这里特指“纯粹"的HTTP service,而不是可通过HTTP访问的pb服务。虽然用不到pb消息,但“纯粹”的HTTP Service也必须定义在.proto文件中,只是request和response都是空的结构体。这么做是确保所有的服务声明集中在proto文件中,而不是散列在.proto、程序、配置等多个地方。示例代码见http_server.cpp。
所有pb service默认都能通过/ServiceName/MethodName来访问,其中ServiceName不包括package。对于公司内的纯HTTP服务,一般来说这种形式的URL也够用了。实现步骤如下:
-
填写proto文件。
下面代码里的HttpRequest和HttpResponse都是空的,因为http数据在Controller中。http request的头在Controller.http_request()中,body在Controller.request_attachment()中。类似的,http response的头在Controller.http_response(),body在Controller.response_attachment()。
option cc_generic_services = true;
message HttpRequest { };
message HttpResponse { };
service HttpService {
rpc Echo(HttpRequest) returns (HttpResponse);
};- 实现Service。和其他pb service一样,也是继承定义在.pb.h中的service基类。
class HttpServiceImpl : public HttpService {
public:
...
virtual void Echo(google::protobuf::RpcController* cntl_base,
const HttpRequest* /*request*/,
HttpResponse* /*response*/,
google::protobuf::Closure* done) {
brpc::ClosureGuard done_guard(done);
brpc::Controller* cntl = static_cast<brpc::Controller*>(cntl_base);
// 这里返回纯文本。
cntl->http_response().set_content_type("text/plain");
// 把请求的query-string和body打印出来,作为回复内容。
butil::IOBufBuilder os;
os << "queries:";
for (brpc::URI::QueryIterator it = cntl->http_request().uri().QueryBegin();
it != cntl->http_request().uri().QueryEnd(); ++it) {
os << ' ' << it->first << '=' << it->second;
}
os << "\nbody: " << cntl->request_attachment() << '\n';
os.move_to(cntl->response_attachment());
}
};- 实现完毕插入Server后可通过如下URL访问,/HttpService/Echo后的部分在 cntl->http_request().unresolved_path()中,unresolved_path总是normalized。
| URL | 访问方法 | cntl->http_request().uri().path() | cntl->http_request().unresolved_path() |
|---|---|---|---|
| /HttpService/Echo | HttpService.Echo | "/HttpService/Echo" | "" |
| /HttpService/Echo/Foo | HttpService.Echo | "/HttpService/Echo/Foo" | "Foo" |
| /HttpService/Echo/Foo/Bar | HttpService.Echo | "/HttpService/Echo/Foo/Bar" | "Foo/Bar" |
| /HttpService//Echo///Foo// | HttpService.Echo | "/HttpService//Echo///Foo//" | "Foo" |
| /HttpService | 访问错误 |
一些资源类的HTTP服务可能会需要这种类型的URL,比如FileService提供对文件的访问,/FileService/foobar.txt代表访问运行目录下的foobar.txt文件,而/FileService/app/data/boot.cfg代表app/data目录下的boot.cfg文件。
实现方法:
- proto文件中应以FileService为服务名,以default_method为方法名。
option cc_generic_services = true;
message HttpRequest { };
message HttpResponse { };
service FileService {
rpc default_method(HttpRequest) returns (HttpResponse);
}- 实现Service。
class FileServiceImpl: public FileService {
public:
...
virtual void default_method(google::protobuf::RpcController* cntl_base,
const HttpRequest* /*request*/,
HttpResponse* /*response*/,
google::protobuf::Closure* done) {
brpc::ClosureGuard done_guard(done);
brpc::Controller* cntl = static_cast<brpc::Controller*>(cntl_base);
cntl->response_attachment().append("Getting file: ");
cntl->response_attachment().append(cntl->http_request().unresolved_path());
}
};- 实现完毕插入Server后可通过如下URL访问,/FileService之后的路径在cntl->http_request().unresolved_path()中 ,unresolved_path总是normalized。
| URL | 访问方法 | cntl->http_request().uri().path() | cntl->http_request().unresolved_path() |
|---|---|---|---|
| /FileService | FileService.default_method | "/FileService" | "" |
| /FileService/123.txt | FileService.default_method | "/FileService/123.txt" | "123.txt" |
| /FileService/mydir/123.txt | FileService.default_method | "/FileService/mydir/123.txt" | "mydir/123.txt" |
| /FileService//mydir///123.txt// | FileService.default_method | "/FileService//mydir///123.txt//" | "mydir/123.txt" |
brpc支持为service中的每个方法指定一个URL。接口如下:
// 如果restful_mappings不为空, service中的方法可通过指定的URL被HTTP协议访问,而不是/ServiceName/MethodName.
// 映射格式:"PATH1 => NAME1, PATH2 => NAME2 ..."
// PATHs是有效的HTTP路径, NAMEs是service中的方法名.
int AddService(google::protobuf::Service* service,
ServiceOwnership ownership,
butil::StringPiece restful_mappings);比如下面的QueueService包含多个http方法。
service QueueService {
rpc start(HttpRequest) returns (HttpResponse);
rpc stop(HttpRequest) returns (HttpResponse);
rpc get_stats(HttpRequest) returns (HttpResponse);
rpc download_data(HttpRequest) returns (HttpResponse);
};如果我们像之前那样把它插入server,那么只能通过/QueueService/start, /QueueService/stop等url来访问。
而在调用AddService时指定第三个参数(restful_mappings)就能定制URL了,如下所示:
if (server.AddService(&queue_svc,
brpc::SERVER_DOESNT_OWN_SERVICE,
"/v1/queue/start => start,"
"/v1/queue/stop => stop,"
"/v1/queue/stats/* => get_stats") != 0) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Fail to add queue_svc";
return -1;
}
// 星号可出现在中间
if (server.AddService(&queue_svc,
brpc::SERVER_DOESNT_OWN_SERVICE,
"/v1/*/start => start,"
"/v1/*/stop => stop,"
"*.data => download_data") != 0) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Fail to add queue_svc";
return -1;
}上面代码中AddService的第三个参数分了三行,但实际上是一个字符串。这个字符串包含以逗号(,)分隔的三个映射关系,每个映射告诉brpc:在遇到箭头左侧的URL时调用右侧的方法。"/v1/queue/stats/*"中的星号可匹配任意字串。
关于映射规则:
- 多个路径可映射至同一个方法。
- service不要求是纯HTTP,pb service也支持。
- 没有出现在映射中的方法仍旧通过/ServiceName/MethodName访问。出现在映射中的方法不再能通过/ServiceName/MethodName访问。
- ==> ===> ...都是可以的。开头结尾的空格,额外的斜杠(/),最后多余的逗号,都不要紧。
- PATH和PATH/*两者可以共存。
- 星号后可以有更多字符,即支持后缀匹配。
- 一个路径中只能出现一个星号。
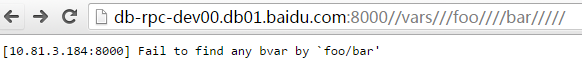
cntl.http_request().unresolved_path() 对应星号(*)匹配的部分,保证normalized:开头结尾都不包含斜杠(/),中间斜杠不重复。比如:
或
unresolved_path都是"foo/bar",左右、中间多余的斜杠被移除了。
注意:cntl.http_request().uri().path()不保证normalized,这两个例子中分别为"//v1//queue//stats//foo///bar//////"和"//vars///foo////bar/////"
/status页面上的方法名后会加上所有相关的URL,形式是:@URL1 @URL2 ...
http header是一系列key/value对,有些由HTTP协议规定有特殊含义,其余则由用户自由设定。
http headers易与query string混淆,后者是URL的一部分,常见形式是key1=value1&key2=value2&...,也可以表达key/value关系,且更容易在界面上操作。但用query string表达key/value并不是HTTP规范的一部分,更多是大家约定成俗的方式。就我的感受而言,由于http headers是协议的一部分,被所有http server认知,所以常用于机器接口,传递框架或协议层面的参数;而query string作为URL的一部分,很方便被人修改和阅读,常用于传递用户层面的参数。
// 获得header中"User-Agent"的值,大小写不敏感。
const std::string* user_agent_str = cntl->http_request().GetHeader("User-Agent");
if (user_agent_str != NULL) { // has the header
LOG(TRACE) << "User-Agent is " << *user_agent_str;
}
...
// 在header中增加"Accept-encoding: gzip",大小写不敏感。
cntl->http_response().SetHeader("Accept-encoding", "gzip");
// 覆盖为"Accept-encoding: deflate"
cntl->http_response().SetHeader("Accept-encoding", "deflate");
// 增加一个value,逗号分隔,变为"Accept-encoding: deflate,gzip"
cntl->http_response().AppendHeader("Accept-encoding", "gzip");Content-type记录body的类型,是一个使用频率较高的header,单独抽取出来方便使用,相应地,GetHeader()获取不到Content-Type。
// Get Content-Type
if (cntl->http_request().content_type() == "application/json") {
...
}
...
// Set Content-Type
cntl->http_response().set_content_type("text/html");如果RPC失败(Controller被SetFailed), Content-Type会框架强制设为text/plain,而response body设为Controller::ErrorText()。
status code是http response特有的字段,标记http请求的完成情况。请使用定义在http_status_code.h中的enum,遵守HTTP协议。
// Get Status Code
if (cntl->http_response().status_code() == brpc::HTTP_STATUS_NOT_FOUND) {
LOG(FATAL) << "FAILED: " << controller.http_response().reason_phrase();
}
...
// Set Status code
cntl->http_response().set_status_code(brpc::HTTP_STATUS_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
cntl->http_response().set_status_code(brpc::HTTP_STATUS_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, "My explanation of the error...");以下代码在302错误时重定向:
cntl->http_response().set_status_code(brpc::HTTP_STATUS_FOUND);
cntl->http_response().SetHeader("Location", "http://bj.bs.bae.baidu.com/family/image001(4979).jpg");如上面的HTTP headers中提到的那样,我们按约定成俗的方式来理解query string,即key1=value1&key2=value2&...。只有key而没有value也是可以的,仍然会被GetQuery查询到,只是值为空字符串,这常被用做bool型的开关。接口定义在uri.h。
const std::string* time_value = cntl->http_request().uri().GetQuery("time");
if (time_value != NULL) { // the query string is present
LOG(TRACE) << "time = " << *time_value;
}
...
cntl->http_request().uri().SetQuery("time", "2015/1/2");打开-http_verbose即可在stderr看到所有的http request和response,注意这应该只用于线下调试,而不是线上程序。
http服务常对http body进行压缩,对于文本网页可以有效减少传输时间,加快页面的展现速度。
设置Controller::set_response_compress_type(baidu::rpc::COMPRESS_TYPE_GZIP)后将尝试用gzip压缩http body。“尝试“指的是压缩有可能不发生,条件有:
- 请求中没有设置Accept-encoding或不包含gzip。比如curl不加--compressed时是不支持压缩的,这时server总是会返回不压缩的结果。
- body尺寸小于-http_body_compress_threshold指定的字节数,默认是512。这是因为gzip并不是一个很快的压缩算法,当body较小时,压缩增加的延时可能比网络传输省下的还多。
出于通用性考虑且解压代码不复杂,brpc不会自动解压request body,用户可以自己做,方法如下:
#include <brpc/policy/gzip_compress.h>
...
const std::string* encoding = cntl->http_request().GetHeader("Content-Encoding");
if (encoding != NULL && *encoding == "gzip") {
butil::IOBuf uncompressed;
if (!brpc::policy::GzipDecompress(cntl->request_attachment(), &uncompressed)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Fail to un-gzip request body";
return;
}
cntl->request_attachment().swap(uncompressed);
}
// cntl->request_attachment()中已经是解压后的数据了要开启HTTPS,首先确保代码依赖了最新的openssl库。如果openssl版本很旧,会有严重的安全漏洞,支持的加密算法也少,违背了开启SSL的初衷。然后设置ServerOptions中的SSLOptions
// Certificate structure
struct CertInfo {
// Certificate in PEM format.
// Note that CN and alt subjects will be extracted from the certificate,
// and will be used as hostnames. Requests to this hostname (provided SNI
// extension supported) will be encrypted using this certifcate.
// Supported both file path and raw string
std::string certificate;
// Private key in PEM format.
// Supported both file path and raw string based on prefix:
std::string private_key;
// Additional hostnames besides those inside the certificate. Wildcards
// are supported but it can only appear once at the beginning (i.e. *.xxx.com).
std::vector<std::string> sni_filters;
};
struct SSLOptions {
// Default certificate which will be loaded into server. Requests
// without hostname or whose hostname doesn't have a corresponding
// certificate will use this certificate. MUST be set to enable SSL.
CertInfo default_cert;
// Additional certificates which will be loaded into server. These
// provide extra bindings between hostnames and certificates so that
// we can choose different certificates according to different hostnames.
// See `CertInfo' for detail.
std::vector<CertInfo> certs;
// When set, requests without hostname or whose hostname can't be found in
// any of the cerficates above will be dropped. Otherwise, `default_cert'
// will be used.
// Default: false
bool strict_sni;
// ... Other options
};其余选项还包括:密钥套件选择(推荐密钥ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384,chrome默认第一优先密钥,安全性很高,但比较耗性能)、session复用等,具体见server.h 另外,开启HTTPS后,原先的HTTP请求也可以通过同一个端口来访问,Server会自动判断哪些是HTTP,哪些是HTTPS;用户也可以在callback中通过Controller接口来判断:
bool Controller::is_ssl() const;没有极端性能要求的产品线都有使用HTTP协议的倾向,特别是移动端产品线,所以我们很重视HTTP的实现质量,具体来说:
- 使用了node.js的http parser(部分来自nginx)解析http消息,这是一个轻量、优秀的实现。
- 使用rapidjson解析json,这是一个主打性能的json库,由一位腾讯专家开发。
- 在最差情况下解析http请求的时间复杂度也是O(N),其中N是请求的字节数。反过来说,如果解析代码要求http请求是完整的,那么它可能会花费O(N^2)的时间。HTTP请求普遍较大,这一点意义还是比较大的。
- 来自不同client的http消息是高度并发的,即使相当复杂的http消息也不会影响对其他客户端的响应。其他rpc和基于单线程reactor的各类http server往往难以做到这一点。
brpc server支持发送超大或无限长的body。方法如下:
-
调用Controller::CreateProgressiveAttachment()创建可持续发送的body。
boost::intrusive_ptr<brpc::ProgressiveAttachment> pa(cntl->CreateProgressiveAttachment());返回的ProgressiveAttachment对象需要用boost::intrusive_ptr<>管理,定义在<brpc/progressive_attachment.h>中。 -
调用ProgressiveAttachment::Write()发送数据。如果写入发生在server回调结束前,发送的数据将会被缓存直到回调结束发送了header部分后才会开始发送数据。如果写入发生在server回调结束后,发送的数据将立刻以chunked mode写出。
-
发送完毕后确保所有的
boost::intrusive_ptr<brpc::ProgressiveAttachment>都析构了。
目前brpc server不支持在接受完http请求的header部分就调用用户的服务回调,即brpc server不适合接收超长或无限长的body。
brpc server同端口支持多种协议,当它遇到非法HTTP请求并解析失败后,无法说这个请求一定是HTTP。server会对query-string及之后出现解析错误的请求返回HTTP 400错误并关闭连接(因为有很大概率是HTTP请求),但如果是HTTP method错误,诸如出现GET、POST、HEAD等标准方法之外的东西或严重的格式错误(可能由HTTP client有bug导致),server仍会直接断开连接,导致nginx的ff。
解决方案: 在使用Nginx转发流量时,可以对$HTTP_method做一下过滤,只放行允许的方法。或者干脆在proxy时设置proxy_method为指定方法,来避免ff。
支持。
根据HTTP协议中的要求,以下字符应该使用%编码
reserved = gen-delims / sub-delims
gen-delims = ":" / "/" / "?" / "#" / "[" / "]" / "@"
sub-delims = "!" / "$" / "&" / "'" / "(" / ")"
/ "*" / "+" / "," / ";" / "="
Base64 编码后的字符串中,会以"="或者"=="作为结尾(比如: ?wi=NDgwMDB8dGVzdA==&anothorkey=anothervalue), 这个字段可能会被正确解析,也可能不会,取决于具体实现,用户不应该做任何假设.
一个解决方法是删除末尾的"=", 不影响Base64的正常解码; 第二个方法是在这个URI在base64之后在使用%编码,使用的地方先进行%解码,然后再用base64解码.