The methods and codes in this repository are described in more detail here: Behr, A.S.; Surkamp, J.; Abbaspour, E.; Häußler, M.; Lütz, S.; Pleiss, J.; Kockmann, N.; Rosenthal, K. Fluent Integration of Laboratory Data into Biocatalytic Process Simulation Using EnzymeML, DWSIM, and Ontologies. Processes 2024, 12, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12030597
This repository contains the code and the MS Excel files (subdirectory ELNs) used as data input for the automated generation of process simulations in DWSIM. Besides an EnzymeML-based Excel file for laboratory data, an additional Excel file is used for the process-related data uptake. To obtain the process simulation, the ontology ./ontologies/BaseOntology.owl is loaded and extended by the data contained in both Excel-files by the code contained in ELNs_to_KG_modules.py. This yields a knowledge graph (./ontologies/KG-DWSIM_EnzML_ELN.owl) that is loaded by the code DWSIM_modules.py and used to generate the DWSIM-file, stored in the subdirectory DWSIM. Furthermore, the data obtained by the process simulation is also stored in the knowledge graph (./ontologies/KG-DWSIM_EnzML_ELN_output.owl) enabling a holistic storage of the related data.
The overall workflow is depicted below, showing the overall data integration. Starting with laboratory data recorded in EnzymeML ELNs on enzyme kinetics and reaction rates investigations of enzymes, data is read in with Python and stored in a structured manner with the help of a tailored ontology as a knowledge graph.
Then, the recorded data is used to automatically generate process simulations, resulting in further insights and eased workflow from laboratory to process simulation data.
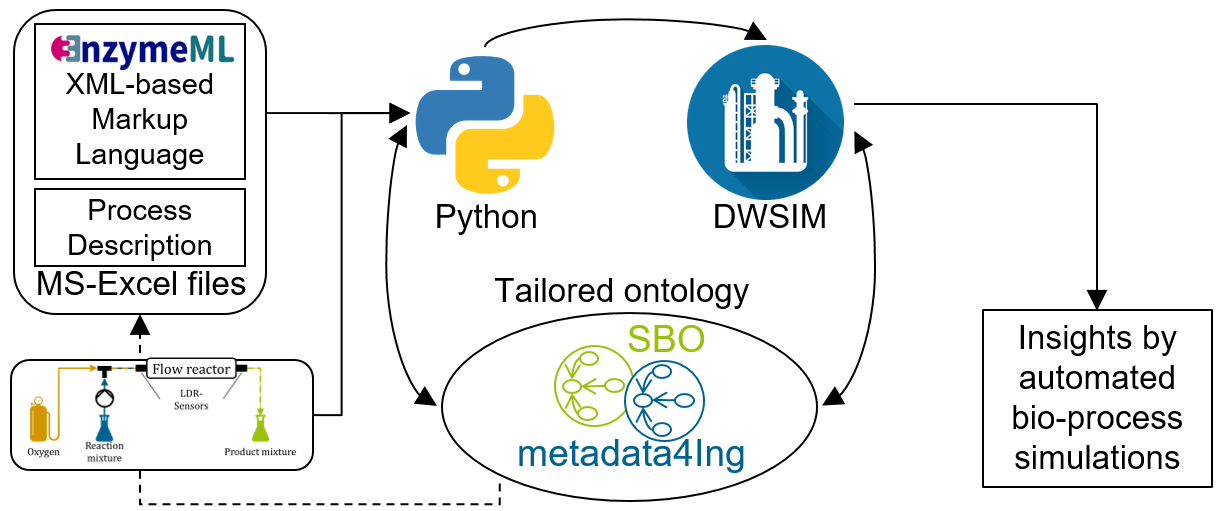
The working principle of the code to create the DWSIM-simulation files is depicted in the figure below. This is executed by the run() function contained in DWSIM_modules.py
First, you need to install the DWSIM-software.
Needed Python modules (list may not be complete!):
pip install owlready2
pip install pythonnet
To run the software, simply execute main.py.
This code executes the two main run() functions of the files mentioned above.
