| Version: | 0.30 |
|---|---|
| Copyright: | 2015 REANNZ. All Rights Reserved. |
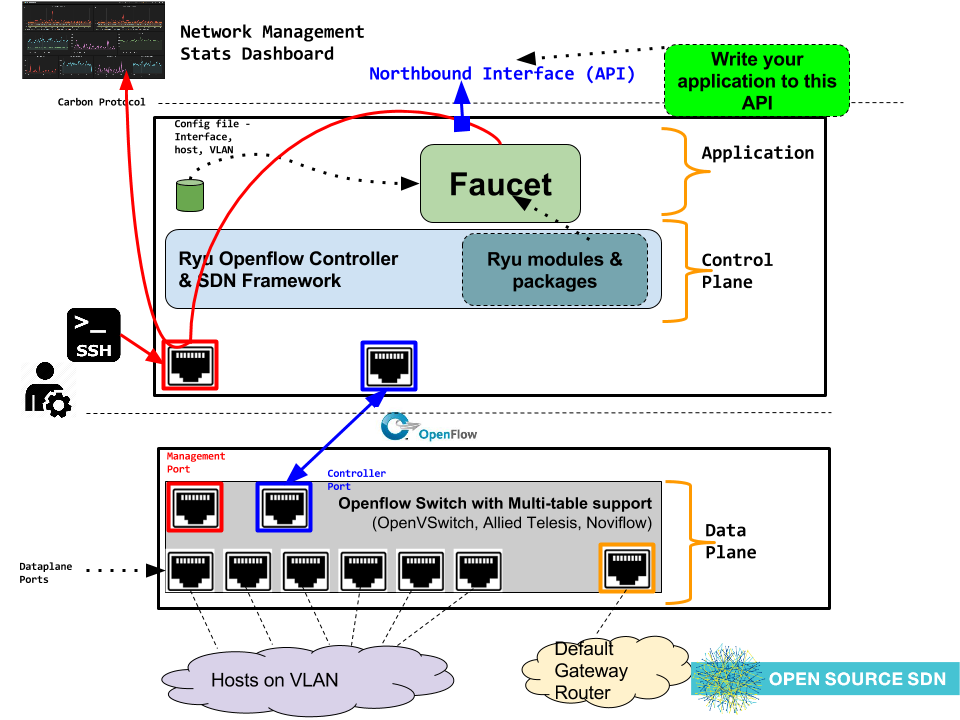
Faucet is an Openflow controller for a layer 2 switch based on OpenvApour's Valve. It handles MAC learning and supports VLANs and ACLs. It is developed as an application for the Ryu Open Flow Controller .
It supports:
- OpenFlow v1.3
- Multiple datapaths
- Mixed tagged/untagged ports
- Port statistics
- Coexisting with other OpenFlow controllers
- ACL support: Rules are added in the order specified. The rule language supports anything the Ryu OpenFlow protocol parser supports (q.v. ofctl to_match()).
- Control unicast flooding by port and by VLAN
- support for IPv4 static routes on both tagged and untagged VLANs
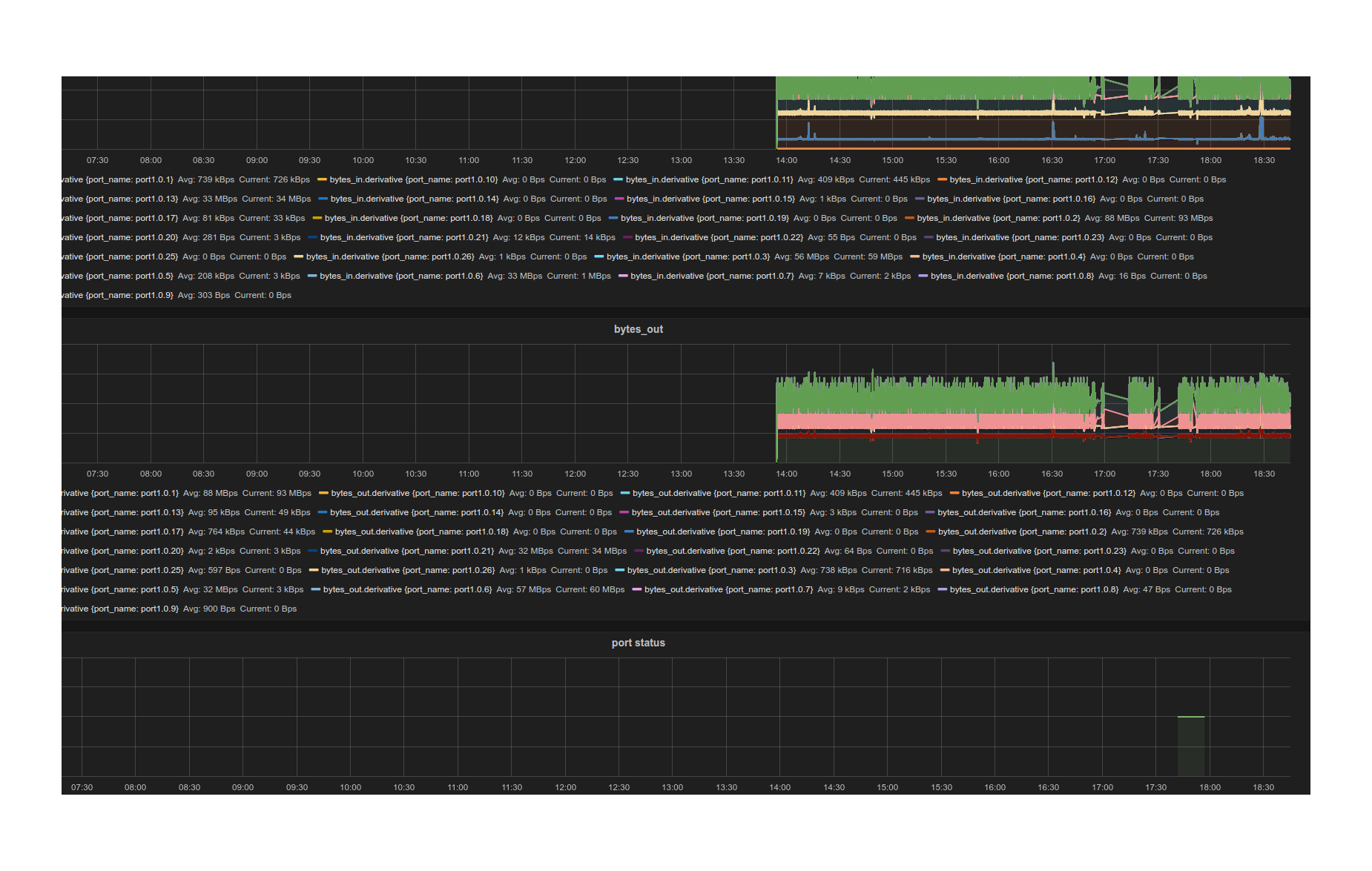
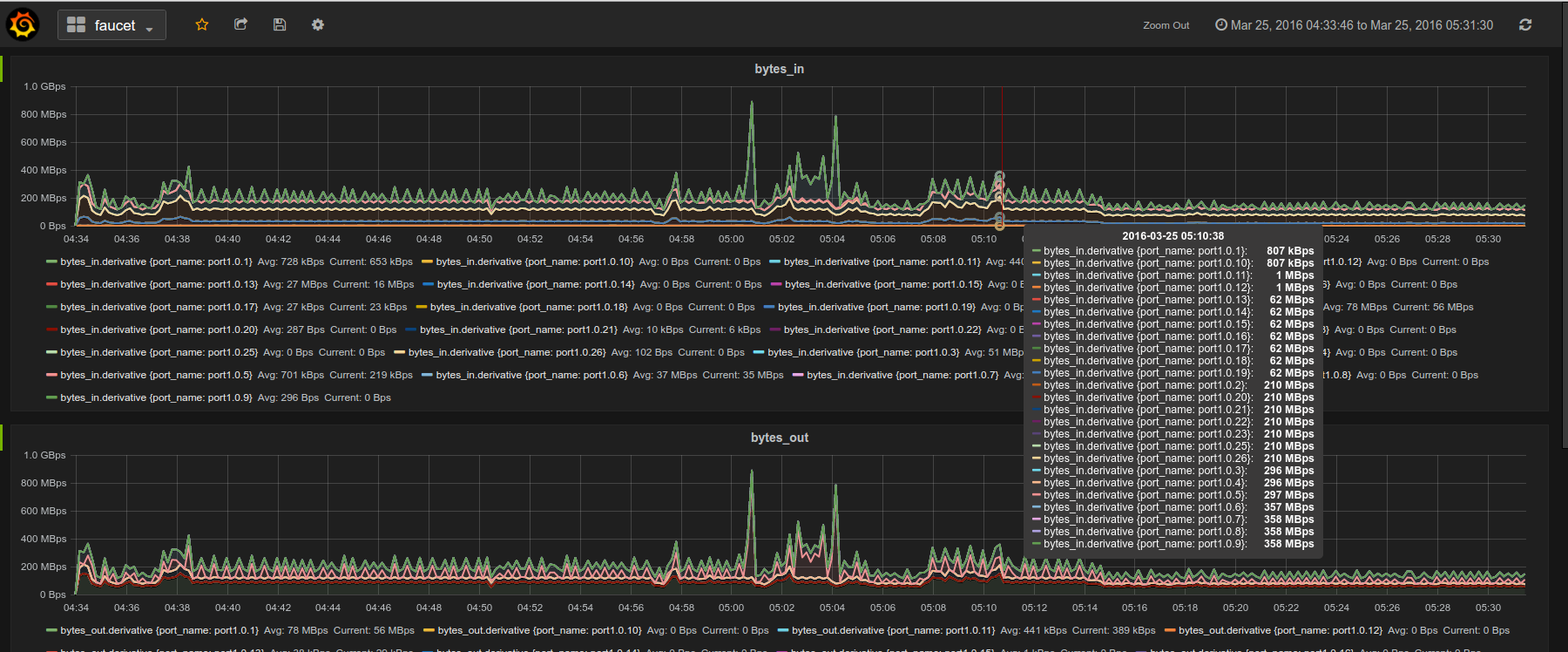
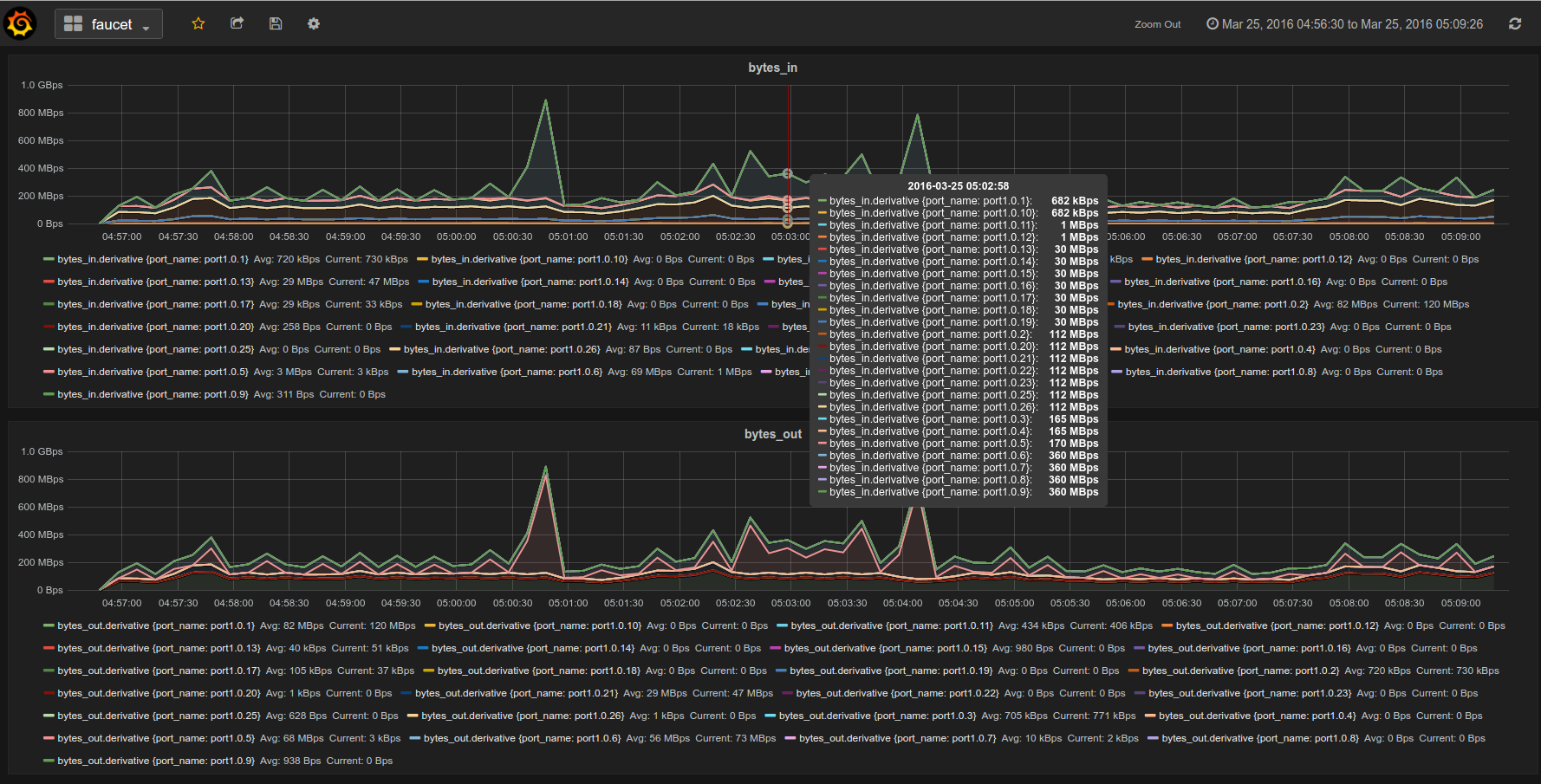
- Integrated support for InfluxDB/Grafana
Rules are added in the order specified. The rule language supports anything the Ryu OpenFlow protocol parser supports (q.v. ofctl to_match()). In this example,configure an ACL on port 1, default deny, that passes an IPv4 subnet and ARP. Following config applies an input ACL to port 1.
Supports any ACL rule that https://github.com/osrg/ryu/blob/master/ryu/lib/ofctl_v1_3.py to_match() supports.
1:
native_vlan: 2040
acl_in: 1
vlans:
2040:
name: "dev VLAN"
acls:
1:
- rule:
nw_dst: "172.0.0.0/8"
dl_type: 0x800
allow: 1
- rule:
dl_type: 0x0806
allow: 1
- rule:
nw_dst: "10.0.0.0/16"
dl_type: 0x800
allow: 0
- rule:
The default is to flood unknown unicast packets (of course). You might not want unicast flooding on a port for security reasons.
If you add unicast_flood: False to a port, then that port will never get unknown destinations flooded to it. So hosts on that port will have to say something to get learned (or someone will need to ND/ARP for it). Broadcasts and Ethernet multicasts are still flooded to that port (so of course ND and ARP work just fine).
You can also add unicast_flood: False to a VLAN, which will override all the ports. On my untrusted VLAN, the default gateway has permanent_learn enabled, and unicast flooding disabled.
Faucet is configured with a YAML-based configuration file. A sample configuration file is supplied in faucet.yaml.
The datapath ID may be specified as an integer or hex string (beginning with 0x).
A port not explicitly defined in the YAML configuration file will be set down and will drop all packets.
Installation automatically installs dependent Python packages [ryu, pyaml, influxdb client] recursively.
You have run this as root or use sudo
# pip install https://pypi.python.org/packages/source/r/ryu-faucet/ryu-faucet-0.30.tar.gz # pip show ryu-faucet
- To setup InfluxDB v0.11 - https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/v0.10/introduction/getting_started/
- To setup Grafana v2.6 - http://docs.grafana.org/installation/
To Uninstall the package
# pip uninstall ryu-faucet
PACKETS IN +------------------------+ +-------------------------+
| | | | |
| | V | V
| +------+--+ +---------+ +----------+ +---------+ +---------+
| |0:VLAN | |1:ACL | |2:ETH_SRC | |3:ETH_DST| |4:FLOOD |
+------>| +-->| +-->+ +-->+ |-->+ |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
+---------+ +---------+ +-----+----+ +---+-----+ +----+----+
| | |
| | |
V | V
+----------+ +------->PACKETS OUT
|CONTROL |
|PLANE |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
+----------+
Note: On your system, depending on how Python is installed, you may have to install some additional packages to run faucet.
Run with ryu-manager (uses /etc/ryu/faucet/faucet.yaml as configuration by default):
# export FAUCET_CONFIG=/etc/ryu/faucet/faucet.yaml # export GAUGE_CONFIG=/etc/ryu/faucet/gauge.conf # export FAUCET_LOG_DIR=/var/log/ryu # $EDITOR /etc/ryu/faucet/faucet.yaml # ryu-manager --verbose faucet.py
To find the location of faucet.py, run
# pip show ryu-faucet to get Location path. Then run:
# ryu-manager --verbose <Location_Path>/ryu_faucet/org/onfsdn/faucet/faucet.py
Alternatively, if OF Controller is using a non-default port of 6633, for example 6653, then:
# ryu-manager --verbose --ofp-tcp-listen-port 6653 <Location_Path>/ryu_faucet/org/onfsdn/faucet/faucet.py
On MacOS X, for example, one would run this as:
# ryu-manager --verbose /opt/local/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ryu_faucet/org/onfsdn/faucet/faucet.py
To specify a different configuration file set the FAUCET_CONFIG environment variable.
Faucet will log to /var/log/ryu/faucet/ by default, this can be changed with the FAUCET_LOG_DIR environment variable.
To tell Faucet to reload its configuration file after you've changed it, simply send it a SIGHUP:
# pkill -SIGHUP -f "ryu-manager faucet.py"
Run the tests to make sure everything works! Mininet test actually spins up virtual hosts and a switch, and a test FAUCET controller, and checks connectivity between all the hosts given a test config. If you send a patch, this mininet test must pass.:
# git clone https://github.com/onfsdn/faucet # cd faucet/tests (As namespace, etc needs to be setup, run the next command as root) # sudo ./faucet_mininet_test.py # ./test_config.py
If you are a hardware vendor wanting to support FAUCET, you need to support all the matches in src/ryu_faucet/org/onfsdn/faucet/valve.py:valve_in_match().
Faucet has been tested against the following switches: (Hint: look at src/ryu_faucet/org/onfsdn/faucet/dp.py to add your switch)
- Open vSwitch v2.1+ - Open Source available at http://www.OpenVSwitch.Org
- Lagopus Openflow Switch - Open Source available at https://lagopus.github.io/
- Allied Telesis x510 and x930 series
- NoviFlow 1248
Faucet's design principle is to be as hardware agnostic as possible and not require TTPs. That means that Faucet excepts the hardware OFA to hide implementation details, including which tables are best for certain matches or whether there is special support for multicast - Faucet excepts the OFA to leverage the right hardware transparently.
Allied Telesis <http://www.alliedtelesis.com/sdn sells their products via distributors and resellers. To order in USA call ProVantage <http://www.provantage.com/allied-telesis-splx10~7ALL912L.htm>. To find a sales office near you, visit Allied Telesis <http://www.AlliedTelesis.com>
- On Allied Telesis all vlans must be included in the vlan database config on the switch before they can be used by Openflow.
NoviFlow <http://noviflow.com/>
It is possible to use Faucet to add layer 2 features to another OpenFlow controller by running Faucet in parallel with that controller. Faucet will only ever modify/remove OpenFlow rules added by itself (identified by a special OpenFlow cookie unique to Faucet), this means the rules installed by the other controller/application will be left untouched.
Simply add Faucet as a second primary OpenFlow controller to your datapath element. You will also probably need to tweak the OpenFlow priority values Faucet uses by modifying priority_offset in the configuration file so that rules installed by the other controller don't override those installed by Faucet.
Gauge is the monitoring application. It polls each port for statistics and periodically dumps the flow table for statistics.
Gauge reads the faucet yaml configuration files of the datapaths it monitors. Which datapaths to monitor is provided in a configuration file containing a list of faucet yaml files, one per line.
The list of faucet yaml config is by default read from /etc/ryu/faucet/gauge.conf. This can be set with the GAUGE_CONFIG environment variable. Exceptions are logged to the same file as faucet's exceptions.
Gauge is run with ryu-manager:
$ $EDITOR /etc/ryu/faucet/gauge.conf
$ ryu-manager gauge.py
If you have any technical questions, problems or suggestions regarding Faucet please send them to [email protected] <mailto:[email protected]>. Mailing list archives are available here <https://groups.google.com/a/openflowsdn.org/forum/#!forum/faucet-dev>.
To create a issue, use Github issues <https://github.com/onfsdn/faucet/issues>