This repository contains code and resources for predicting stock prices using machine learning techniques. The goal is to develop a model that can accurately predict future stock prices based on historical data.
Stock price prediction is a challenging task due to the volatility and complexity of financial markets. This project aims to leverage machine learning algorithms to make accurate predictions based on historical stock price data.
To run this project locally, follow these steps:
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/Shengwei-Peng/Stock-Price-Prediction.git cd Stock-Price-Prediction -
Install the required dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
The dataset used in this project consists of historical stock prices fetched using the twstock library. Here is an example of how to fetch the data:
import twstock
import pandas as pd
# Fetch historical stock data for stock code '2330' from January 2014 to present
stock = twstock.Stock('2330')
data = pd.DataFrame(stock.fetch_from(2014, 1))
# Save the data to a CSV file
data.to_csv("2330.csv", index=False)Below is a brief description of each column in the dataset and a sample table to illustrate the data format:
| Column | Description | Data Type | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Date | The trading date | YYYY-MM-DD | |
| Capacity | The total traded volume of stocks | int | Shares |
| Turnover | The total value of traded stocks | int | TWD |
| Open | The opening price of the stock | float | TWD |
| High | The highest price during the day | float | TWD |
| Low | The lowest price during the day | float | TWD |
| Close | The closing price of the stock | float | TWD |
| Change | The price change compared to the previous day | float | TWD |
| Transaction | The number of transactions | int | Transactions |
| Date | Capacity | Turnover | Open | High | Low | Close | Change | Transaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014-01-02 | 15133724 | 1578860796 | 105.0 | 105.5 | 103.5 | 104.5 | -1.0 | 4136 |
| 2014-01-03 | 41160529 | 4220062918 | 103.0 | 103.0 | 102.0 | 102.5 | -2.0 | 8524 |
| 2014-01-06 | 23729719 | 2432745661 | 102.0 | 103.0 | 102.0 | 102.5 | 0.0 | 4874 |
To use the stock price prediction tool, follow these steps:
- Prepare your dataset: Ensure your dataset is in the correct format and located in the
datadirectory. - Run the main script: Execute the following command to start the process:
python main.py --data_path data/2330.csv --model transformer --test_size 20 --window_size 20 --seed 0
The script will perform the following steps:
- Preprocessing: Clean and prepare the data for analysis.
- Training: Train the prediction models on the prepared data.
- Evaluation: Assess the performance of the trained models and generate performance metrics.
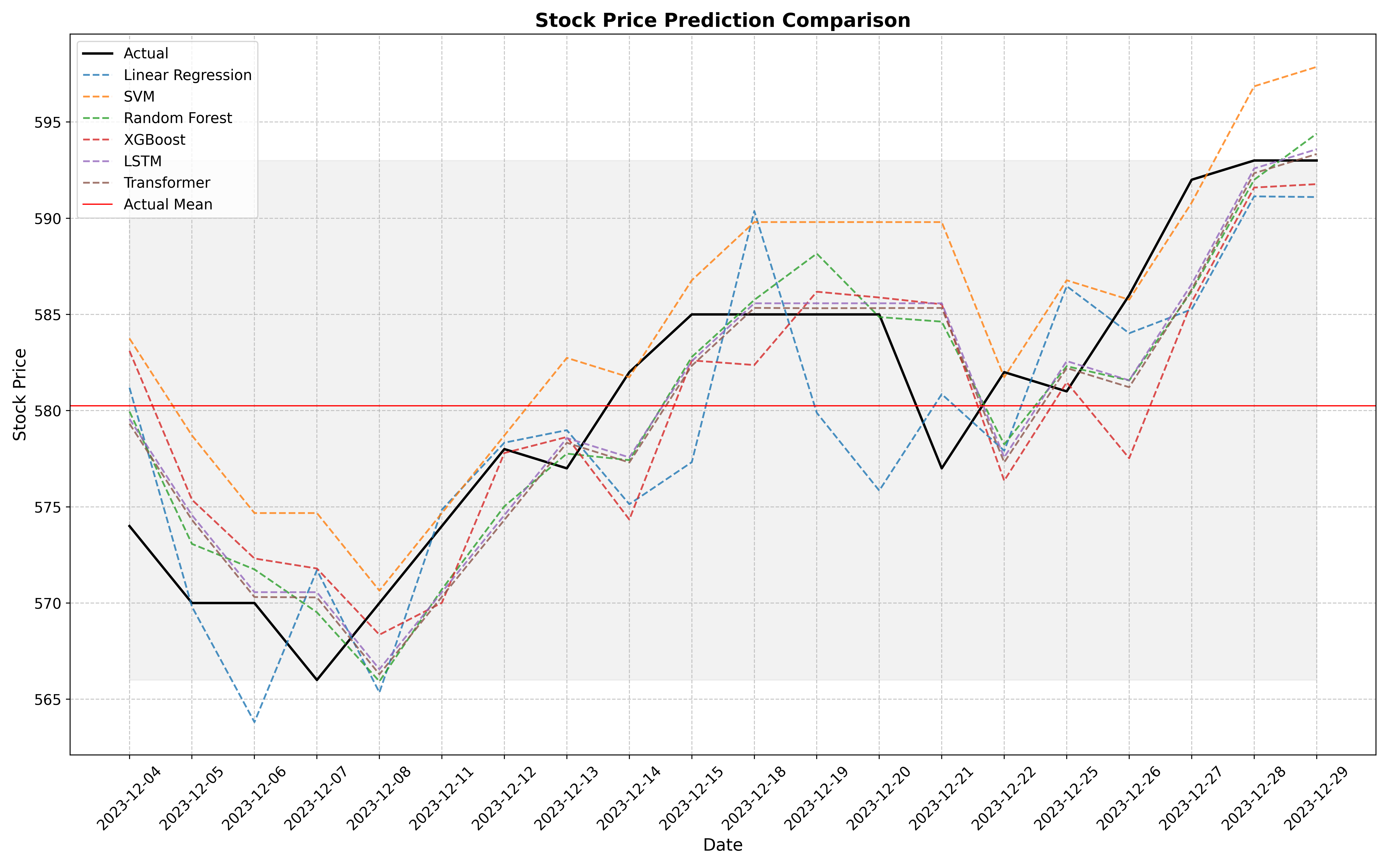
- Visualization: Create visualizations to compare the predicted stock prices with actual prices.
You can customize the behavior of the tool using various configuration options. Here are some examples:
data_path: Specify the path to the input data file.model: Choose the machine learning model to use. Options includelinear_regression,svm,random_forest,xgboost,lstmandtransformer.test_size: Specify the number of latest trading days to use as the test set.window_size: Specify the number of past days (D) to use for predicting the next day (D+1).seed: Set a random seed for reproducibility of results.
For a complete list of arguments, refer to the parse_args function in utils.py.
The tool generates various plots to help understand the performance of the models. It includes:
- Line plots: Comparing the predicted and actual stock prices over time.
- Residual plots: Visualizing the residuals (differences between true and predicted values) over time to identify any patterns or anomalies.
- Scatter plots: Comparing the true prices with the predicted prices to assess the model's accuracy visually.
These visualizations help in analyzing the accuracy and effectiveness of the predictions.
The performance of each model is evaluated using various metrics, including R², MSE, RMSE, MAE and NDEI. Below are the evaluation results for the implemented models:
| Model | R² | MSE | RMSE | MAE | NDEI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Regression | 0.5790 | 25.5890 | 5.0586 | 4.3584 | 0.6488 |
| SVM | 0.4966 | 30.5983 | 5.5316 | 4.2504 | 0.7095 |
| Random Forest | 0.7832 | 13.1793 | 3.6303 | 3.0765 | 0.4656 |
| XGBoost | 0.6167 | 23.2974 | 4.8267 | 3.8451 | 0.6191 |
| LSTM | 0.7675 | 14.1318 | 3.7592 | 3.0583 | 0.4822 |
| Transformer | 0.7645 | 14.3175 | 3.7838 | 3.0347 | 0.4853 |
- R² (Coefficient of Determination): Indicates how well the predictions match the actual values. A negative R² indicates that the model is performing worse than a horizontal line (mean prediction).
- MSE (Mean Squared Error): Measures the average squared difference between the predicted and actual values. Lower values indicate better performance.
- RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error): The square root of MSE, providing an error metric in the same unit as the target variable. Lower values indicate better performance.
- MAE (Mean Absolute Error): Measures the average absolute difference between the predicted and actual values. Lower values indicate better performance.
- NDEI (Non-dimensional Error Index): The ratio of the RMSE to the standard deviation of the actual values. Lower values indicate better performance, and it is useful for comparing the error relative to the variability of the data.
- Stock: TSMC (2330)
- Date Range: January 2014 to December 2023
- Test Set: The last 20 trading days
The models were trained on data spanning nearly a decade to capture various market conditions and trends. The final 20 trading days of this period were reserved for testing to evaluate the models' performance on recent data.
Contributions are welcome! Please follow these steps to contribute:
- Fork the repository.
- Create a new branch (
git checkout -b feature-branch). - Commit your changes (
git commit -am 'Add new feature'). - Push to the branch (
git push origin feature-branch). - Create a new Pull Request.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
For any questions or inquiries, please contact [email protected]