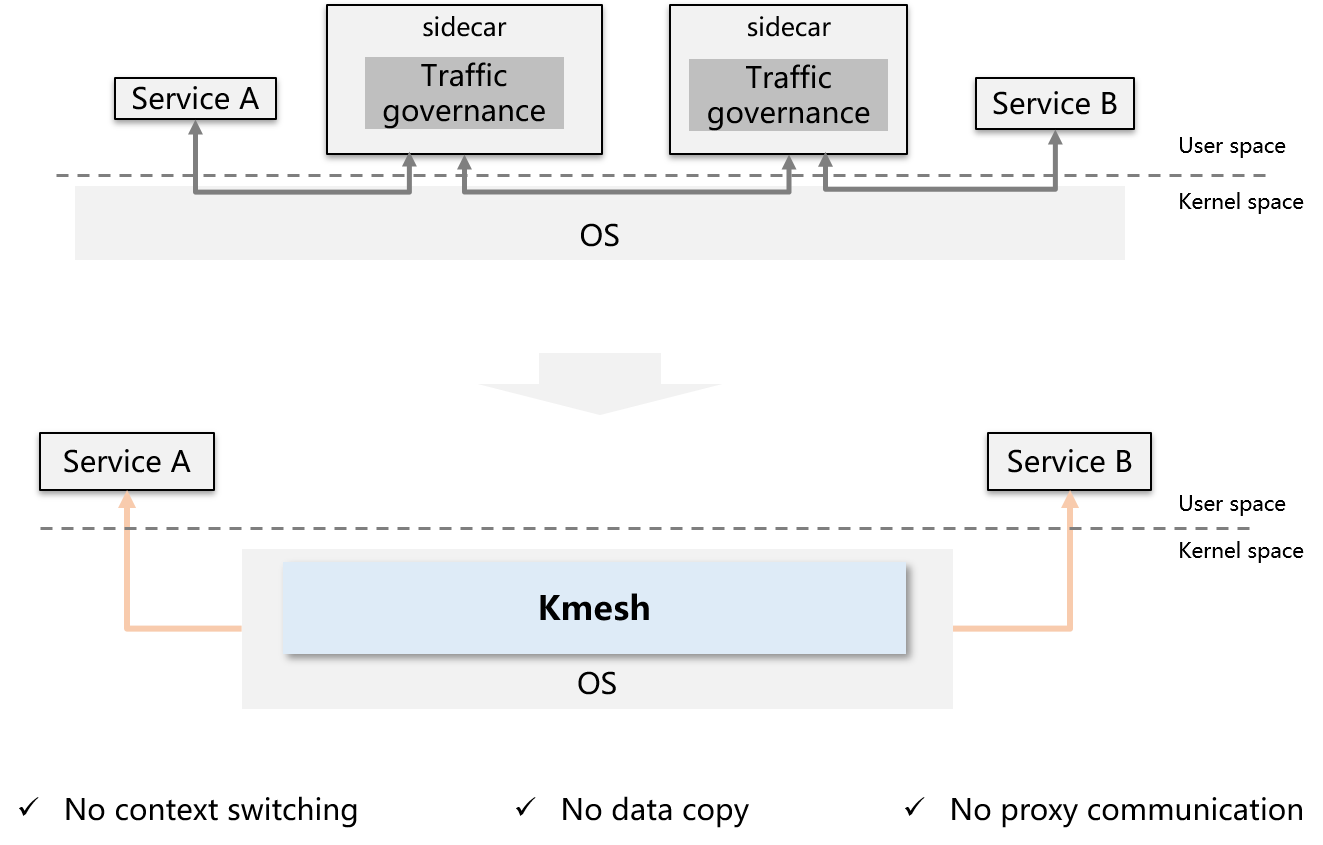
Kmesh is a high-performance service mesh data plane software based on programmable kernel. Provides high-performance service communication infrastructure in service mesh scenarios.
The service mesh software represented by Istio has gradually become popular and has become an important component of cloud infrastructure. However, the current service mesh still face some challenges:
- Extra latency overhead at the proxy layer: Single hop service access increases by 2~3ms, which cannot meet the SLA requirements of latency-sensitive applications. Although the community has come up with a variety of data plane solutions to this problem, the overhead introduced by agents cannot be completely reduced.
- High resources occupation: The agent occupies extra CPU/MEM overhead, and the deployment density of service container decreases.
Kmesh innovatively proposes to move traffic governance to the OS, and build a transparent sidecarless service mesh without passing through the proxy layer on the data path.
Smooth Compatibility
- Application-transparent Traffic Management
- Automatically interconnecting with Istiod
High Performance
- Forwarding delay 60%↓
- Service startup performance 40%↑
Low Overhead
- ServiceMesh data plane overhead 70%↓
Safety Isolation
- eBPF Virtual machine security
- Cgroup level orchestration isolation
Full Stack Visualization
- E2E observation*
- Integration with Mainstream Observability Platforms*
Open Ecology
- Supports XDS protocol standards
Note: * Planning
-
prerequisite
- Currently, Kmesh connects to the Istio control plane. Before starting Kmesh, install the Istio control plane software. For details, see https://istio.io/latest/docs/setup/getting-started/#install.
- The complete Kmesh capability depends on the OS enhancement. Check whether the execution environment is in the OS list supported by Kmesh. For other OS environments, see Kmesh Compilation and Building.You can also try the kmesh image in compatibility mode in other OS environments.For information on various Kmesh images, please refer to the detailed document.
-
Docker Images
Kmesh achieves the ability to completely sink traffic management below the OS through kernel enhancements. When releasing images, the range of OS for which the image is applicable must be considered. To this end, we consider releasing three types of images:
-
Supported OS versions with kernel enhancement modifications
The current openEuler 23.03 OS natively supports the kernel enhancement features required by Kmesh. Kmesh release images can be directly installed and run on this OS. For a detailed list of supported OS versions with kernel enhancement modifications, please refer to this link.
-
For all OS versions:
To be compatible with different OS versions, Kmesh provides online compilation and running images. After Kmesh is deployed, it will automatically select Kmesh features supported by the host machine's kernel capabilities, to meet the demand for one image to run in different OS environments.
Considering the universality of kmesh, we have released an image for compiling and building kmesh. Users can conveniently create a kmesh image based on this, which can run on their current OS version. By default, it is named
ghcr.io/kmesh-net/kmesh:latest, but the user can adjust it as needed. Please refer to [Kmesh Build Compilation](docs/kmesh_compile.md#build docker image) for more details.make docker TAG=latest
-
-
Start Kmesh
- Install from Helm
[root@ ~]# helm install kmesh ./deploy/helm -n kmesh-system --create-namespace
- Install from Yaml
# get kmesh.yaml from deploy/yaml/kmesh.yaml [root@ ~]# kubectl apply -f kmesh.yaml [root@ ~]# kubectl apply -f clusterrole.yaml [root@ ~]# kubectl apply -f clusterrolebinding.yaml [root@ ~]# kubectl apply -f serviceaccount.yaml
By default, the Kmesh base function is used, other function can be selected by adjusting the startup parameters in the yaml file.
-
Check kmesh service status
[root@ ~]# kubectl get pods -A | grep kmesh kmesh-system kmesh-l5z2j 1/1 Running 0 117m
-
View the running status of kmesh service
[root@master mod]# kubectl logs -f -n kmesh-system kmesh-l5z2j time="2024-02-19T10:16:52Z" level=info msg="service node sidecar~192.168.11.53~kmesh-system.kmesh-system~kmesh-system.svc.cluster.local connect to discovery address istiod.istio-system.svc:15012" subsys=controller/envoy time="2024-02-19T10:16:52Z" level=info msg="options InitDaemonConfig successful" subsys=manager time="2024-02-19T10:16:53Z" level=info msg="bpf Start successful" subsys=manager time="2024-02-19T10:16:53Z" level=info msg="controller Start successful" subsys=manager time="2024-02-19T10:16:53Z" level=info msg="command StartServer successful" subsys=manager time="2024-02-19T10:16:53Z" level=info msg="start write CNI config\n" subsys="cni installer" time="2024-02-19T10:16:53Z" level=info msg="kmesh cni use chained\n" subsys="cni installer" time="2024-02-19T10:16:54Z" level=info msg="Copied /usr/bin/kmesh-cni to /opt/cni/bin." subsys="cni installer" time="2024-02-19T10:16:54Z" level=info msg="kubeconfig either does not exist or is out of date, writing a new one" subsys="cni installer" time="2024-02-19T10:16:54Z" level=info msg="wrote kubeconfig file /etc/cni/net.d/kmesh-cni-kubeconfig" subsys="cni installer" time="2024-02-19T10:16:54Z" level=info msg="command Start cni successful" subsys=manager
More compilation methods of Kmesh, See: Kmesh Compilation and Construction
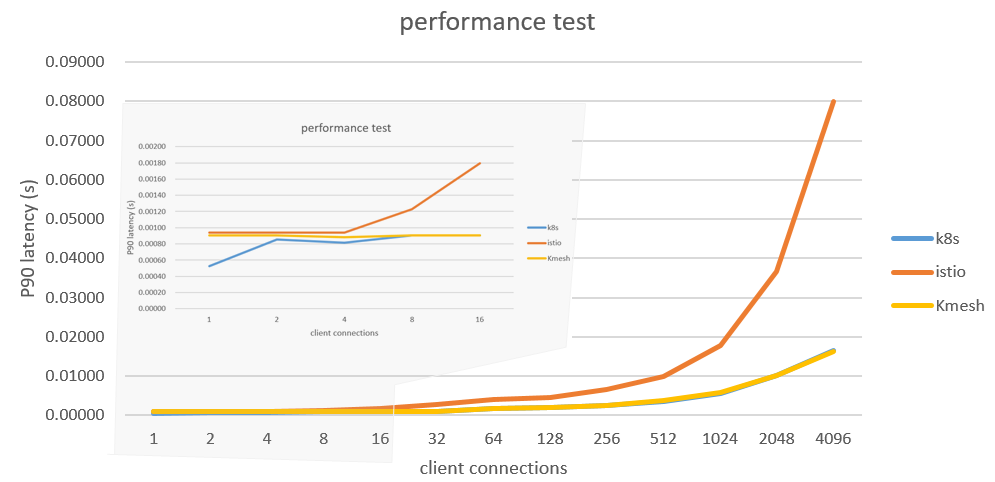
Based on Fortio, the data plane execution performance of Kmesh and Envoy was compared and tested. The test results are as follows:
For a complete performance test, please refer to Kmesh Performance Test.
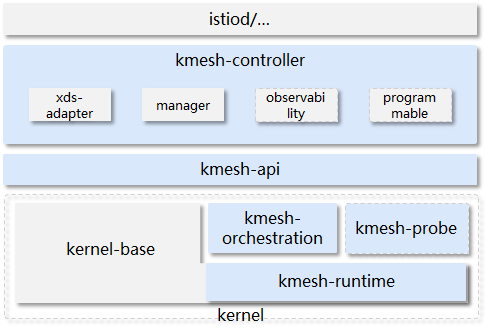
The main components of Kmesh include:
-
kmesh-controller:
Kmesh management program, responsible for Kmesh lifecycle management, XDS protocol docking, observation and DevOps, and other functions.
-
kmesh-api:
The API interface layer provided by Kmesh mainly includes: orchestration API after xds conversion, observation and DevOps channels, etc.
-
kmesh-runtime:
The runtime implemented in the kernel that supports L3~L7 traffic orchestration.
-
kmesh-orchestration:
Implement L3-L7 traffic scheduling based on ebpf, such as routing, grayscale, load balance, etc.
-
kmesh-probe:
Observation and DevOps probes, providing end-to-end observation capabilities.
-
Command List
-
Demo
| Feature Field | Feature | 2023.H1 | 2023.H2 | 2024.H1 | 2024.H2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traffic management | sidecarless mesh data plane | √ | |||
| sockmap accelerate | √ | ||||
| Programmable governance based on ebpf | √ | ||||
| http1.1 protocol | √ | ||||
| http2 protocol | √ | ||||
| grpc protocol | √ | ||||
| quic protocol | √ | ||||
| tcp protocol | √ | ||||
| Retry | √ | ||||
| Routing | √ | ||||
| load balance | √ | ||||
| Fault injection | √ | ||||
| Gray release | √ | ||||
| Circuit Breaker | √ | ||||
| Rate Limits | √ | ||||
| Service security | mTLS | √ | |||
| L7 authorization | √ | ||||
| Cgroup-level isolation | √ | ||||
| Traffic monitoring | Governance indicator monitoring | √ | |||
| End-to-End observability | √ | ||||
| Programmable | Plug-in expansion capability | √ | |||
| Ecosystem collaboration | Data plane collaboration (Envoy etc.) | √ | |||
| Operating environment support | container | √ |
If you have questions, feel free to reach out to us in the following ways:
If you're interested in being a contributor and want to get involved in developing the Kmesh code, please see CONTRIBUTING for details on submitting patches and the contribution workflow.
Kmesh is under the Apache 2.0 license. See the LICENSE file for details.
Kmesh documentation is under the CC-BY-4.0 license.
This project was initially incubated in the openEuler community, thanks openEuler Community for the help on promoting this project in early days.