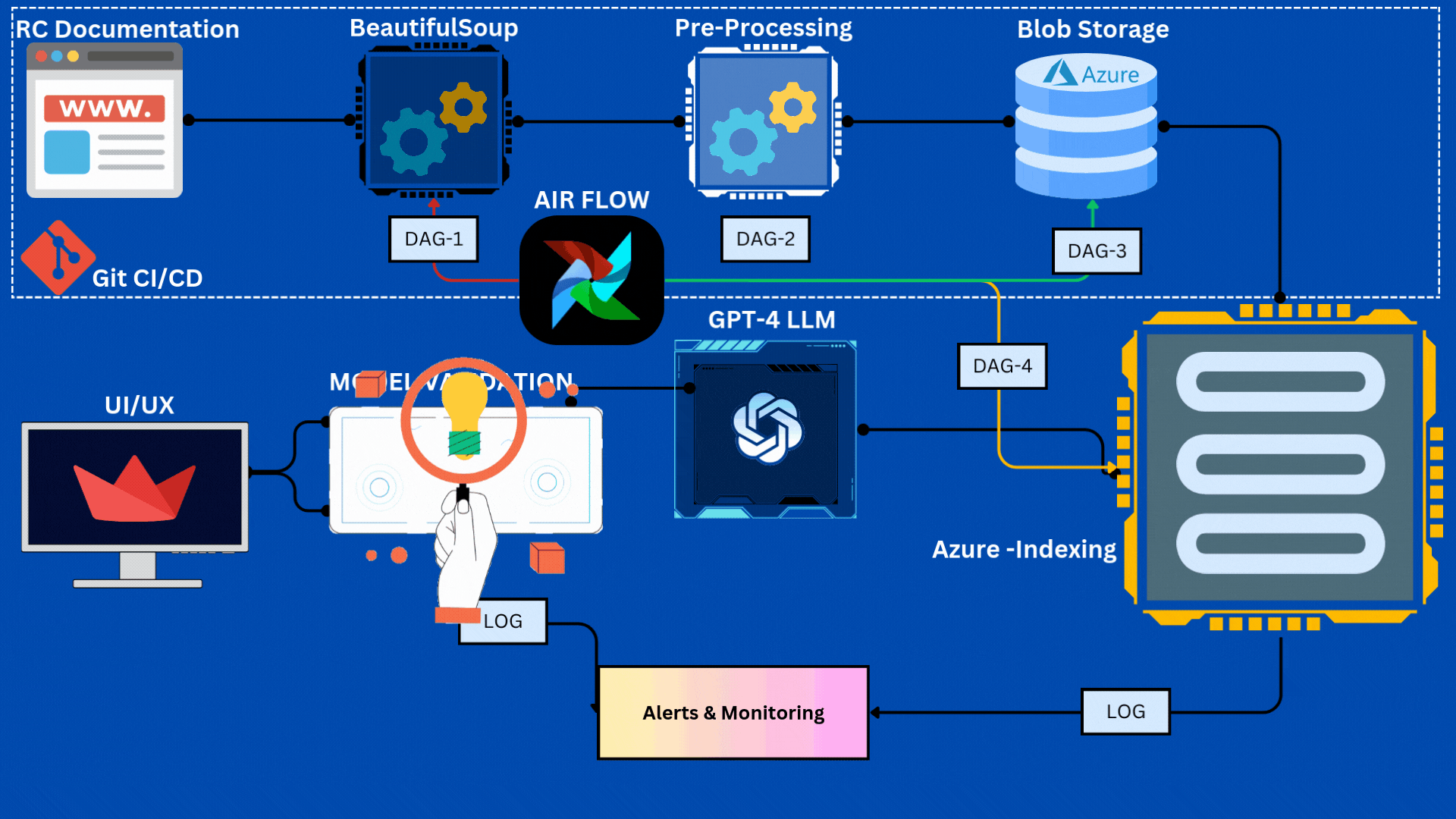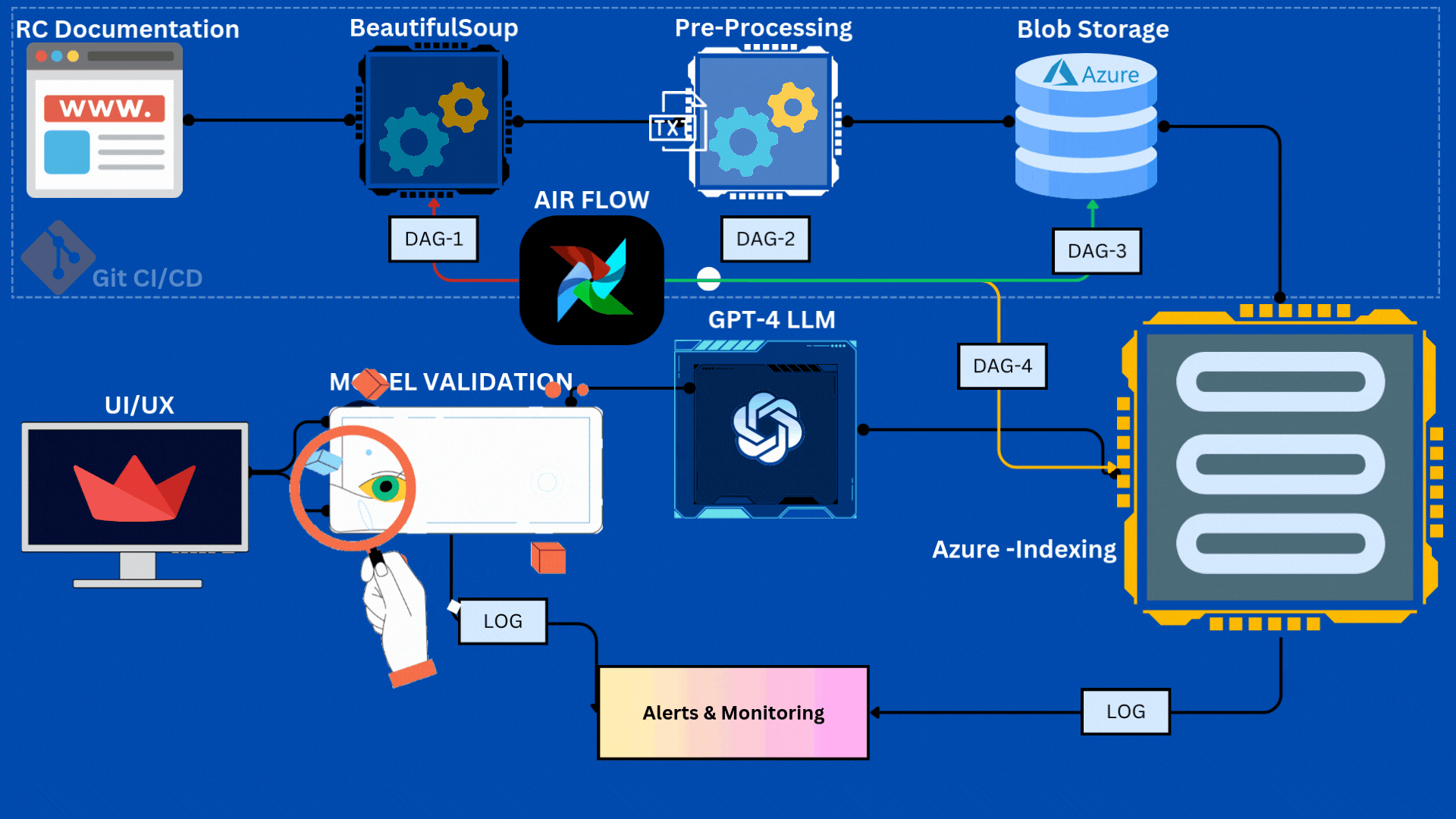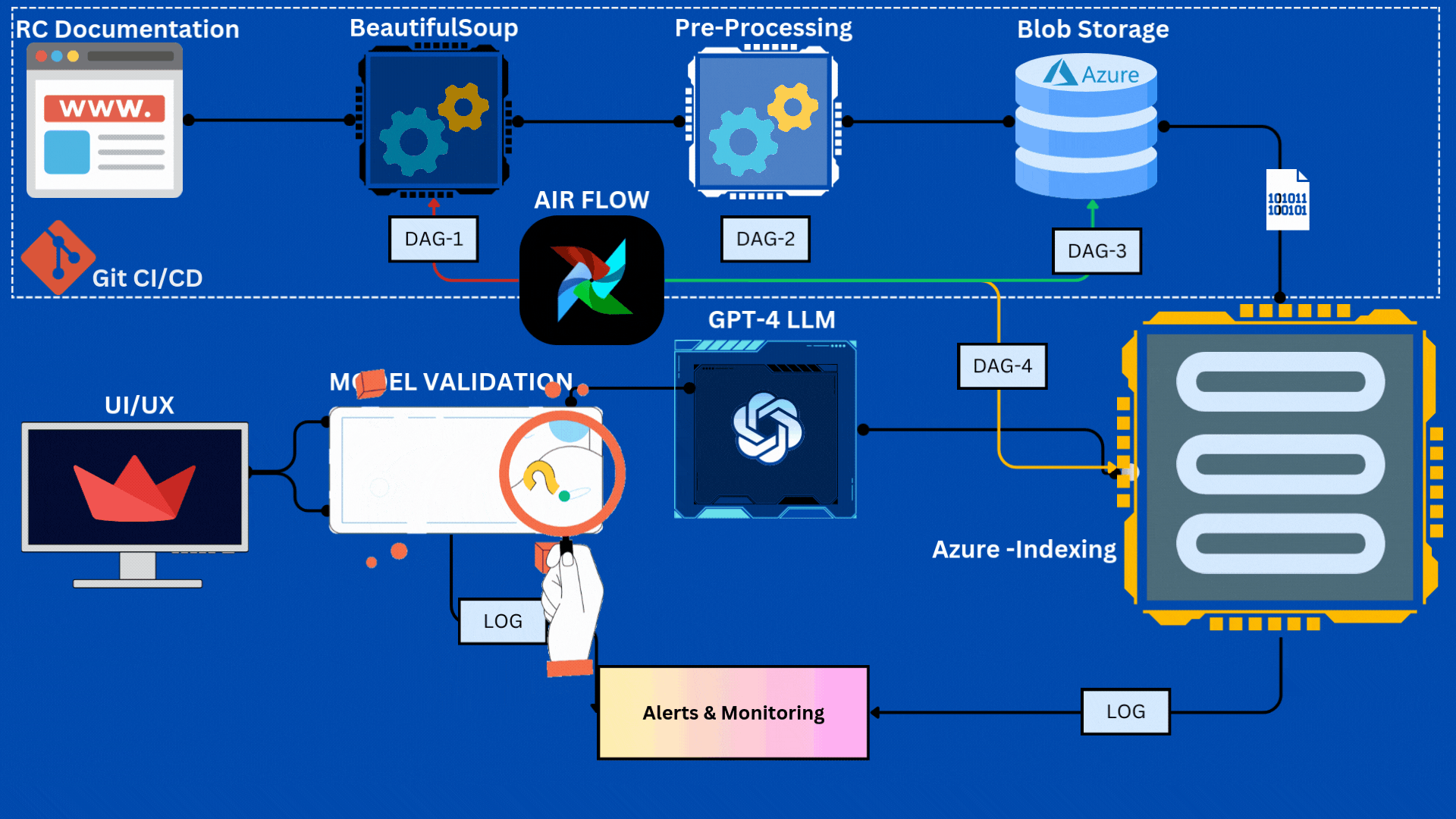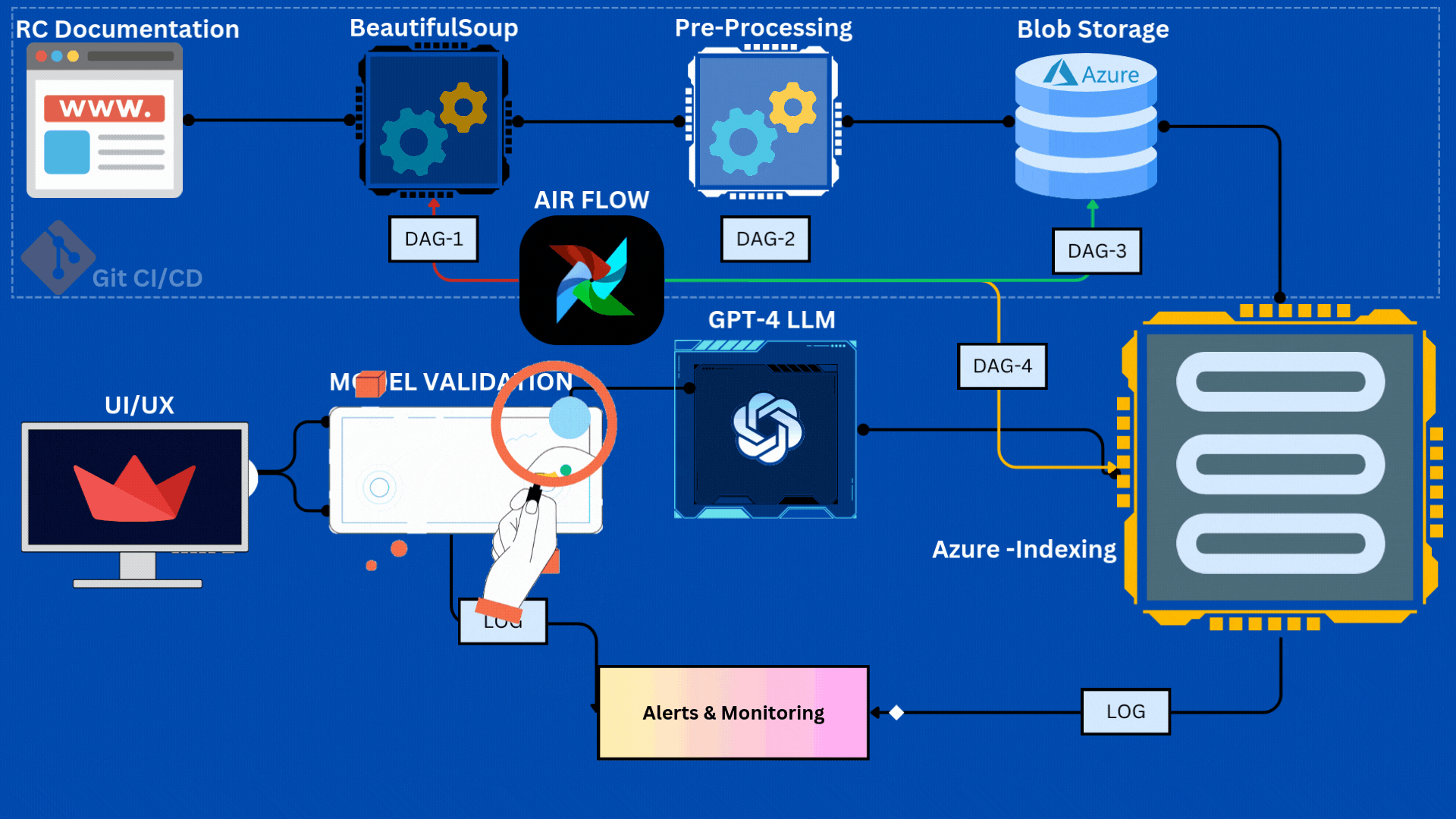
- Pipeline Components
- Data Management and Version Control
- Anomaly Detection and Alerts
- Bias Detection
- Cloud Deployment and User Interface
The Research Computing Department at Northeastern University offers numerous resources to researchers, yet these offerings are underutilized due to a lack of awareness. This project aims to develop a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) chatbot to address these issues by providing an interactive platform where users can ask questions and receive relevant, informative responses based on existing documentation.
By developing this chatbot, we will enhance awareness of the Research Computing Department's offerings and simplify the process of accessing resources, ultimately promoting more effective use of these valuable services.
RAG-based chatbots are ideal because they combine information retrieval with generation, ensuring responses are factually accurate and traceable to source documents. This solution is designed to promote resource discovery while maintaining the integrity and accuracy of the information being provided to users.
Our project includes developing an end-to-end Machine Learning Operations (MLOps) pipeline, including data ingestion, preprocessing, model training, and deployment. The chatbot will be deployed as a scalable serverless endpoint, enabling users to seamlessly interact and get the information they need.
The dataset will primarily come from the Research Computing Department's website at Northeastern University. This includes FAQs, documentation, and resource descriptions. Our chatbot will use this data to answer relevant queries accurately.
- Dataset Size: Flexible; new documents can be added as the department updates its resources.
- Data Format: Textual data extracted from HTML pages and PDFs.
- Data Types: Text-based segments, categorized into FAQs, resource descriptions, and procedural documentation.
- Data Processing: Data will be segmented, encoded into embeddings, and stored for efficient retrieval by the RAG model.
- Website: Research Computing Department website at Northeastern University.
- Documents: HTML pages, PDF files, and other hosted resources.
All public data on the Research Computing Department's website is eligible for educational use per Northeastern University's data policies. The project will ensure FERPA compliance and adhere to ethical web scraping practices, ensuring no personal or sensitive information is collected or processed.
The repository will follow this structure:
- askRC (root directory): Contains the main project components.
- airflow: Configurations and DAGs for workflow automation.
- azure: Infrastructure scripts and logic apps specific to Azure services.
- data: Divided into
raw,processed, andembeddingssubfolders. - dvc: Data Version Control files, including
dvc.yaml. - docker:
Dockerfileanddocker-compose.yamlfor containerization. - github_actions: Workflow automation scripts.
- mlflow: Directories for tracking model experiments.
- snoopy: Monitoring scripts for the pipeline.
- src: Divided into
data_ingestion,model_training,evaluation, anddeploymentfolders. - README.md: Project documentation.
- requirements.txt: Lists all dependencies for the project.
- Lack of Awareness: Researchers are often unaware of the services offered by the Research Computing Department.
- Access to Resources: Navigating the information on the department's website is challenging for researchers, leading to difficulty in accessing resources.
- Incident Overload: Due to the challenges of finding information, many issues that could be resolved through self-service result in a large number of incident reports, increasing the workload for research assistants and employees.
- Manual Search: Currently, researchers manually browse the website to find relevant information, which is inefficient and time-consuming.
- Incident Tickets: Every time an issue arises, a ticket is created, and the researcher must wait for the issue to be resolved by a research assistant, leading to delays in productivity.
- RAG-based Chatbot: Develop a RAG chatbot that can efficiently answer common questions related to the department's resources and services.
- Improved Resource Discovery: Leverage existing information from the department's website to enhance the chatbot’s accuracy in responding to user queries, making resource discovery more efficient.
The Data Acquisition component is designed to dynamically fetch data from specific sections of a website based on the current week. This is achieved through the scraper.py and get_all_url.py modules, which handle URL scraping and link gathering, respectively.
-
Section Management:
scraper.pydefines the URLs for different sections of the website and manages the logic to scrape sections incrementally based on the current week.- The
scrape_sections_up_to_current_week()function uses theget_current_week()function to determine which sections to scrape, ensuring it stays within the total number of sections available.
-
Recursive Link Gathering:
- The
get_all_url.pymodule contains theget_all_links()function, which fetches all links from a given URL up to a specified depth. It recursively visits sub-links within the same domain, ensuring a thorough link gathering process without exceeding a defined depth limit to avoid overloading the crawler. - By converting relative URLs to absolute URLs and using a set to track visited URLs, this function avoids duplicating links, maintaining an efficient recursive crawl within each section.
- The
-
Data Fetching and Arrangement:
- The
fetch_and_print_links()function retrieves links for each section by callingget_all_links()on each URL provided. The number of links found is printed for each section to provide feedback on the volume of data captured. - After links are fetched, the
arrange_scraped_data()function organizes the data into structured directories, ensuring ease of access and reusability.
- The
The Data Preprocessing component is responsible for preparing raw text data for further processing. This involves several key steps, outlined in modular functions that ensure code reusability and clarity:
-
Text Cleaning:
- The
clean_text()function preprocesses text by converting it to lowercase, removing special characters and numbers, and excluding common English stopwords. This function enhances text quality by retaining only meaningful words.
- The
-
Content Splitting:
- The
split_content()function splits large chunks of text into smaller parts to meet the maximum term size constraint (MAX_TERM_SIZE) for Azure Search. This is crucial for efficiently managing large data within Azure's storage limits.
- The
-
Text File Processing:
- The
preprocess_text_file()function applies text cleaning and splitting to a single text file. It saves the cleaned and split text as separate JSON files, each with a unique ID, allowing easy identification and retrieval.
- The
-
Batch Processing:
- The
preprocess_data()function iterates through all text files in an input folder, applying cleaning and splitting functions to each file. The processed data is stored in an output folder, with organized JSON files that are easy to access and further process.
- The
The Azure Blob Storage Integration component facilitates the storage of preprocessed data in Azure, ensuring accessibility and durability. This is handled through functions in the azure_uploader.py module:
- Authentication Setup: Azure credentials (client ID, client secret, tenant ID, and storage account URL) are loaded from environment variables using the
ClientSecretCredentialfromazure.identity. - Blob Service Client Setup: Establish a connection to the Blob service.
- Container Client Access: Access the specific container (
preprocessed-data). - File Upload to Blob Storage: The
upload_to_blob()function uploads preprocessed JSON files to a specified container in Azure Blob Storage.
After data is uploaded to Azure Blob Storage, we implement a data indexing process in Azure Search to facilitate efficient similarity scoring and fast search capabilities for our RAG chatbot.
- Azure Client Setup: Secure connections for Blob Storage and Azure Search.
- Data Retrieval from Blob Storage: Iterates over each blob in
preprocessed-dataand validates document size. - Indexing in Azure Search: Valid documents are indexed in the specified Azure Search index (
askrcindex), enhancing search efficiency and accuracy.
To ensure the robustness of our data pipeline, we use pytest for unit tests and GitHub Actions for continuous integration. Key components include:
- Data Retrieval Test
- Data Format Test
- Error Handling Test
- Continuous Integration: GitHub Actions automate the testing process.
The Pipeline Orchestration component uses Airflow to manage and automate the workflow from scraping to indexing.
- DAG Configuration: Scheduled daily, with retry logic and alerts.
- Task Dependencies:
scrape_task → preprocess_task → blob_storage_task → index_task.
DVC is set up to track data/raw and data/processed. Version history and collaboration are enabled through GitHub integration.
Airflow’s built-in logging tracks task progress, errors, and provides alerts.
Automated email notifications ensure the team is alerted to any failures, enhancing pipeline reliability.
Although bias detection is not mandatory due to the standardized nature of the source material, proactive measures ensure neutrality:
- Sentiment Analysis: Verifies neutral tone.
- Data Slicing by Sentiment: Allows observation of any unintentional tone patterns.
- Topic Modeling and Keyword Frequency Analysis: Ensures chatbot responses are representative of the full breadth of available information.
The project is designed for cloud deployment using Azure as the cloud provider, leveraging Azure Web App for hosting the model, application, and user interface. The deployment ensures robust, scalable, and secure delivery of services over the internet.
The RAG chatbot backend is hosted on Azure Web App, utilizing its managed infrastructure to expose RESTful endpoints for seamless interaction with the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) model. The user interface, created using Streamlit, provides an intuitive platform for users to interact with the chatbot and visualize responses.
The web version of the application is deployed at https://rakshith2605.github.io/askrc_web/. This includes an option to connect to the ASKRC bot for real-time interactions.
The solution integrates with Azure Blob Storage, where preprocessed data files are securely stored, and Azure Cognitive Search, which indexes these files to enable efficient and precise information retrieval during chatbot interactions. This architecture ensures high performance, scalability, and ease of management for both the backend services and the user interface.