A library built for ES6 iteration protocol.
function* numbers() {
let n = 1;
while (true) {
yield n++;
}
}
const s = query(numbers()).map(n => 1 / (n * n)).take(1000).sum();
console.log(Math.sqrt(6 * s));
// 3.1406380562059946itiriri provides similar functions as the natives for arrays: filter, slice, map, reduce, every, some etc. and more. The functions are optimized for ES6 iterators and can be chained to write simple but powerful queries over iterables.
Using npm:
$ npm install 'itiriri' --saveImporting:
import { query } from 'itiriri';The itiriri library can be used with any ES6 compatible runtime.
An iterator is a structured pattern for pulling information from a source in one-at-a-time fashion (Y-D-N-JS).
Starting with ES6, built-in types like arrays, Map, Set are iterables and can all be used with itiriri. A generator is also an iterable.
import { query } from 'itiriri';
function* values() {
yield 2;
yield 0;
yield 4;
yield 8;
}
const s = query(values()).map(n => n / 2).reverse();
console.log(s.toString()); // 4,2,0,1JavaScript's array methods like filter, slice and others that return an array create a shallow copy for the result and are executed once called.
itiriri functions that return iterables are not executed unless chained with a function that reduces a value or transforms to a built-in type.
Let's see what happens in the below example.
import { query } from 'itiriri';
function* fibonacci() {
let [a, b] = [0, 1];
while (true) {
yield a;
[a, b] = [b, a + b];
}
}
// Finding first 3 Fibonacci numbers that contain 42
const result = query(fibonacci())
.filter(x => x.toString().indexOf('42') !== -1)
.take(3);
for (const e of result) {
console.log(e);
}
// outputs: 514229, 267914296, 7778742049Step by step:
-
resultis assigned to a query. At this pointnumbersarray is not iterated, the execution is deferred until the result is being iterated. -
filtermethod creates an iterator to pipe only numbers passing the predicate.filterdoes not buffer elements and only pipes them one-by-one totakeas it is iterated. -
takepipes only first three elements as it is iterated and breaks. -
for...ofinstruction starts iteration and requests elements one at a time.
Due to deferred execution, most of the functions that don't need entire sequence of elements to build an iterator (like filter, map, concat etc.) can be used with infinite iterables (like Fibonacci in the above example). These functions are also optimized to pass elements through and do not buffer them resulting in a more optimized memory usage.
Functions like sort, reverse, shuffle etc. that require entire sequence of elements in order to build an iterator expect to receive a finite iterable.
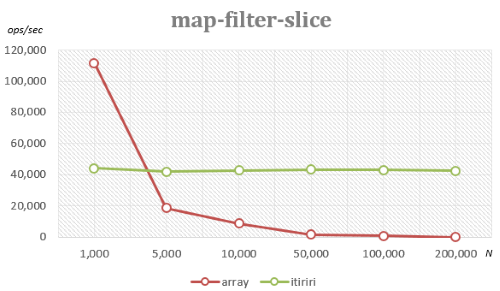
Using itiriri is considerable faster than using array methods when processing large inputs.
In filter-map-slice example arrays of different size are used to filter and map a result of 100 elements:
| Array size (N) | array |
itiriri |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 111,611 ops/sec ±9.63% (86 runs) | 44,213 ops/sec ±1.92% (88 runs) |
| 5000 | 18,507 ops/sec ±0.67% (90 runs) | 42,103 ops/sec ±2.63% (84 runs) |
| 10000 | 8,655 ops/sec ±0.70% (91 runs) | 42,803 ops/sec ±2.20% (86 runs) |
| 50000 | 1,640 ops/sec ±0.79% (88 runs) | 43,446 ops/sec ±2.17% (88 runs) |
| 100000 | 848 ops/sec ±0.93% (87 runs) | 43,137 ops/sec ±2.15% (87 runs) |
| 200000 | 46.38 ops/sec ±0.74% (59 runs) | 42,445 ops/sec ±2.48% (90 runs) |
Using array methods, performance drops significantly for large inputs due to creation of intermediary states for filter and map.
Using itiriri iteration always stops after 100 elements are found, therefore the size of the input doesn't affect the performance.
There are examples in /benchmark.
$ npm install
$ npm test- average
- concat
- distinct
- entries
- every
- exclude
- fill
- filter
- find
- findIndex
- findLast
- findLastIndex
- first
- flat
- forEach
- groupBy
- groupJoin
- includes
- indexOf
- intersect
- join
- keys
- last
- lastIndexOf
- leftJoin
- length
- map
- max
- min
- nth
- prepend
- reduce
- reduceRight
- reverse
- rightJoin
- shuffle
- skip
- skipWhile
- slice
- some
- sort
- splice
- sum
- take
- takeWhile
- toArray
- toGroups
- toMap
- toSet
- toString
- union
- values
Returns the average value.
Syntax
average(): number;
average(selector: (element: T, index: number) => number): number;Parameters
selector- (optional) a value transformer that accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element- returns a number
For a sequence with no elements returns undefined.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([41, 42, 43]).average() // returns 42
query([{value: 1}, {value: 2}]).average(elem => elem.value) // returns 1.5
query([]).average() // returns undefinedConcatenates the sequence with another one.
Syntax
concat(other: Iterable<T>): IterableQuery<T>;Parameters
other- (required) sequence to concatenate
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]).concat([4, 5]).toArray() // returns [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]concat is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns a sequence of unique elements.
Syntax
distinct(): IterableQuery<T>;
distinct<S>(selector: (element: T) => S): IterableQuery<T>;Parameters
selector- (optional) a function to get element's value for comparison. Accepts one argument:element- current element- returns a value to be used for comparison
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 42, 3, 4, 1]).distinct().toArray(); // returns [1, 42, 3, 4]
query([{value: 1}, {value: 2}, {value: 1}])
.distinct(elem => elem.value)
.toArray(); // returns [{value: 1}, {value: 2}]distinct is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns a sequence of key/value pair for each element and its index.
Syntax
entries(): IterableQuery<[number, T]>;Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query(['Alice', 'Bob', 'David']).entries().toArray();
// returns [[0, 'Alice'], [1, 'Bob'], [2, 'David']]entries is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Tests whether all the elements pass the predicate.
Syntax
every(predicate: (element: T, index: number) => boolean): boolean;Parameters
predicate- (required) function to test for each elementelement- the current elementindex- the index of the current element- returns
trueorfalse
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([2, 4, 9]).every(elem => elem > 0); // returns true
query([7, 23, 3]).every(elem => elem % 3 === 0); // returns falseReturns a sequence of elements not contained in a given sequence.
Syntax
exclude<S>(others: Iterable<T>): IterableQuery<T>;
exclude<S>(others: Iterable<T>, selector: (element: T) => S): IterableQuery<T>;Parameters
others- (required) a sequence of elements to be excludedselector- (optional) a function to get element's value for comparison, accepts one argument:element- current element- returns a value to be used for comparison
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([2, 0, 1, 8, 2]).exclude([0, 1]).toArray(); // returns [2, 8, 2]
query([{id: 1}, {id: 2}])
.exclude([{id: 2}, elem => elem.id])
.toArray(); // returns [{id: 1}]exclude is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns a sequence filled from a start index to an end index with a static value. The end index is not included.
Syntax
fill(value: T): IterableQuery<T>;
fill(value: T, start: number): IterableQuery<T>;
fill(value: T, start: number, end: number): IterableQuery<T>;Parameters
value- (required) value to fillstart- (optional) start index, defaults to 0end- (optional) end index, defaults to sequence length
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).fill([7]).toArray(); // returns [7, 7, 7, 7, 7]
query([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).fill([7, 3]).toArray(); // returns [1, 2, 3, 7, 7]
query([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).fill([7, 1, 3]).toArray(); // returns [1, 7, 7, 4, 5]fill is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns a sequence of elements that pass the predicate.
Syntax
filter(predicate: (element: T, index: number) => boolean): IterableQuery<T>;Parameters
predicate- (required) function to test for each element that accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).filter(elem => elem < 3).toArray(); // returns [1, 2]
query([1, 2, 3]).filter(elem > 10).toArray(); // returns []filter is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Finds the first element that satisfies the specified predicate.
Syntax
find(predicate: (element: T, index: number) => boolean): T;Parameters
predicate- (required) function to test for each element, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
If no element satisfies the predicate, returns undefined.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).find(elem => elem % 2 === 0); // returns 2
query([1, 2, 3]).find(elem > 10); // returns undefinedFinds the first index at which a given element satisfies the specified predicate.
Syntax
findIndex(predicate: (element: T, index: number) => boolean): number;Parameters
predicate- (required) function to test for each element, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
If no element satisfies the predicate, returns -1.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([7, 12, 15]).findIndex(elem => elem > 10 && elem < 15); // returns 1
query([1, 2, 3]).findIndex(elem > 10); // returns -1Finds the last element that satisfies the specified predicate.
Syntax
findLast(predicate: (element: T, index: number) => boolean): T;Parameters
predicate- (required) function to test for each element, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
If no element satisfies the predicate, returns undefined.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([11, 7, 21]).findLast(elem => elem > 10); // returns 21
query([1, 2, 3]).findLast(elem > 10); // returns undefinedFinds the last index at which a given element satisfies the specified predicate.
Syntax
findLastIndex(predicate: (element: T, index: number) => boolean): number;Parameters
predicate- (required) function to test for each element, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
If not present, returns -1.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([11, 7, 21]).findLastIndex(elem => elem > 10); // returns 2
query([1, 2, 3]).findLastIndex(elem > 10); // returns -1Returns the first element in a sequence.
Syntax
first(): T;For an empty sequence returns undefined.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query(['a', 'b', 'c']).first(); // returns 'a'
query([]).first(); // returns undefinedReturns a sequence with all sub-sequences concatenated.
Syntax
flat<S>(selector: (element: T, index: number) => Iterable<S>): IterableQuery<S>;Parameters
selector- (required) a transformation function to map each element to a sequence, accepts two argumentselement- the current elementindex- the index of the current element- returns an iterable
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([{value: [1, 2], {values: [7, 9]}]).flat(elem => elem.value).toArray();
// returns [1, 2, 7, 9]flat is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Runs through every element and applies a given function.
Syntax
forEach(action: (element: T, index: number) => void): void;Parameters
action- (required) function to apply on each element, accepts two argumentselement- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]).forEach(elem => console.log(elem));
// 1
// 2
// 3Groups elements by a given key, optionally applying a transformation over each element.
Syntax
groupBy<K>(
keySelector: (element: T, index: number) => K): IterableQuery<[K, IterableQuery<T>]>;
groupBy<K, E>(
keySelector: (element: T, index: number) => K,
valueSelector: (element: T, index: number) => E): IterableQuery<[K, IterableQuery<E>]>;Parameters
keySelector- (required) function that provides group's key, accepts two argumentselement- the current elementindex- the index of the current element- returns the group key of current element
valueSelector- (optional) function to transform values, accepts two argumentselement- the current elementindex- the index of the current element- returns a transformation of current element
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
const students = [
{name: 'Alice', gender: 'female'},
{name: 'Bob', gender: 'male'},
{name: 'David', gender: 'male'},
];
query(students).groupBy(elem => elem.gender, elem => elem.name).toArray();
// [['female', ['Alice']], ['male', ['Bob', 'David']]]groupBy is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns a sequence of correlated elements where each element from the current sequence is matched with zero or more elements from the other sequence.
Syntax
groupJoin<TKey, TRight, TResult>(
other: Iterable<TRight>,
leftKeySelector: (element: T, index: number) => TKey,
rightKeySelector: (element: TRight, index: number) => TKey,
joinSelector: (left: T, right: TRight[]) => TResult,
): IterableQuery<TResult>;Parameters
other- (required) sequence to joinleftKeySelector- (required) function that provides the key of each element from source sequence, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element- returns element's key
rightKeySelector- (required) function that provides the key of each element from joined sequence, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element- returns element's key
joinSelector- (required) a transformation function to apply on each joined element with group, accepts two arguments:left- element from the original sourceright- array of elements from the joined source that have the same key as left element's key
The joinSelector function is called on each element from the source sequence and the array of matched
elements from the joined sequence.
When an element from the source sequence doesn't match with any of the elements from the joined sequence,
the joinSelector function will be called with an empty array.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
const books = [
{title: 'Clean code', categoryId: 1 },
{title: 'Code complete', categoryId: 1},
{title: 'Scrum', categoryId: 2},
];
const categories = [
{id: 1, name: 'CS'},
{id: 2, name: 'Agile'},
];
query(categories).groupJoin(
books,
category => category.id,
book => book.categoryId,
(category, books) => ({ category: category.name, books: books.map(b => b.title) })
).toArray();
// [
// {category: 'CS', books: ['Clean code', 'Code complete']},
// {category: 'Agile'}, books: ['Scrum']
// ]groupJoin is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Determines whether the sequence includes a certain element.
Syntax
includes(element: T): boolean;
includes(element: T, fromIndex: number): boolean;Parameters
element- (required) the element to search forfromIndex- (optional) starting index, defaults to0
includes uses triple equals === to compare elements.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]).includes(2); // returns true
query([1, 2, 3]).includes(0); // returns falseReturns the first (zero-based) index at which a given element can be found.
Syntax
indexOf(element: T): number;
indexOf(element: T, fromIndex: number): number;Parameters
element- (required) the element to search forfromIndex- (optional) starting index, defaults to0
When an element is not found, returns -1.
indexOf uses triple equals === to compare elements.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query(['a', 'b', 'c']).indexOf('c'); // returns 2
query(['a', 'b', 'c']).indexOf('x'); // returns -1Returns a set intersection with a given sequence.
Syntax
intersect(others: Iterable<T>): IterableQuery<T>;
intersect<S>(other: Iterable<T>, selector: (element: T) => S): IterableQuery<T>;Parameters
other- (required) the sequence to intersect withselector- (optional) a value transformer function to be used for comparisons, accepts one argument:element- the current element
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]]).intersect([2, 3, 4]).toArray(); // returns [2, 3]
query([{id: 1, name: 'Alice'}, {id: 2, name: 'Bob'})
.intersect([{id: 3, name: 'David'}, {id: 1, name: 'Alice'}], elem => elem.id)
.toArray(); // returns [{id: 1, name: 'Alice'}]intersect is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns a sequence of correlated elements transformation that match a given key.
Syntax
join<TKey, TRight, TResult>(
other: Iterable<TRight>,
leftKeySelector: (element: T, index: number) => TKey,
rightKeySelector: (element: TRight, index: number) => TKey,
joinSelector: (left: T, right: TRight) => TResult,
): IterableQuery<TResult>;Parameters
other- (required) sequence to joinleftKeySelector- (required) function that provides the key of each element from source sequence, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element- returns element's key
rightKeySelector- (required) function that provides the key of each element from joined sequence, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element- returns element's key
joinSelector- (required) a transformation function to apply on each matched tuple, accepts two arguments:left- element from the source sequenceright- element from the joined sequence- returns a new result
The join method works as an sql inner join.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3])
.join([2, 3, 4], n => n, n => n, (a, b) => `${a}-${b}`)
.toArray();
// returns ['2-2', '3-3']
query([{countryId: 1, code: '+1'}, {countryId: 2, code: '+44'}]])
.join(
[{ id: 1, country: 'US' }, {id: 3, country: 'MD'}],
left => left.countryId,
right => right.id,
(left, right) => ({country: right.country, code: left.code}))
.toArray();
// returns [{country: 'US', code: '+1'}]join is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns a sequence of keys for each index in the source sequence.
Syntax
keys(): IterableQuery<number>;Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query(['a', 'b', 'c']).keys().toArray(); // returns [0, 1, 2]keys is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns the last element in a sequence.
Syntax
last(): T;For an empty sequence returns undefined.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query(['a', 'b', 'c']).last(); // returns 'c'
query([]).last(); // returns undefinedReturns the last index at which a given element can be found.
Syntax
lastIndexOf(element: T): number;
lastIndexOf(element: T, fromIndex: number): number;Parameters
element- (required) the element to search forfromIndex- (optional) starting index, defaults to0
When an element is not found, returns -1.
lastIndexOf uses triple equals === to compare elements.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query(['a', 'c', 'c']).lastIndexOf('c'); // returns 2
query(['a', 'b', 'c']).lastIndexOf('x'); // returns -1Returns a sequence of correlated elements transformation that match a given key.
Syntax
leftJoin<TKey, TRight, TResult>(
other: Iterable<TRight>,
leftKeySelector: (element: T, index: number) => TKey,
rightKeySelector: (element: TRight, index: number) => TKey,
joinSelector: (left: T, right?: TRight) => TResult,
): IterableQuery<TResult>;Parameters
other- (required) sequence to joinleftKeySelector- (required) function that provides the key of each element from source sequence, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element- returns element's key
rightKeySelector- (required) function that provides the key of each element from joined sequence, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element- returns element's key
joinSelector- (required) a transformation function to apply on each matched tuple, accepts two arguments:left- element from the source sequenceright- element from the joined sequence, orundefinedif no match was found- returns element's key
The leftJoin method works as an sql left join.
When an element from the left sequence doesn't match with any of the elements from the right sequence,
the joinSelector function is called with an undefined right value.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3])
.leftJoin([2, 3, 4, 2], n => n, n => n, (a, b) => `${a}-${b || '#'}`)
.toArray();
// returns ['1-#', '2-2', '2-2', '3-3']
query([{book: 'History', owner: 3}, {book: 'Math', owner: 2}, {book: 'Art'}]])
.leftJoin(
[{id: 1, name: 'Alice'}, {id: 2, name: 'Bob'}, {id: 3, name: 'Eve'}],
left => left.owner,
right => right.id,
(left, right) => ({book: left.book, owner: right && right.owner || '--'}))
.toArray();
// returns [
// {book: 'History', owner: 'Eve'},
// {book: 'Math', owner: 'Bob'},
// {book: 'Art', owner: '--'}]leftJoin is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns the number of elements in a sequence.
Syntax
length(): number;
length(predicate: (element: T, index: number) => boolean): number;Parameters
predicate- (optional) a function to count only the elements that match the predicate, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).length(); // returns 5
query([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).length(elem => elem > 2); // returns 3Returns a sequence of transformed values.
Syntax
map<S>(selector: (element: T, index: number) => S): IterableQuery<S>;Parameters
selector- (required) a value transformer function to apply to each element, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]).map(elem => elem * 10).toArray(); // returns [10, 20, 30]map is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns the maximum element in a sequence.
Syntax
max(): T;
max(compareFn: (a: T, b: T) => number): T;Parameters
compareFn- (optional) a comparer function that compares two elements from a sequence and returns:-1whenais less thanb1whenais greaterb0whenaequals tob
If sequence is empty, returns undefined.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]).max(); // returns 3
query([]).max(); // returns undefined
query([7, 3, 11, 5]).max((a, b) => (1 / a) - (1 / b)); // returns 3Returns the minimum element in a sequence.
Syntax
min(): number;
min(compareFn: (a: T, b: T) => number): T;Parameters
compareFn- (optional) a comparer function that compares two elements from a sequence and returns:-1whenais less thanb1whenais greaterb0whenaequals tob
If sequence is empty, returns undefined.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]).min(); // returns 1
query([]).min(); // returns undefined
query([7, 3, 11, 5]).min((a, b) => (1 / a) - (1 / b)); // returns 11Returns the element at a specified index.
Syntax
nth(index: number): T;Parameters
index- (required) zero based index at which to get the element
For a negative index returns the element from the end of the sequence.
If index is out of the range, returns undefined .
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']).nth(2) // returns 'c'
query(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']).nth(-1) // returns 'd'
query(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']).nth(10) // returns undefinedReturns a sequence with given elements at the beginning.
Syntax
prepend(other: Iterable<T>): IterableQuery<T>;Parameters
other- (required) the sequence to be added at the beginning
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]).prepend([9, 10]).toArray(); // returns [1, 2, 3, 9, 10]prepend is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Applies a function against an accumulator and each element (from left to right) to reduce it to a single value.
Syntax
reduce(
callback: (accumulator: T, current: T, index: number) => T,
): T;
reduce<S>(
callback: (accumulator: S, current: T, index: number) => S,
initialValue: S,
): S;Parameters
callback- (required) function to execute on each element in the sequence, taking three argumentsaccumulatorthe accumulator accumulates the callback's return values;currentthe current element being processed;currentIndexthe index of the current element being processed;
initialValue- (optional) value to use as the first argument to the first call of thecallback
Calling reduce on an empty sequence without an initial value throws an error.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([ 1, 2, 42, 0 ]).reduce((acc, elem) => Math.max(acc, elem)); // returns 42
query([ 1, 2, 3 ]).reduce((acc, elem) => acc + elem, 10); // returns 16Applies a function against an accumulator and each element (from right to left) to reduce it to a single value.
Syntax
reduceRight(
callback: (accumulator: T, current: T, index: number) => T,
): T;
reduceRight<S>(
callback: (accumulator: S, current: T, index: number) => S,
initialValue: S,
): S;Parameters
callback- (required) function to execute on each element in the sequence, taking three argumentsaccumulatorthe accumulator accumulates the callback's return values;currentthe current element being processed;currentIndexthe index of the current element being processed;
initialValue- (optional) value to use as the first argument to the first call of thecallback
Calling reduceRight on an empty sequence without an initial value throws an error.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([ 1, 2, 42, 0 ]).reduceRight((acc, elem) => Math.max(acc, elem)); // returns 42
query([ 1, 2, 3]).reduceRight((acc, elem) => acc.concat(elem), []); // returns [3, 2, 1]Returns a sequence of elements in a reversed order.
Syntax
reverse(): IterableQuery<T>;Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]).reverse().toArray(); // returns [3, 2, 1]reverse is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns a sequence of correlated elements transformation that match a given key.
Syntax
rightJoin<TKey, TRight, TResult>(
other: Iterable<TRight>,
rightKeySelector: (element: TRight, index: number) => TKey,
leftKeySelector: (element: T, index: number) => TKey,
joinSelector: (right: TRight, left?: T) => TResult,
): IterableQuery<TResult>;Parameters
other- (required) sequence to joinrightKeySelector- (required) function that provides the key of each element from joined sequence, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element- returns element's key
leftKeySelector- (required) function that provides the key of each element from source sequence, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element- returns element's key
joinSelector- (required) a transformation function to apply on each matched tuple, accepts two arguments:right- element from the joined sequenceleft- element from the source sequence, orundefinedif no match found- returns new result
The rightJoin method works as an sql right join.
When an element from the right sequence doesn't match with any of the elements from the left sequence,
the rightJoin function is called with an undefined left value.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3])
.rightJoin([2, 3, 4, 2], n => n, n => n, (a, b) => `${a || '#'}-${b}`)
.toArray();
// returns ['2-2', '3-3', '#-4', '2-2']
query([{book: 'History', owner: 3}, {book: 'Math', owner: 2}]])
.rightJoin(
[{id: 1, name: 'Alice'}, {id: 2, name: 'Bob'}, {id: 3, name: 'Eve'}],
right => right.id,
left => left.owner,
(right, left) => ({student: right.name, book: left && left.book || '--'}))
.toArray();
// returns [
// {student: 'Alice', book: '--'},
// {student: 'Bob', book: 'Math'},
// {student: 'Eve', book: 'History'}]rightJoin is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns the sequence of elements in a random order.
Syntax
shuffle(): IterableQuery<T>;This method is implemented using Fisher–Yates
algorithm for generating the random permutation. Math.rand() is used to generate random numbers.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).shuffle().toArray();
// returns a random permutation of the same elements
// like: [2, 5, 3, 1, 4]shuffle is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Skips the specified number of elements from the beginning of sequence and returns the remaining ones.
Syntax
skip(count: number): IterableQuery<T>;Parameters
count- (required) number of elements to skip
When count is greater than actual number of elements, results in an empty sequence.
Accepts also a negative count, in which case skips the elements from the end of the sequence.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).skip(2).toArray(); // [3, 4, 5]
query([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).skip(10).toArray(); // []
query([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).skip(-2).toArray(); // [1, 2, 3]skip is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Skip elements while they satisfy the predicate.
Syntax
skipWhile<T>(predicate: (element: T, index: number) => boolean): IterableQuery<T>;Parameters
predicate- (required) function to test for each element, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]).skipWhile(() => true); // returns []
query([1, 2, 3]).skipWhile(() => false); // returns [1, 2, 3]
query([1, 2, 3]).skipWhile(e => e < 3); // returns [3]
query([1, 2, 3]).skipWhile(e => e % 2 === 0); // returns [1, 2, 3]skipWhile is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns a sequence that represents the range of elements from start to end.
Syntax
slice(start: number): IterableQuery<T>;
slice(start: number, end: number): IterableQuery<T>;Parameters
start- (required) zero-based index at which to begin extractionend- (optional) zero-based index before which to end extraction
The end index is not included in the result.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).slice(1, 3).toArray(); // returns [2, 3]slice is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Tests whether at least one element passes the predicate.
Syntax
some(predicate: (element: T, index: number) => boolean): boolean;Parameters
predicate- (required) function to test for each element, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3, 42, 5]).some(elem => elem > 40); // returns true
query([1, 2, 3, 42, 5]).some(elem => elem < 0); // returns falseReturns a sequence of sorted elements.
Syntax
sort(): IterableQuery<T>;
sort(compareFn: (a: T, b: T) => number): IterableQuery<T>;Parameters
compareFn- (optional) a comparer function that compares two elements from a sequence and returns:-1whenais less thanb1whenais greaterb0whenaequals tob
This method fallbacks to native JavaScript array sort.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([7, 9, 0, 4, 12]).sort().toArray(); // returns [0, 4, 7, 9, 12]
query([
{score: 1, value: 'a'},
{score: 0, value: 'b'},
{score: 2, value: 'c'}])
.sort((a, b)) => a.score - b.score);
// returns [
// {score: 0, value: 'b'},
// {score: 1, value: 'a'},
// {score: 2, value: 'c'}]sort is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns a sequence that skips elements and/or adds new elements.
Syntax
splice(start: number, deleteCount: number, ...items: T[]): IterableQuery<T>;Parameters
start- (required) index at which to start changing the sequencedeleteCount- (optional) an integer indicating the number of original elements to skipitems- (optional) elements to add to the sequence
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query(['angel', 'clown', 'mandarin', 'sturgeon'])
.splice(2, 0, 'drum').toArray();
// returns ['angel', 'clown', 'drum', 'mandarin', 'sturgeon']
query(['angel', 'clown', 'drum', 'mandarin', 'sturgeon'])
.splice(3, 1).toArray();
// returns ['angel', 'clown', 'drum', 'sturgeon']splice is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns the sum of all elements.
Syntax
sum(): number;
sum(selector: (element: T, index: number) => number): number;Parameters
selector- (optional) a value transformer function to apply to each element, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
Optionally, a function can be provided to apply a transformation and map each element to a value.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]).sum(); // returns 6
query([{value: 1}, {value: 2}]).sum(elem => elem.value); // returns 3Returns a specified number of elements from the beginning of sequence.
Syntax
take(count: number): IterableQuery<T>;Parameters
count- (required) number of elements to take
If a negative count is specified, returns elements from the end of the sequence.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]).take(2); // returns [1, 2]
query([1, 2, 3]).take(-2); // returns [2, 3]
query([1, 2, 3]).take(10); // returns [1, 2, 3]take is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns elements while they satisfy the predicate.
Syntax
takeWhile<T>(predicate: (element: T, index: number) => boolean): IterableQuery<T>;Parameters
predicate- (required) function to test for each element, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]).takeWhile(() => true); // returns [1, 2, 3]
query([1, 2, 3]).takeWhile(() => false); // returns []
query([1, 2, 3]).takeWhile(e => e < 3); // returns [1, 2]
query([1, 2, 3]).takeWhile(e => e % 2 === 0); // returns []takeWhile is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Creates an array copy of the sequence.
Syntax
toArray(): T[];
toArray<S>(selector: (element: T, index: number) => S): S[];Parameters
selector- (optional) a value transformer function to apply to each element
When providing a selector function, creates an array of values returned by applying the function on each element.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]).toArray(); // returns [1, 2, 3]
query([{value: 1}, {value: 2}]).toArray(elem => elem.value); // returns [1, 2]Creates a map of element groups by a given key.
Syntax
toGroups<M>(
keySelector: (element: T, index: number) => M): Map<M, T[]>;
toGroups<M, N>(
keySelector: (element: T, index: number) => M,
valueSelector: (element: T, index: number) => N): Map<M, N[]>;Parameters
keySelector- (required) a transformer function to apply to each element to get its key, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
valueSelector- (optional) a transformer function to apply to each element, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
Method toGroups creates a JavaScript Map
of key-value pairs where each key is the result from keySelector and value is an array of elements
(or the result of applying valueSelector on each element) from the original sequence for which the key is the same.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 7, 14, 4, 9]).toGroups(elem => elem % 2 === 0);
// returns Map {0 => [14, 4], 1 => [1, 7, 9]}
query([
{name: 'Alice', gender: 'female'},
{name: 'Bob', gender: 'male'},
{name: 'David', gender: 'male'}
])
.toGroups(elem => elem.gender, elem => elem.name);
// returns Map {'female' => ['Alice'], 'male' => ['Bob', 'David']}Creates a map of elements by a given key.
Syntax
toMap<M>(
keySelector: (element: T, index: number) => M): Map<M, T>;
toMap<M, N>(
keySelector: (element: T, index: number) => M,
valueSelector: (element: T, index: number) => N): Map<M, N>;Parameters
keySelector- (required) a transformer function to apply to each element to get its key, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
valueSelector- (optional) a transformer function to apply to each element, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
Method toMap returns a JavaScript Map
of key-value pairs where each key is the result from keySelector and value is the element
(or the result of applying valueSelector on the element) that corresponds to the key.
If the sequence contains two elements with the same key, method toMap throws an error.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query(['a', 'b', 'c']).toMap(elem => elem.charCodeAt(0));
// returns Map {97 => 'a', 98 => 'b', 99 => 'c'}
query(['a', 'b', 'c']).toMap(elem => elem.charCodeAt(0), elem => elem.toUpperCase());
// returns Map {97 => 'A', 98 => 'B', 99 => 'C'}
query([1, 1]).toMap(elem => elem);
// throws an ErrorCreates a set of elements.
Syntax
toSet(): Set<T>;
toSet<S>(selector: (element: T, index: number) => S): Set<S>;Parameters
selector- (optional) a transformer function to apply to each element to get its value, accepts two arguments:element- the current elementindex- the index of the current element
Method toSet returns a JavaScript Set
of the original elements in the sequence, or their transformation when a selector is provided.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3, 1, 3]).toSet(); // returns Set {1, 2, 3}
query([{value: 1}, {value: 2}, {value: 1}])
.toSet(elem => elem.value); // returns Set {1, 2}Returns a string representing the specified sequence and its elements.
Syntax
toString(): string;Method toString calls .toString() function on each element and joins the result by ,.
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]).toString(); // returns 1,2,3
query([1, null, 3]).toString(); // returns 1,,3
query([{value: 1}, {value: 2}]).toString(); // returns [object Object],[object Object]Returns a set union with a given sequence.
Syntax
union(other: Iterable<T>): IterableQuery<T>;
union<S>(other: Iterable<T>, selector: (element: T) => S): IterableQuery<T>;Parameters
other- (required) the sequence to join withselector- (optional) a value transformer function to be used for comparisons, accepts one argument:element- the current element
Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]]).union([2, 3, 4]).toArray(); // returns [1, 2, 3, 4]
query([{id: 1, name: 'Alice'}, {id: 2, name: 'Bob'})
.union([{id: 3, name: 'David'}, {id: 1, name: 'Alice'}], elem => elem.id)
.toArray();
// returns [
// {id: 1, name: 'Alice'},
// {id: 2, name: 'Bob'},
// {id: 3, name: 'David'}]union is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
Returns a sequence of values for each index in the source sequence.
Syntax
values(): IterableQuery<T>;Example
import { query } from 'itiriri';
query([1, 2, 3]]).values().toArray(); // returns [1, 2, 3]values is a deferred method and is executed only when the result sequence is iterated.
iterator iterable filter map query collections deferred lazy