Read this in other languages: 🇨🇳简体中文
This repository contains C++ based examples of many popular algorithms and data structures.
Each algorithm and data structure has its own separate README with related explanations and links for further reading.
☝ Note that this project is meant to be used for learning and researching purposes only, and it is not meant to be used for production.
A data structure is a particular way of organizing and storing data in a computer so that it can be accessed and modified efficiently. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the functions or operations that can be applied to the data.
Remember that each data has its own trade-offs. And you need to pay attention more to why you're choosing a certain data structure than to how to implement it.
B - Beginner, A - Advanced
BArrayBStatic ArrayBDynamic ArrayBString
BLinked ListBSingly Linked ListBDoubly Linked List
BQueueBStackBHash Table
An algorithm is an unambiguous specification of how to solve a class of problems. It is a set of rules that precisely define a sequence of operations.
B - Beginner, A - Advanced
Every directorys under /data-structures or /algorithms should be treated as a independent project. For example, the LinkedList under data-structures has this structure:
.
├── assets
│ └── linkedlist.jpg
├── build.sh
├── clean.sh
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── include
│ └── LinkedList.h
├── README.md
├── src
│ └── LinkedList.cpp
└── __test__
└── test_LinkedList.cpp
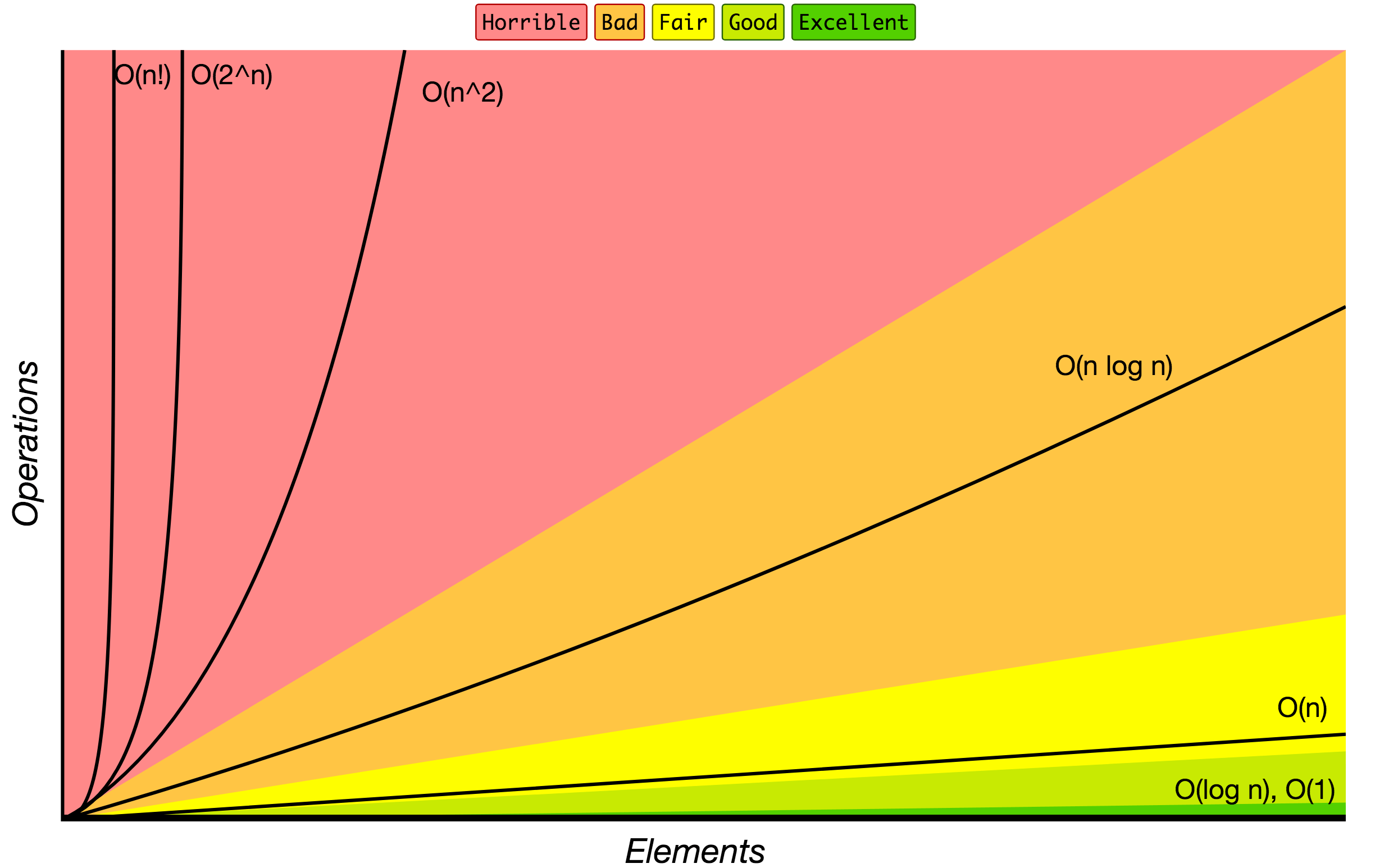
Big O notation is used to classify algorithms according to how their running time or space requirements grow as the input size grows. On the chart below you may find most common orders of growth of algorithms specified in Big O notation.
Source: Big O Cheat Sheet.
Below is the list of some of the most used Big O notations and their performance comparisons against different sizes of the input data.
| Big O Notation | Type | Computations for 10 elements | Computations for 100 elements | Computations for 1000 elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O(1) | Constant | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| O(log N) | Logarithmic | 3 | 6 | 9 |
| O(N) | Linear | 10 | 100 | 1000 |
| O(N log N) | n log(n) | 30 | 600 | 9000 |
| O(N^2) | Quadratic | 100 | 10000 | 1000000 |
| O(2^N) | Exponential | 1024 | 1.26e+29 | 1.07e+301 |
| O(N!) | Factorial | 3628800 | 9.3e+157 | 4.02e+2567 |
| Data Structure | Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Array | 1 | n | n | n | |
| Stack | n | n | 1 | 1 | |
| Queue | n | n | 1 | 1 | |
| Linked List | n | n | 1 | n | |
| Hash Table | - | n | n | n | In case of perfect hash function costs would be O(1) |
| Binary Search Tree | n | n | n | n | In case of balanced tree costs would be O(log(n)) |
| B-Tree | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | |
| Red-Black Tree | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | |
| AVL Tree | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | |
| Bloom Filter | - | 1 | 1 | - | False positives are possible while searching |
| Name | Best | Average | Worst | Memory | Stable | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bubble sort | n | n2 | n2 | 1 | Yes | |
| Insertion sort | n | n2 | n2 | 1 | Yes | |
| Selection sort | n2 | n2 | n2 | 1 | No | |
| Heap sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | n log(n) | 1 | No | |
| Merge sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | n log(n) | n | Yes | |
| Quick sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | n2 | log(n) | No | Quicksort is usually done in-place with O(log(n)) stack space |
| Shell sort | n log(n) | depends on gap sequence | n (log(n))2 | 1 | No | |
| Counting sort | n + r | n + r | n + r | n + r | Yes | r - biggest number in array |
| Radix sort | n * k | n * k | n * k | n + k | Yes | k - length of longest key |