Run Laravel Artisan commands from within Visual Studio Code.
- Supports multiple instances of artisan in the same workspace hierarchy
- Make files (Controllers, Migrations, Models, etc)
- Run Custom Commands
- Manage the database
- Clear Caches
- Generate Keys
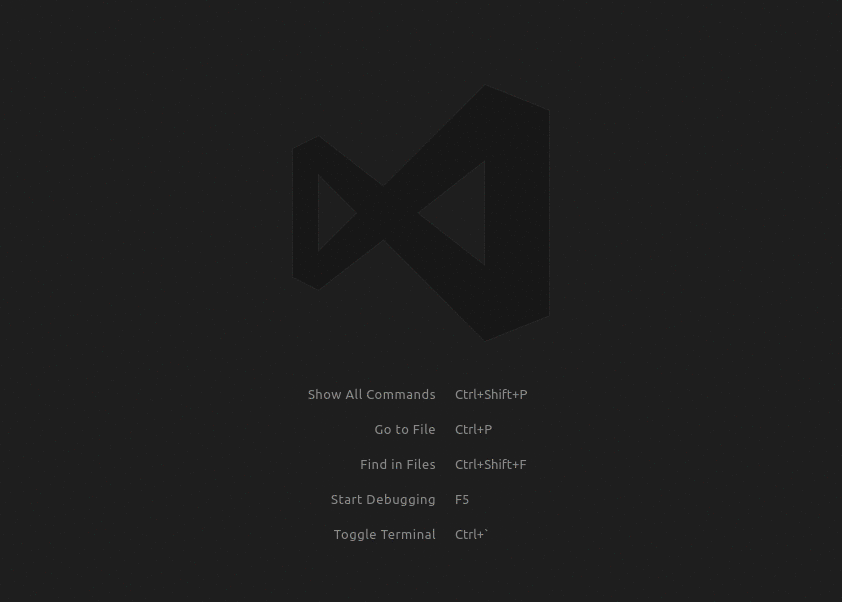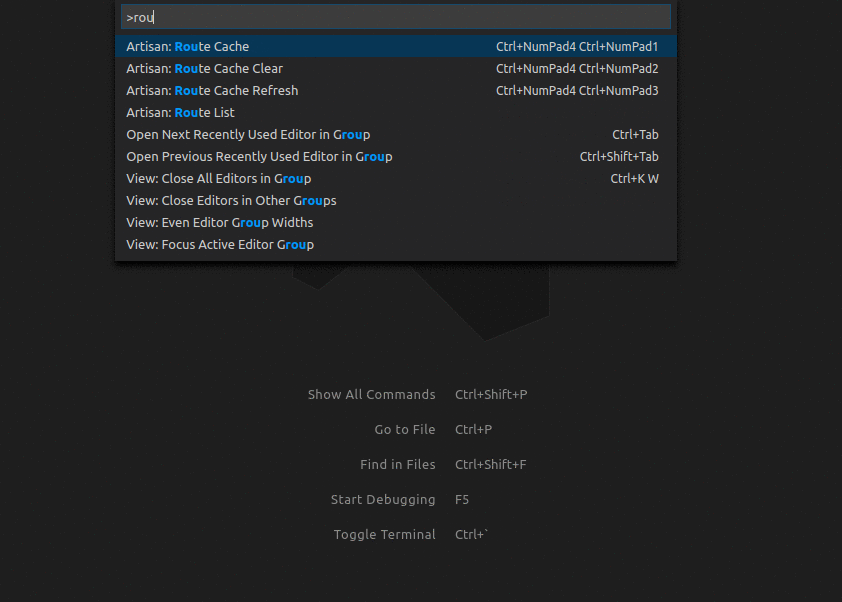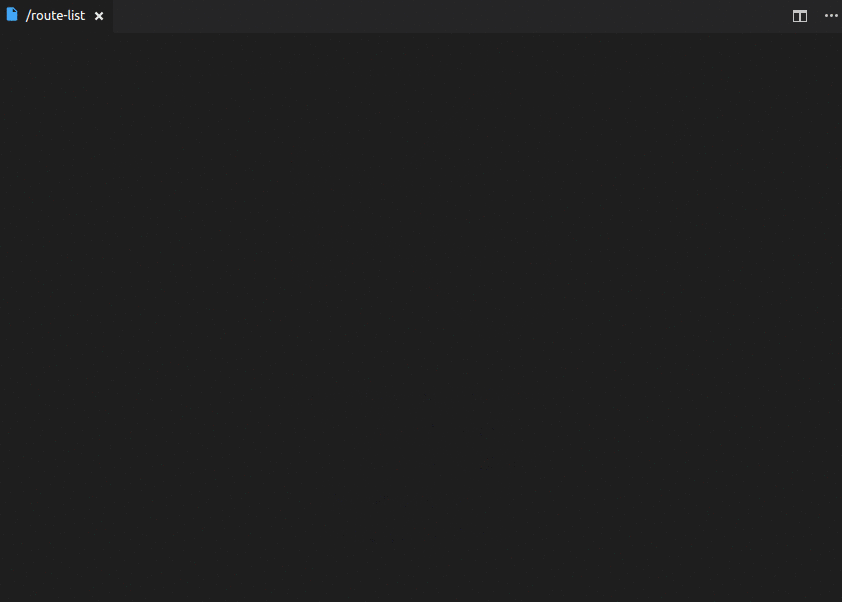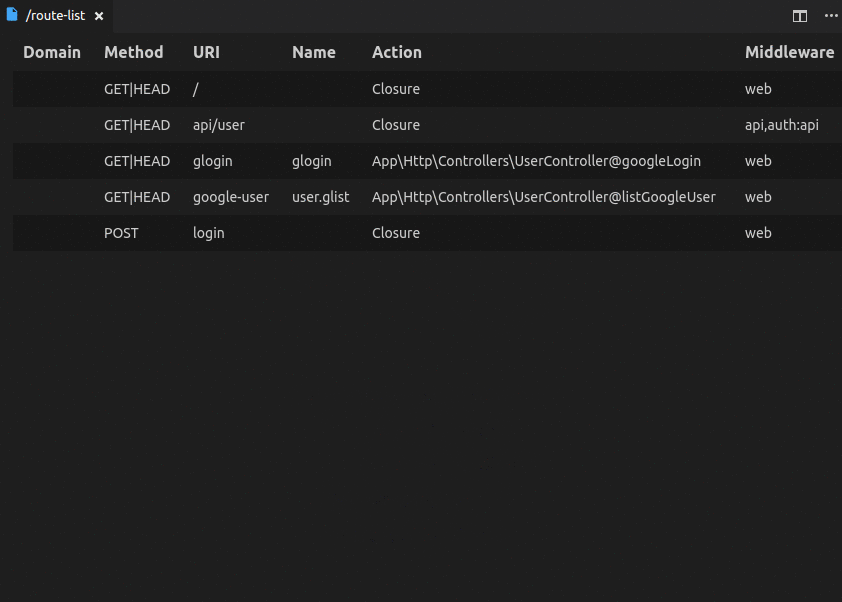
- View all routes
- Start/stop a local php server for test purposes
- Docker support
Note: The php setting is optional if the setting artisan.php.location is set in your settings.json file and points to a valid php executable. If this setting is set, the extension will prefer the setting over the one within the path.
- A useable version of
phpthat can be ran on the command line such asphp-cli(This should be in your path)- The following command should yield a php version:
php -v- If no php version is returned you don't have php setup correctly.
- If you get a version back you are good to go!
- A Laravel install that has
artisanin the workspace root- cd into your root directory and run the following command:
php artisan -v- If an error is returned you don't have laravel setup correctly.
- If you get a Laravel version and a list of commands you are good to go!
Once you have installed the extension, it will become active once you open a workspace that has at least one artisan file within the workspace.
You can then open the command pallet, and start running the commands.
Just type Artisan: to get a list of commands. If you have more than one artisan file within the workspace, then this will ask which artisan file you want to use to execute the selected command.
Many commands have optional input questions, leave them blank to use the defaults, or enter your own value.
All commands are accessible through Artisan: Run Command, here you can access your custom commands as well as built in commands.
You can also right click on some files and folders to run commands, the context menu will only show commands that are relevant to the file or folder you have right clicked on. The context menu will show on child folders and files as well as the main folder.
- app – Run app related commands.
- Make – To make app files.
- Serve – To start/stop a local php server.
- database – Run database related commands.
- Make – To make database files.
- Migrate – To run migrations.
- resources – Run resource related commands.
- routes – Run route related commands.
- Misc – Run misc commands (displayed on all files & folders).
If you are running Laravel with Docker you can set config vars like this, considering your docker-compose.yml is placed on project's root.
{
"artisan.docker.enabled": true,
"artisan.docker.command": "docker-compose exec <app>"
}Where <app> is your container name. Note this is a base command that will prepend to artisan commands.
Example:
docker-compose exec app php artisan make:model PostBefore running any commands, make sure the containers are running (docker-compose up).
If php is installed with WSL (Windows Subsystems for Linux), add the path to the executable in settings.json like below
When using the newer versions of WSL, you can set the artisan.wsl setting to true and the artisan.php.location setting to /usr/bin/php to use the default php installation.
{
// Opens wsl and runs the command in the wsl shell
"artisan.wsl.enabled": true,
// Optional if you have php installed in a different location that the one in the path:
"artisan.php.location": "/path/to/php"
}- Replace
<username>with the correct user name - Replace
CanonicalGroupLimited.Ubuntu18.04onWindows_79rhkp1fndgscwith the proper package name - Replace
usr\\bin\\phpif php is installed in different location
{
"artisan.php.location": "C:\\Users\\<username>\\AppData\\Local\\Packages\\CanonicalGroupLimited.Ubuntu18.04onWindows_79rhkp1fndgsc\\LocalState\\rootfs\\usr\\bin\\php"
}