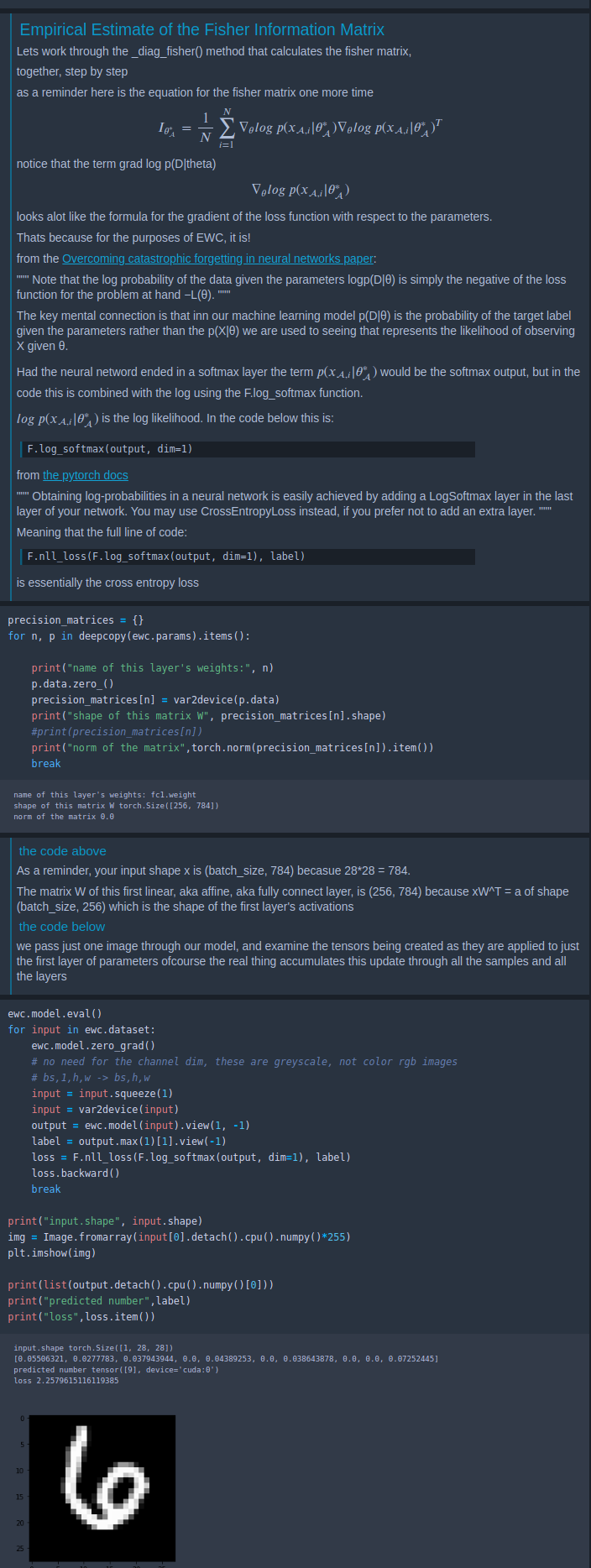
This is a tutorial to connect the mathematics and machine learning theory to practical implementations addressing the continual learning problem of artificial intelligence. We will learn this in python by examining and deconstructing a method called elastic weight consolidation (EWC).
I wish there were more learning tools in this style that directly try to help the learner connect the math to the code, and do it using a simple but completely end to end project. While it is true that the average programmer can load a "out of the box" library in 5 minutes and be running the latest model solving a common task in 15 minutes, I often hear from engineers that although they are engineers, they feel under-developed in the math that underlies recent academic research in machine learning. I have received criticism from some that believe tutorials like this provide a shortcut for "average" engineers to "think" they understand the math behind a new flashy artificial intelligence concept, who think the joy of reading these papers should be reserved for the traditionally trained academics that have gone through the years of formal coursework. I think there is nothing wrong with motivating learners using a cool AI concept to learn more of the fundamental math on their own.
"anyone can cook" - ratatouille
The ability to learn tasks in a sequential fashion is crucial to the development of artificial intelligence. When an artificial neural network is trained on a new training set, unless that new training set includes all the old tasks combined with the new task, it generally is subject to catastrophic forgetting, whereby learning to solve new task B accompanies degradation of performance at old task A. In contrast, human neural networks can maintain expertise on tasks that they have not experienced for a long time. EWC addresses this problem by selectively slowing down learning on the weights (ie parameters, synaptic strengths) important for those old tasks.
- Ubuntu 18.04.3 LTS (bionic)
- Python 3.8
- Cuda 10.1
- cudnn7.6.4
- PyTorch 1.10.0
you@you:/path/to/folder$ pip3 install virtualenv
you@you:/path/to/folder$ virtualenv venv --python=python3.8
you@you:/path/to/folder$ source venv/bin/activate
(venv) you@you:/path/to/folder$ pip3 install -r requirements.txt
(venv) you@you:/path/to/folder$ jupyter notebook