SharedHashmap Application is a Spring Boot application developed in Java. The main purpose of this application is to implements a simple HTTP API that mimics the functionalities of a HashMap. The application is designed to be sharded, meaning that the data is partitioned across multiple servers to improve performance and scalability.
Sharding is a type of database partitioning that separates very large databases into smaller, faster, more easily managed parts called data shards. The word shard means a small part of a whole. Sharding is used in databases to improve performance and make it easier to manage and scale your application.
Each shard is held on a separate database server instance, to spread load and reduce the risk of a single point of failure. Sharding can be done in many different ways, including range partitioning, list partitioning, and hash partitioning.
The design of the project based on a distributed system architecture. The application is designed to be sharded, meaning that the data is partitioned across multiple servers. Here is the main components of the design :
-
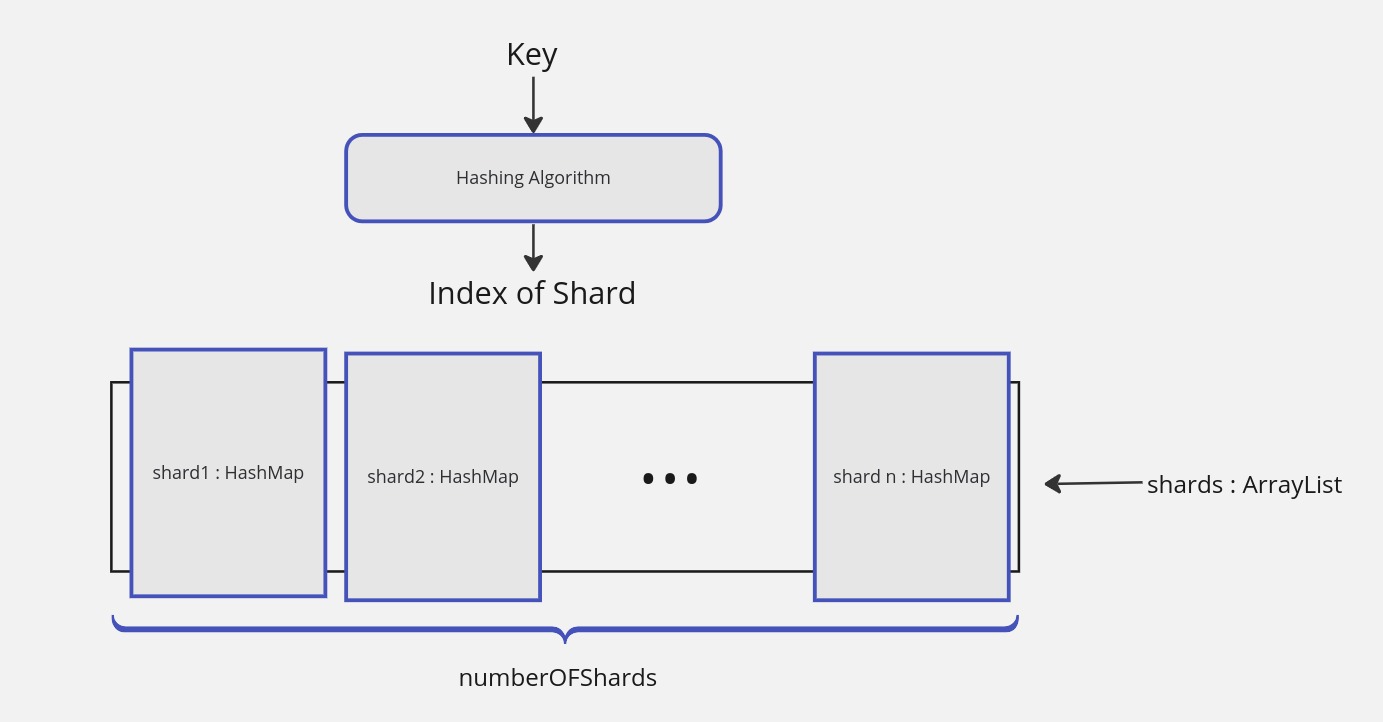
Hashing Strategy : We used
hashed sharding, while the key is hashed and the hash value is used to determine which shard the key-value pair should be stored in. It's based on Java's built-inhashCode()method for the String class, which computes a hash value for the input string. -
Shards/Database Servers : To simplify the design, we used a list of
HashMap<String, String>to represent the shards. Each shard is aHashMapthat stores key-value pairs. In a real-world scenario, each shard would be a separate database server instance. In this application we have defined the number of shards in theapplication.propertiesfile at the attributeapp.numberOfShards. -
API Features : The application provides the following features through its HTTP API:
- POST
/api: Add a key-value pair to the appropriate shard. - GET
/api/{key}: Retrieve the value associated with the given key from the appropriate shard. - DELETE
/api/{key}: Delete the key-value pair associated with the given key from the appropriate shard.
- POST
In this project, we have implemented sharding using a custom sharding strategy. This method involves using an interface IShardingStrategy that has a method getShardForKey(). This method takes a key as input and returns the index of the shard that the key-value pair should be stored in.
The HashMapService class uses this sharding strategy to determine which shard to use for a given key. It maintains a list of shards, each of which is a HashMap<String, String>. When a key-value pair is added, the add() method of the HashMapService class uses the getShardForKey() method of the sharding strategy to determine which shard to add the key-value pair to. Similarly, the retrieve() and delete() methods use the getShardForKey() method to determine which shard to retrieve a value from or delete a key from, respectively.
The benefits of using this sharding scheme include:
- Improved performance: By distributing the data across multiple shards, we can reduce the load on each shard and improve the overall performance of the application.
- Scalability: As the amount of data increases, we can easily add more shards to accommodate the additional data.
- Flexibility: By using an interface for the sharding strategy, we can easily switch to a different sharding scheme if needed. All we need to do is implement the
IShardingStrategyinterface with the new sharding scheme.
We have used a HashMap list based database server to represent the shards because of some reasons :
- Simplicity : A list of hashmaps is a simple data structure that is easy to understand and implement. It doesn't require any additional libraries or dependencies, and it's built into most programming languages, including Java. As a result, we will implement a simple sharding algorithm without the need for complex database systems.
- Flexibility : A list of hashmaps can easily be sharded, as we've done in our project. Each hashmap in the list can act as a separate shard, and keys can be distributed among the shards using a hashing function. This allows for easy scaling of the database.
- In-memory storage : A list of hashmaps is stored in memory, which allows for faster access times compared to disk-based storage.
- Colision Handling : The hashmap has a built-in mechanism for handling collisions, which can occur when two keys hash to the same value. This makes it easy to store and retrieve key-value pairs without worrying about collisions.
However, this also means that the data is not persistent and will be lost if the application is stopped or crashes.
Method 1 : Using IntelliJ IDEA IDE
The simplest way to build and run the project is to use IntelliJ IDEA IDE or any other IDE that supports Java and Maven.
- Clone the repository to your local machine :
git clone- Open the project in IntelliJ IDEA.
- Download the dependencies by clicking on the
Reimportbutton in the Maven tool window or by navigating to thepom.xmlfile and clicking on theImport Changesbutton. - Run the project by clicking on the green play button in the top right corner of the IDE.
- The project will start, and you can access the API by sending HTTP requests to
http://localhost:8080/api.
Method 2 : Using the Command Line
To build and run this project, you need to have the following dependencies installed on your host:
- Java 21
- Maven last version
- Spring Boot 3.2.4
Once you have these dependencies installed, you can build the project by running the following command in the root directory of the project:
mvn clean installhis command will build the project and create a JAR file in the target directory.
To run the project, navigate to the target directory and run the following command:
java -jar ShardedHashmapApplication.jarThis command will start the Spring Boot application.
You can access the API by sending HTTP requests to http://localhost:8080/api using postman or simply curl tool from the terminal.
Here are some examples of how to use the API:
- Adding Data
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"key":"myKey", "value":"myValue"}' 'http://localhost:8080/api'- Retrieving Data
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:8080/api/myKey'- Deleting Data
curl -X DELETE 'http://localhost:8080/api/myKey'If you have any questions or suggestions, feel free to contact me or put a comment.