Tendis is a high-performance distributed storage system which is fully compatible with the Redis protocol. 中文文档
Tendis is a high-performance distributed storage system which is fully compatible with the Redis protocol. It uses RocksDB as the storage engine, and all data is stored to disks through RocksDB. Users can access Tendis using a Redis client, and the application hardly needs to be changed. In addition, Tendis supports storage capacity far exceeding memory, which can greatly reduce user storage costs.
Similar to Redis clusters, Tendis uses a decentralized distributed solution. The gossip protocol is used for communication between nodes, and all nodes in a cluster can be routed to the correct node when a user accesses. Cluster nodes support automatic discovery of other nodes, detect faulty nodes, and ensure the application is almost not affected when the master node failed.
-
Redis compatibility
Redis protocol and commands supported in Tendis are compatible with Redis.
-
Persistent storage
Using RocksDB as storage engine. All data is stored in RocksDB in a specific format, supporting PB-level storage capacity.
-
Decentralized distributed cluster
Distributed implementation like Redis clusters, using a gossip protocol to intercommunicate between nodes.
-
Horizontal scalability
Data migration online between nodes. High performance and linear scalability up to 1,000 nodes.
-
Failover
Auto-detect non-working nodes, and promote replica nodes to master when a failure occurs.
-
Key component for Tendis Hybrid Storage Edition
Thanks to the design and internal optimization, Redis and Tendis can work together to be Hybrid Storage Edition. It is suitable for KV storage scenarios, as it balances performance and cost, and greatly reduces your business operating costs by 80% in the scenarios where cold data takes up a lot of storage space.
- g++ (required by c++17, version >= 5.5)
- cmake (version >= 3.13.0)
$ git clone https://github.com/Tencent/tendis.git --recursive
$ git submodule update --init --recursive
$ mkdir bulid
$ cd build & cmake ..
$ make -j12
$ ./build/bin/tendisplus tendisplus.conf
Connect to the server via redis-cli
$ redis-cli -p 51002
You can make some change to the code and make sure the following test script pass.
$ sh ./testall.sh
CPU:2.50 GHz,48 core
DISK:NVMe SSD
MEM:192GB
tendisplus: workers = 56
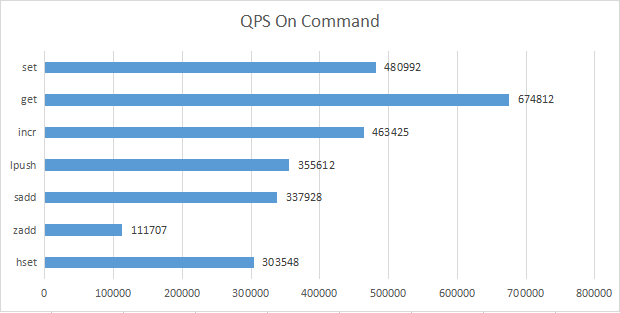
./memtier_benchmark -t 20 -c 50 -s 127.0.0.1 -p 51002 --distinct-client-seed --command="set __key__ __data__" --key-prefix="kv_" --key-minimum=1 --key-maximum=500000000 --random-data --data-size=128 --test-time=1800
./memtier_benchmark -t 20 -c 50 -s 127.0.0.1 -p 51002 --distinct-client-seed --command="get __key__" --key-prefix="kv_" --key-minimum=1 --key-maximum=500000000 --test-time=1800
./memtier_benchmark -t 20 -c 50 -s 127.0.0.1 -p 51002 --distinct-client-seed --command="incr __key__" --key-prefix="int_" --key-minimum=1 --key-maximum=1000000 --test-time=1800
./memtier_benchmark -t 20 -c 50 -s 127.0.0.1 -p 51002 --distinct-client-seed --command="lpush __key__ __data__" --key-prefix="list_" --key-minimum=1 --key-maximum=1000000 --random-data --data-size=128 --test-time=1800
./memtier_benchmark -t 20 -c 50 -s 127.0.0.1 -p 51002 --distinct-client-seed --command="sadd __key__ __data__" --key-prefix="set_" --key-minimum=1 --key-maximum=1000000 --random-data --data-size=128 --test-time=1800
./memtier_benchmark -t 20 -c 50 -s 127.0.0.1 -p 51002 --distinct-client-seed --command="zadd __key__ __key__ __data__" --key-prefix="" --key-minimum=1 --key-maximum=1000000 --random-data --data-size=128 --test-time=1800
./memtier_benchmark -t 20 -c 50 -s 127.0.0.1 -p 51002 --distinct-client-seed --command="hset __key__ __data__ __data__" --key-prefix="hash_" --key-minimum=1 --key-maximum=1000000 --random-data --data-size=128 --test-time=1800
latency:
SET 1.6ms 99%
SET 2.2ms 99.9%
SET 6.9ms 99.99%
SET 9.4ms 100.00%
tendisplus: workers = 56
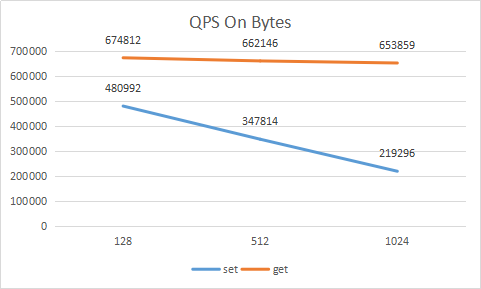
./memtier_benchmark -t 20 -c 50 -s 127.0.0.1 -p 51002 --distinct-client-seed --command="set __key__ __data__" --key-prefix="kv_" --command-key-pattern=R --random-data --data-size=128 --test-time=1800
./memtier_benchmark -t 20 -c 50 -s 127.0.0.1 -p 51002 --distinct-client-seed --command="get __key__" --key-prefix="kv_" --command-key-pattern=R --test-time=1800
we test set for half an hour, and then test get key half an hour. because the data is not big enough, most of the data is in memory, so the get qps for different payload is nearly the same.
For more information regarding contributing issues or pull requests, checkout CONTRIBUTING
Checkout support for FAQs or join our discussion groups.
Tendis is licensed under the GNU General Public License Version 3.0. Copyright and license information can be found in the file LICENSE.txt.