In this project, I have tried to recognize emotions from audio signals of IEMOCAP dataset. The audio files are in english language. IEMOCAP is an acted, multimodal and multispeaker database, recently collected at SAIL lab at USC. It contains 12 hours of audiovisual information. Different windows of audio sessions has been tagged with one of the eight emotions(frustrated, angry, happiness, sadness, excited, surprised, disgusted and neutral). Details of dataset can be found here. In this approach, I have only utilized the audio part of the data
- Pytorch
- torch
- matplotlib
- numpy
- pandas
- librosa
- multiprocessing
- joblib
- re
- soundfile
The objective of the attempt was to evaluate multi-modal implementation using features extracted from audio signals. Following are the steps applied to arrive at the final model:
- Analyzed audio signals, extracted labels tagged to sessions. Each session has been tagged with different emotions based on timestamp
- Low Level Descriptors are expected to capture emotion related information. Extracted acoustic features like MFCC, Mel, pitch, contrast, flatness, zero crossing rate, chroma and harmonic means. Apart from using these acoustic features directly, I have applied aggregators and summarizers like mean, min, max, standard deviation etc
- These extracted features will be used as input in different models
- trained an LSTM model using acoustic feature as embeddings to the model
- trained an ensemble model using GBM, Random Forest, XG Boost
- trained a DNN (Deep Neural Network) using MFCC features
-
Using the audio signal, generated images of mel-spectrogram. A spectrogram is a representation of speech over time and frequency. 2D convolution filters help capture 2D feature maps in any given input. Such rich features cannot be extracted and applied when speech is converted to text and or phonemes. Spectrograms, which contain extra information not available in just text, gives us further capabilities in our attempts to improve emotion recognition Below is an example:
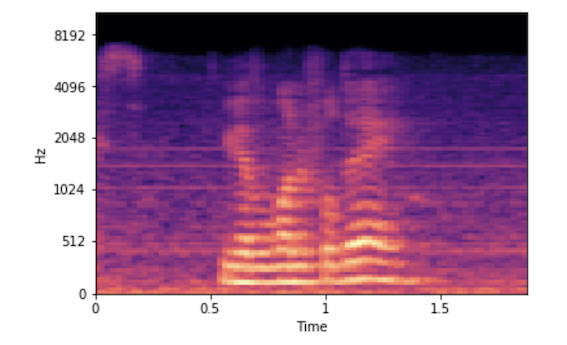
-
PyTorch based ResNet models are trained using the 2D spectrograms. I have trained three different models.
- A CNN with 4 layers
- ResNet with 18 layers
- ResNet with 34 layers and SGD as optimizer
-
Finally, used average ensembling of probabilities predicted by follwing models to get the final accuracy of 65%
- PyTorch with 34 layers
- DNN with MFCC
- ML ensemble model
Following is the code base tree with explanation of files:
speech-emotion-recognition-iemocap
├── README.md
├── code
│ ├── data_prep
│ │ ├── acoustic_feature_extraction
│ │ │ ├── audio_analysis.ipynb
│ │ │ ├── extract_acoustic_features_from_audio_vectors.ipynb
│ │ │ └── extract_labels_for_audio.ipynb
│ │ ├── spectrogram_generation
│ │ │ └── saving_spectrogram_audio_data_parallel.ipynb
│ │ └── train_test
│ │ └── creating_train_test_folder.ipynb
│ └── models
│ ├── dl_models_using_spectrogram
│ │ ├── PyTorch_CNN.ipynb
│ │ ├── PyTorch_ResNet18.ipynb
│ │ └── PyTorch_ResNet34_SGD.ipynb
│ ├── lstm_model_using_acoustic_features
│ │ └── data_prep_and_lstm.ipynb
│ ├── ml_dl_models_using_mfcc
│ │ ├── DNN_with_MFCC.ipynb
│ │ ├── ML_with_MFCC_Normalized.ipynb
│ │ └── features_analysis.ipynb
│ └── text_model
│ └── data_preparation_for_text_based_model.ipynb
└── image
└── mel-spectrogram.png
- audio_analysis.ipynb - analysis of audio signals
- extract_acoustic_features_from_audio_vectors.ipynb - extracting audio features using librosa
- extract_labels_for_audio.ipynb - extracting emotion labels for audio clips of ecah session
- saving_spectrogram_audio_data_parallel.ipynb - generating 2D spectrogram images
- creating_train_test_folder.ipynb - creating training and test dataset using extracted features and images above
- PyTorch_CNN.ipynb - simple CNN using PyTorch
- PyTorch_ResNet18.ipynb - 18 layered ResNet training
- PyTorch_ResNet34_SGD.ipynb - 34 layered ResNet training
- data_prep_and_lstm.ipynb - training lstm model using acoustic features as embeddings or input
- DNN_with_MFCC.ipynb - training 2 layered DNN using MFCC from acoustic features
- ML_with_MFCC_Normalized.ipynb - training ensemble model using normalized MFCC
- features_analysis.ipynb - analyzing acoustic features to spot difference between values across 4 emotion classes
- data_preparation_for_text_based_model.ipynb - text data preparation to be used as an input in multi-modal approach
- train a CNN or LSTM model using features from text. Features could be either tf-idf vectors of dialogues or embedding from a pretrained network
- create a multi modal pipeline to pool 34 layered PyTorch model, ML Ensemble model, text based model