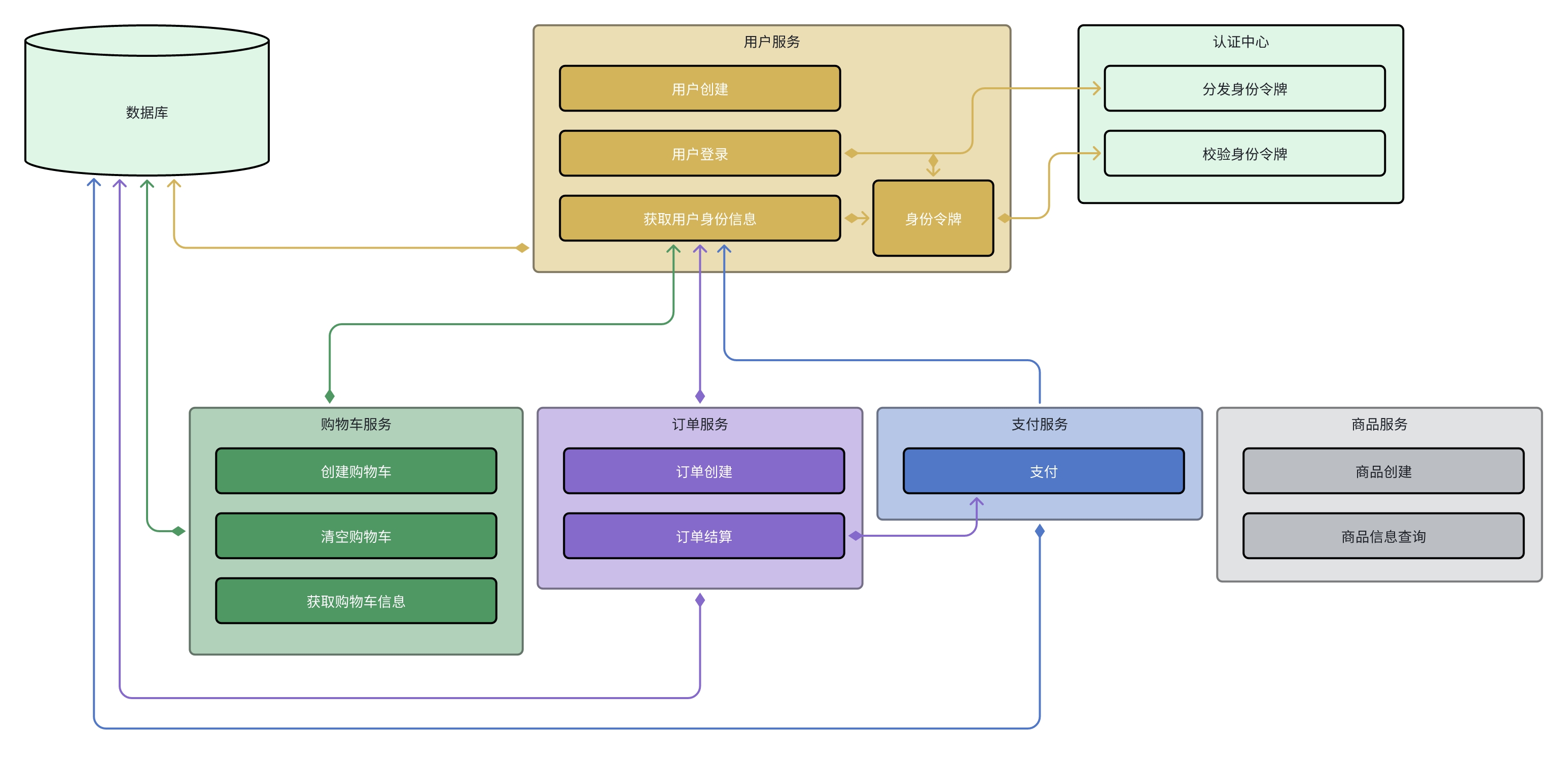
app目录下的每一个目录都是一个微服务。微服务的运行方式都是相同的。
- 进入微服务目录(以 auth 服务为例)
dyshop$ cd app/auth- 运行微服务程序
dyshop/app/auth$ go run .⚠ 注意:
各个微服务请从自己的微服务目录中运行,不要在项目路径或其他路径中运行。
微服务的搜索路径与起始路径有关,在其他地方运行服务,可能会导致conf文件读取错误 ❌或其他问题。
- 微服务启动后,默认没有输出,但是会使终端处于阻塞状态。你可以自己控制微服务的输出。
为了测试微服务是否可用,在本项目中有三种进行测试的方式。
- 离线测试:
使用go的go test编写 test 函数,进行离线测试。
package service
// this file must end with _test.go
// for example: example_test.go
import (
"testing"
)
// optional function
// if you have some common initialization operations
// for all test functions please write in this function
func init(){
// init operations before test...
}
// TestXXX this function must start with Test
func TestXXX(t *testing.T) {
// write your test code here...
}运行 go test 的方式也比较简单
go test -run TestXXX -v # 运行某个测试函数,并且详细输出结果
go test -file example_test.go -v # 运行某个测试文件的所有测试函数💡 这种方式能够在本地得到 service 函数的执行结果,并且可以设置测试样例,进行覆盖测试。
💡 这也是一种在非main包情况下运行某个函数的方式。 2. 本地 RPC 调用测试
我们已经提供了本地的 RPC 客户端的实现,就在当前微服务的 cmd/client 目录下。
package main
import (
"fmt"
pbauth "github.com/asmile1559/dyshop/pb/backend/auth"
// ...
)
func main() {
// initialization operations
cc, err := grpc.NewClient("localhost:"+viper.GetString("server.port"), grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials()))
if err != nil {
logrus.Fatal(err)
}
cli := pbauth.NewAuthServiceClient(cc)
// you can call your rpc functions here by grpc
resp, err := cli.DeliverTokenByRPC(context.TODO(), &pbauth.DeliverTokenReq{UserId: 1})
// other operations
}执行命令如下:
# 1. start up microservice server
dyshop/app/auth$ go run .
# 2. open a new terminal and run client
dyshop/app/auth$ go run cmd/client/main.go❗ 这种方式首先需要启动 RPC 服务,也即运行微服务本身。
- 标准请求方式
标准请求方式是外部请求从浏览器发起,经过 frontend(gateway)进行转发处理,并最终将结果返回给浏览器的过程。
这是实际上我们最终需要实现的。
执行命令如下:
# 1. start up microservice server
dyshop/app/auth$ go run .
# 2. open a new terminal and start up frontend
dyshop/app/frontend$ go run .
# 3. request by browser, postman or curl
# recommend browser and postman
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"user_id": 1}' \
http://localhost:10166/test/login👍 推荐在进行最后功能测试时使用这种方式
-
环境(框架功能的开发环境),一般情况下不需要改自己的环境
Go version: go1.23.5 linux/amd64
IDE:GoLand/VSCode(VSCode 有时候会出现找不到模块的报错)
OS:Linux/(Debian12,Ubuntu2204) -
将代码克隆到本地。推荐使用 ssh 模式。也可以 fork 之后 clone 自己的。
git clone [email protected]:asmile1559/dyshop.git- 新建一个分支
# example需要替换为自己负责的模块
git branch feat/example
git checkout feat/example- 安装
protoc,protoc-gen-go,protoc-gen-go-grpc.
# 1. 安装 protoc
# 参考 https://grpc.io/docs/protoc-installation/
PB_REL="https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases"
curl -LO $PB_REL/download/v29.3/protoc-29.3-linux-x86_64.zip
unzip protoc-29.3-linux-x86_64.zip -d $HOME/.local
# 可以写到 $HOME/.profile 或 $HOME/.bashrc 中
export PATH="$PATH:$HOME/.local/bin"
# 2. 安装 protoc-gen-go 和 protoc-gen-go-grpc
# 参考:https://grpc.io/docs/languages/go/quickstart/
go install google.golang.org/protobuf/cmd/protoc-gen-go@latest
go install google.golang.org/grpc/cmd/protoc-gen-go-grpc@latest
# 可以写到 $HOME/.profile 或 $HOME/.bashrc 中
export PATH="$PATH:$(go env GOPATH)/bin"- 生成 proto 文件,可以不生成(当需要修改 proto 文件时,需要运行下面的命令)
make gen-frontend-proto
make gen-backend-proto- 开始编写代码吧。
微服务的业务代码一般在下面三个文件中编写。
app/xxx/main.goapp/xxx/handler.goapp/xxx/service/*.go
👍 推荐 (不是硬性规定) 👍
- 😀 在
app/xxx/main.go文件中编写运行初始化、服务注册等部分代码。- 😁 在
app/xxx/handler.go中编写与 RPC 相关部分的代码。- 😊 在
app/xxx/service/*.go中编写具体的业务代码。💡
auth部分的业务逻辑已经实现,如果需要编写自己部分的业务逻辑,可以参考。
- 推送分支
# 追踪文件
git add .
# 本地提交
git commit -m "example commit"
# 如果是多人协调一个分支
git pull origin feat/example
# 本地处理冲突
...
# 推送到远端
git push origin feat/example- 发起一个 PR 请求
你可以考虑自己自己与主分支 merge,也可以和别人进行 code review 后进行 merge。
推荐与别人讨论后再 merge。
dyshop/ # 工程根目录
├── app # 微服务目录
│ ├── auth # 鉴权与认证服务
│ │ ├── biz # 业务代码
│ │ │ ├── dal # 数据库相关操作
│ │ │ ├── model # 模型定义
│ │ │ └── service # 服务代码
│ │ │ ├── deliver_token.go
│ │ │ ├── deliver_token_test.go
│ │ │ ├── verify.go
│ │ │ └── verify_test.go
│ │ ├── cmd # 客户端实现
│ │ │ └── client
│ │ │ └── main.go
│ │ ├── conf # 配置文件
│ │ │ ├── config.yaml
│ │ │ ├── model.conf
│ │ │ └── policy.csv
│ │ ├── docker-compose.yaml # 当前服务启动的容器
│ │ ├── go.mod
│ │ ├── go.sum
│ │ ├── handler.go # RPC相关代码
│ │ ├── main.go # 微服务入口
│ │ ├── middleware # 中间件函数
│ │ ├── script # 脚本
│ │ └── utils # 当前微服务使用的工具函数
│ ├── ... # 其他微服务
├── pb # protoc 生成的文件
│ ├── backend
│ ├── frontend
│ └── go.mod
├── proto # proto源文件
│ ├── backend
│ └── frontend
├── utils
│ ├── balancerx # 负载均衡
│ ├── configx # 配置
│ ├── ctool # 加密
│ ├── db # 数据库
│ ├── example # 示例
│ ├── filex # 文件操作
│ ├── registryx # 服务注册
│ ├── jwt # token
│ ├── logx # 日志
│ └── go.mod
├── assets # README.md 使用的资源目录
├── deploy # 微服务部署
├── README.md # 说明
├── dyshop.postman_collection.json # postman请求测试文件
├── go.work # workspace文件
└── Makefile # 常用命令
- 外部请求通过 RESTful API 发送至 gateway(frontend)
- 当一个 app 启动时,会向注册中心进行注册
- 内部服务之间的访问,通过注册中心找到对应的服务,并通过 grpc 调用传输。
- 建议每一个微服务使用自己独立的数据库,这样一方面加快数据库的查找速度,另一方面更加安全。
- 在 proto 目录下的前端和后端模块中,编写所需要的 proto 文件(或者修改原本的 proto 文件)。
syntax = "proto3"; // proto 协议版本 [required]
package hello; // 当前proto文件的包名,用于 proto 之间的 import [required]
// option go_package = "example.com/user/project/whatever;whatever"
// ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
// proto选项 | 生成的 go 包的参数 按照项目填写 生成go包名 |其他包的引用名
// ⚠注意:生成的go包路是 go_out 路径加 example.com/user/project/whatever/**.go
option go_package = "github.com/asmile1559/dyshop/pb/backend/hello;hello";
// The greeter service definition.
service Greeter {
// ↑
// service的名字,一个大的service有很多小的rpc调用(小的service)
// 这里的service会由grpc提供 client 和 server 接口
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {}
// ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
//声明rpc|RPC调用名|RPC调用参数|声明返回值|RPC调用返回值|可拓展参数
}
// The request message containing the user's name.
message HelloRequest {
// ↑ ↑
//声明消息 消息名,对应调用参数和返回值
string name = 1;
// ↑ ↑ ↑
// 类型 参数名 序列号
}
// The response message containing the greetings
message HelloReply {
string message = 1;
}- 在工程目录下,运行
make gen-backend-proto或者make gen-frontend-proto。它会在 pb 目录下的对应位置生成你需要的 go 文件。 - 在 app 目录下找到或者新建你的微服务。如
auth。并按照 project architecture 的结构创建文件。 - 模仿某一个 app 的
biz/service的内容编写自己的 service,最好添加测试,可以测试自己service的可用性。推荐的写法如下:
package service
import (
pbhello "github.com/asmile1559/dyshop/pb/backend/hello"
"context"
)
type SayHelloService struct {
ctx context.Context
}
func NewSayHelloService(c context.Context) *SayHelloService {
return &SayHelloService{ctx: c}
}
func (s *SayHelloService) Run(req *pbhello.HelloRequest) (*pbhello.HelloReply, error) {
// TODO: finish your business code...
//
return
}
- 在 handler 中实现对应 rpc 的方法。
package main
// 1. 导入对应的依赖
import (
"context"
// service 是自己实现的service
service "github.com/asmile1559/dyshop/app/hello/biz/service"
// pbhello 是 protoc 生成的的文件
pbhello "github.com/asmile1559/dyshop/pb/backend/hello"
)
type Greeter struct{
// 包含这个未实现的 server 即可
pbhello.UnimplementedGreeterServer
}
func (s *Greeter) SayHello(ctx context.Context, req *pbhello.HelloRequest) (*pbhello.HelloReply, error) {
// 这一部分可以根据自己的需求修改
// 如果不想调用 service 也可以直接在这里完成 RPC 的所有请求和响应
resp, err := service.NewSayHelloService(ctx).Run(req)
return resp, err
}- 在
app/frontend/biz/handler和app/frontend/biz/service完成类似的代码。 - 在
app/frontend/biz/router中的模块中添加对应的路由。 - 在
app/frontend/rpc/client.go中添加 rpc client 的全局变量。具体写法可以参照其他变量修改。 - 完善前端页面。
前端页面均放在 app/frontend/templates 中,对应的 css/js/图片文件存放在 app/frontend/static 中
- index.html: 主页
- user.html: 用户页面
- cart.html: 购物车页面
- order.html: 订单页面
- payment.html: 支付页面
- search.html: 搜索结果页面
- product-page.html: 商品详情页
- register.html: 注册页面
- login.html: 登录页面
- pong.html: Ping-Pong 测试页面
浏览器会向后端发起 GET 请求, 以获取页面. 后端需要响应前端请求, 提供后端数据. 所有的数据均需要通过 gin 接口进行传递, 其基本方式是:
c.HTML(http.StatusOk, "xxx.html", gin.H{xxx}) 或 c.HTML(http.StatusOk, "xxx.html", &yourStruct).
在 app/frontend/main.go 中的 ping 响应为例子
router.GET("/ping", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 1. 方式 1
resp := struct {
Code int `json:"code"`
Host string `json:"host"`
Pong string `json:"pong"`
}{http.StatusOK, "192.168.191.130:10166", "Pong"}
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "pong.html", &resp)
// 2. 方式 2
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "pong.html", gin.H{
"Code": http.StatusOK,
"Host": "192.168.191.130:10166",
"Pong": "Pong",
})
})前端的请求参数和响应均在app/frontend/example.go中, 在实际使用时, 需要将 app/frontend/predef.go 中的参数和 app/frontend/static/js/router.js 的路径.
现在的路径为
// app/frontend/static/js/router.js
const DefaultURL = "http://192.168.191.130:10166";
const OperationRouters = {
home: "/example/", // GET
switchShowcase: "/example/showcase/", // GET
updateUserInfo: "/example/user/info/", // POST
updateUserImg: "/example/user/info/upload/", // POST
registerMerchant: "/example/user/role/merchant/", // GET
updateUserAccount: "/example/user/account/", // POST
deleteUserAccount: "/example/user/account/delete/", // POST
updateAddress: "/example/user/address/", // POST
deleteAddress: "/example/user/address/delete/", // POST
setDefAddress: "/example/user/address/setDefault/", // POST
updateProduct: "/example/user/product/", // POST
deleteProduct: "/example/user/product/delete/", // POST
getProduct: "/example/product/", // GET
buy: "/example/product/buy/", // POST
addToCart: "/example/product/add2cart/", // POST
getCart: "/example/cart/", // GET
deleteCartItem: "/example/cart/delete/", // POST
cartCheckout: "/example/cart/checkout/", // POST
getOrder: "/example/order/", // GET
cancelOrder: "/example/order/cancel/", // POST
submitOrder: "/example/order/submit/", // POST
checkout: "/example/checkout/", // GET
cancelCheckout: "/example/checkout/cancel/", // POST
payment: "/example/payment/", // POST
search: "/example/search/", // GET
register: "/example/user/register/", // GET|POST
login: "/example/user/login/", // GET|POST
verify: "/example/verify/", // POST
};// predef.go
package main
import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
var (
PageRouter = gin.H{
"HomePage": "/example/",
"LoginPage": "/example/user/login/",
"RegisterPage": "/example/user/register/",
"UserPage": "/example/user/",
"ProductPage": "/example/product/",
"OrderPage": "/example/order/",
"CartPage": "/example/cart/",
"SearchPage": "/example/search/",
"PaymentPage": "/example/payment/",
}
)- 前端路由(提供的路由接口框架基本完成,缺少前端页面的配合)
- 后端各模块的 rpc 通信接口(提供的 rpc 通信接口已完成,位于 handler.go 文件)
- 日志(日志初始化函数)
- 数据库(数据库开启函数)
- 加密算法
- 加盐的密码加密算法
- config(基于 etcd 的参数保存、取用和 watch)
- 服务注册与发现(基于 etcd 的服务注册模块已经完成)
- etcd
-
consul
- 鉴权和认证
- jwt
- casbin
-
satoken
- 负载均衡
- 前端页面
- 可观测性
- 日志(日志初始化函数)
- Metrics:Prometheus (with auto detection service)
- Trace
- rpc 通信
- Token 的生成与分发
- Token 验证,并通过 casbin 进行访问控制
- 服务注册