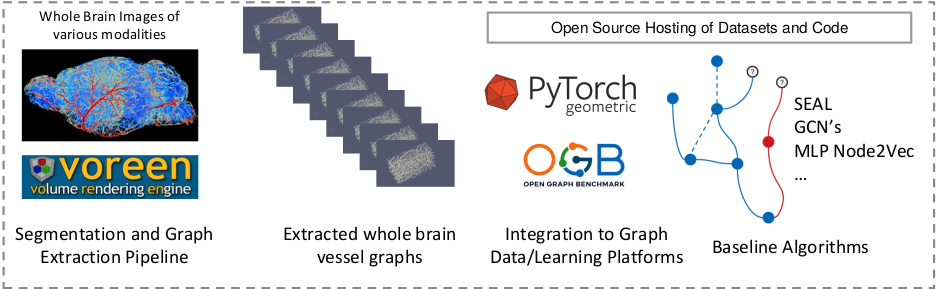
Welcome to the project page of VesselGraph A Dataset and Benchmark for Graph Learning and Neuroscience.
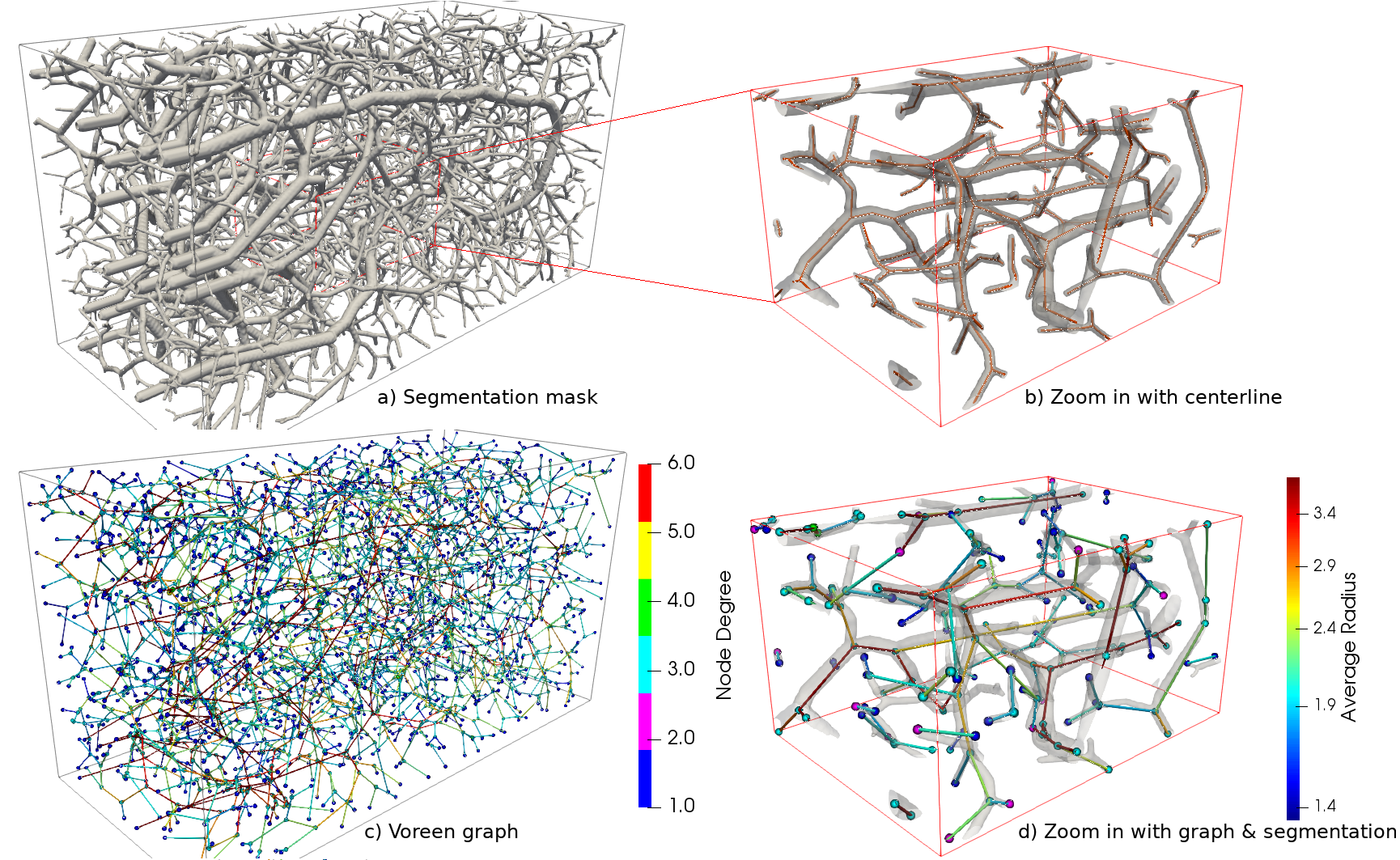
Biological neural networks define human and mammalian brain function and intelligence and form ultra-large, spatial, structured graphs. Their neuronal organization is closely interconnected with the spatial organization of the brain's microvasculature, which supplies oxygen to the neurons and builds a complementary spatial graph. In this project we are providing an extendable dataset of whole-brain vessel graphs based on various multi-center imaging protocols.
This new dataset paves a pathway towards translating advanced graph learning research into the field of neuroscience. Complementarily, the new dataset raises challenging graph learning research questions for the machine learning community, for example how to incorporate biological priors in a meaningful and interpretable way into learning algorithms.
- Whole brain vessel graphs: are the key for research questions to Biology and Neuroscience, including Neuronal organisation, stroke modeling and hemodynamics
- Ready-to use and large set of data: We are providing whole brain graphs from different research groups and will continously update our dataset.
- Data-Loaders: We are providing extensive functions to readily process our data for machine learning research, including the community standard OGB and pyG dataloaders
- Benchmarks: We benchmarked a comprehensive set of state of the art methods in link prediction and node classification; we provide all codes and detailed instructions
- Open-source, “living” initiative: VesselGraph is an open source initiative. We want to expand our datasets as soon as other brain imaging becomes publicly available
@misc{paetzold2021brain,
title={Whole Brain Vessel Graphs: A Dataset and Benchmark for Graph Learning and Neuroscience (VesselGraph)},
author={Johannes C. Paetzold and Julian McGinnis and Suprosanna Shit and Ivan Ezhov and Paul Büschl and Chinmay Prabhakar and Mihail I. Todorov and Anjany Sekuboyina and Georgios Kaissis and Ali Ertürk and Stephan Günnemann and Bjoern H. Menze},
year={2021},
eprint={2108.13233},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG}
}
Please cite this work if any of our code or datasets are helpful for your research. Considering the specific graphs and baseline models please also cite the respective original articles as described in the preprint.
Our software is licensed under the MIT license. The data is licensed under a Creative Commons Namensnennung-Nicht kommerziell 4.0 International Lizenz.
NOTE: Currently, our graphs are not officially included in the OGB dataset yet. Please use our custom version of ogb in ./source/ instead of the official pip ogb package for now. (See Issue #4.)
We provide our graphs as preprocessed OGB datasets (OGBN and OGBL) that are automatically retrieved by the dataloaders when executing the algorithms in ./source/baseline_models/.
If you would rather work with customized solutions (different datasplits, etc.), we provide you with all steps of our pipeline to generate, preprocess and convert the raw graphs to PyG and OGB formats. In the following section, we describe how our graphs have been built. You are invited to skip this section if you prefer working with our preprocessed graphs.
For this step, please run ./source/ogb_dataset/link_prediction/update_ogbl_master.sh and ./source/ogb_dataset/node_classification/update_ogbn_master.sh once after including your own dataset, so it will be broadcasted to the ogb dataloaders, before you execute any of the algorithms in ./source/baseline_models.
This is the description about how we prepared the dataset. The parameters are described as used in the paper
Use Voreen Graph Generation Tool to make the node_list and edge_list from a segmentation volume.
Go to ./source/dataset_preprocessing/ and run process_edge_list.py with arguments of --node_list and --edge_list
| Dataset Name | Raw | Preprocessed |
|---|---|---|
BALBc_no1 |
download | download |
BALBc_no2 |
download | download |
BALBc_no3 |
download | download |
C57BL_6_no1 |
download | download |
C57BL_6_no2 |
download | download |
C57BL_6_no3 |
download | download |
CD1-E_no1 |
download | download |
CD1-E_no2 |
download | download |
CD1-E_no3 |
download | download |
C57BL_6-K1 |
download | download |
C57BL_6-K2 |
download | download |
C57BL_6-K3 |
download | download |
Synth. Graph 1 |
download | download |
Synth. Graph 2 |
download | download |
Synth. Graph 3 |
download | download |
Synth. Graph 4 |
download | download |
Synth. Graph 5 |
download | download |
We are currently verifying the C57BL_6-K** graph representations with the Kleinfeld Lab at UC San Diego. As the raw data is not processed using Voreen (our default graph generation pipeline), we are in contact with the authors of the original paper and want to ensure a similar interface to this data.
Go to ./source/feature_generation/atlas_annotation/ and run generate_node_atlas_labels.py with arguments of --node_list and --edge_list
Go to ./source/pytorch_dataset/ and run link_dataset.py and node_dataset.py to create pytorch-geometric compatible dataset for link-prediction and node-classification task.
- For Graph
G
and run python3 generate_ogbl_dataset.py --dataset BALBc_no1 --splitting_strategy random --train_val_test 0.8 0.1 0.1 --data_root_dir data
Argument list:
--dataset: from the list of `Dataset Name` in the table above
--splitting_strategy: either `random` or `spatial`
--seed: if any other random split than the default one
--train_val_test: if any other train val test split % than the default one
--data_root_dir: root directory where the data will be stored
- Subsequently run
update_ogbl_master.shfor compiling the ogb repository locally.
- For Line Graph
L(G)
and run python3 generate_ogbn_dataset.py --dataset BALBc_no1 --train_val_test 0.8 0.1 0.1 --data_root_dir data
Argument list:
--dataset: from the list of `Dataset Name` in the table above
--seed: if any other random split than the default one
--train_val_test: if any other train val test split % than the default one
--data_root_dir: root directory where the data will be stored
-
Subsequently run
update_ogbn_master.shfor compiling the ogb repository locally. -
We use the following options
Enter indices of desired features (Use "," to separate them): 0,1,2
Enter feature index of desired label: 4
Choose between a certain number of balanced classes (bc) or define classes by pixel boundaries (pb): pb
Enter desired radius boundaries as pixel values (Use "," to separate them): 5,13.33- Subsequently run
update_ogbn_master.shfor node-classification task.
We provide PyG dataset classes for link and node prediction tasks in ./source/pytorch_dataset/. Utilize LinkVesselGraph and NodeVesselGraph respectively. See the ./vesselgraph.ipnb for a toy example.
We store our graphs as OGBN (OGB Node Prediction) and OGBL (Link Prediction) graphs. All algorithms in ./source/baseline_models/ rely on OGB Dataloaders and process the graphs in OGB compatible format.
All baseline model can be run out-of-the-box with the following commands which automatically downloads the processed dataset.
1.1 Training
To create the node embeddings go to ./source/baseline_models/link_prediction/OGB_Node2Vec/ and runpython3 node2vec.py --dataset ogbl-BALBc_no1_spatial_no_edge_attr
Subsequently go to ./source/baseline_models/link_prediction/ and enter a MODEL directory to run
| Model Name | Script |
|---|---|
| Adamic Adar | python3 seal_link_pred.py --dataset ogbl-BALBc_no1_spatial_no_edge_attr --use_heuristic AA |
| Common Neighbors | python3 seal_link_pred.py --dataset ogbl-BALBc_no1_spatial_no_edge_attr --use_heuristic CN |
| Resource Allocation | python3 seal_link_pred.py --dataset ogbl-BALBc_no1_spatial_no_edge_attr --use_heuristic RA |
| Matrix Factorization | python3 mf.py --dataset ogbl-BALBc_no1_spatial_no_edge_attr |
| MLP | python3 mlp.py --dataset ogbl-BALBc_no1_spatial_no_edge_attr |
| GCN GCN | python3 gnn.py --dataset ogbl-BALBc_no1_spatial_no_edge_attr |
| GCN GCN + embeddings | python3 gnn.py --dataset ogbl-BALBc_no1_spatial_no_edge_attr --use_node_embedding |
| GCN SAGE + embeddings | python3 gnn.py --dataset ogbl-BALBc_no1_spatial_no_edge_attr --use_node_embedding --use_sage --num_layers 3 --hidden_channels 128 |
| GCN SAGE | python3 gnn.py --dataset ogbl-BALBc_no1_spatial_no_edge_attr --use_sage --num_layers 3 --hidden_channels 128 |
| SEAL | python3 seal_link_pred.py --dataset ogbl-BALBc_no1_spatial_no_edge_attr --dynamic_train --dynamic_val --dynamic_test --use_feature |
For the dataset name, we follow the OGB convention. For example, to run the BALBc_no1 whole brain with a spatial splitting strategy, and without edge features (edge attributes),
use python3 gnn.py --dataset ogbl-BALBc_no1_spatial_no_edge_attr.
We also provide a memory-friendly alternative (a selected Region of Interest of the entire graph). To run the models on the selected region of interest,
use python3 gnn.py --dataset ogbl-link_vessap_roi3_spatial_no_edge_attr.
If you are unsure what options are available, simply run the following command that will list all available datasets:
use python3 gnn.py --dataset ogbl-xyz.
1.2 Testing
Download Trained Weights and place them in the respective model folder
| Model Name | Checkpoint |
|---|---|
| Adamic Adar | [heuristic, not applicable] |
| Common Neighbors | [heuristic, not applicable] |
| Resource Allocation | [heuristic, not applicable] |
| Matrix Factorization | download |
| MLP | download |
| GCN GCN | download |
| GCN GCN + embeddings | download |
| GCN SAGE + embeddings | download |
| GCN SAGE | download |
| SEAL | download |
Go to ./source/baseline_models/link_prediction/ and select go a MODEL directory to run
e.g. to run GCN, one needs to use the following python3 gnn.py --dataset ogbl-BALBc_no1_spatial_no_edge_attr --load_state_dict --test_only
The same applies for the other models with two additional flags --load_state_dict and --test_only
2.1 Training
Go to ./source/baseline_models/node_classification/ and select a MODEL directory to run
| Model Name | Script |
|---|---|
| GCN | python3 gnn.py --dataset ogbn-BALBc_no1_pb_minRadiusAvg |
| GraphSAGE | python3 gnn.py --dataset ogbn-BALBc_no1_pb_minRadiusAvg --use_sage --num_layers 4 --hidden_channels 128 |
| GraphSAINT | python3 graph_saint.py --dataset ogbn-BALBc_no1_pb_minRadiusAvg --num_layers 4 --hidden_channels 64 --walk_length 7 |
| SIGN | python3 sign.py --dataset ogbn-BALBc_no1_pb_minRadiusAvg --hidden_channels 128 |
| Cluster-GCN | python3 cluster_gcn.py --dataset ogbn-BALBc_no1_pb_minRadiusAvg --num_layers 4 --num_partitions 9 |
| MLP | python3 mlp.py --dataset ogbn-BALBc_no1_pb_minRadiusAvg |
| SpecMLP-W + C&S | python3 mlp_cs.py --dataset ogbn-BALBc_no1_pb_minRadiusAvg |
| SpecMLP-W + C&S + Node2Vec | python3 mlp_cs.py --dataset ogbn-BALBc_no1_pb_minRadiusAvg --use_embed |
2.2 Testing
Download Trained Weights and place them in the respective model folder
| Model Name | Checkpoint |
|---|---|
| GCN | download |
| GraphSAGE | download |
| GraphSAINT | download |
| SIGN | download |
| Cluster-GCN | download |
| MLP | download |
| SpecMLP-W + C&S | download |
| SpecMLP-W + C&S + N2Vec | download |
Go to ./source/baseline_models/node_classification/ and select go a MODEL directory to run
e.g. to run GNN, one needs to use the following python3 gnn.py --model_states STATE_DICT_NAME --test_only --dataset DATASET_NAME
The same applies for the other models.
We are a living and continously maintained repository! Therefore, we welcome contributions of additional datasets and methods! There are multiple ways to contribute; if you are willing to share whole brain segmentations and graphs ....