Important disclaimer:
This is not an officially supported Google product
A Terminal like interface over UART.
- Targeted at embedded systems engineers and researchers who want to explore the hardware by writing small functions that can be triggered from a shell like interface.
- A UART based shell that enables finer control of CPU by allowing functions to be exposed as commands to be triggered from the prompt.
- Low memory footprint of < 4kB
this is a perfect tool for getting up and running with a new board in less than 1 hour.
- Low footprint shell implementation.
- Commands with same foot print as
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){} - Export function as command using a macro (
ADD_CMD()available inshell.h). - Supported Languages: C, C++ and Assembly.
- Automatic source file discovery
.c,.cppand.Ssource files in the Project and shell directory are automatically picked for compilation (No need to modify any Makefile. The build system automatically figrues the source files).
- Automatic Header discovery.
- location for
.hand.hppfiles is automatically passed to the compiler for header file lookup.
- location for
examples/ implements a hello world example for the processor variety listed below:
| Architecture | Processor | Example Location | Board |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARM v7 A-class 32 bit | Cortex-a7 (quadcore) | examples/emulation/armv7A-32-Rpi2 | raspberry pi 2b (Emulated on Qemu) |
| ARM v8 A-class 32 bit | Cortex-a53 | examples/emulation/armv8A-32-RPi3b | raspberry pi 3b (Emulated on Qemu) |
| ARM v7 M-class 32 bit | Cortex-m3 | examples/emulation/armv7M-32 | mps2-an385 (Emulated on Qemu) |
| ARM v8 A-class 64 bit | Cortex-a72 | examples/emulation/armv8A-64 | virt (Emulated on Qemu) |
| ARM v8 A-class 64 bit | Cortex-a72 (quadcore) | examples/emulation/armv8A-64-smp (multicore) | virt (Emulated on Qemu) |
| ARM v8 M-class 32 bit | Cortex-m33 (dualcore) | examples/emulation/armv8M-32 (multicore) | mps3-an524 (Emulated on Qemu) |
| RISC-V 64 bit | rv64g | examples/emulation/riscv-64 | virt (Emulated on Qemu) |
| RISC-V 32 bit (RV32IMAC) | SiFive E31 | examples/physical/hifive | hifive1-revb (Physical Board) |
| ARM v7 M-class 32 bit | Cortex-m4 | examples/physical/nucleo-f401re | nucleo-f401re (Physical Board) |
| ARM v7 M-class 32 bit | Cortex-m4 | examples/physical/tiva-c | tiva-c (Physical Board) |
Execute ./manage -s or .scripts/setup to install all the dependencies.
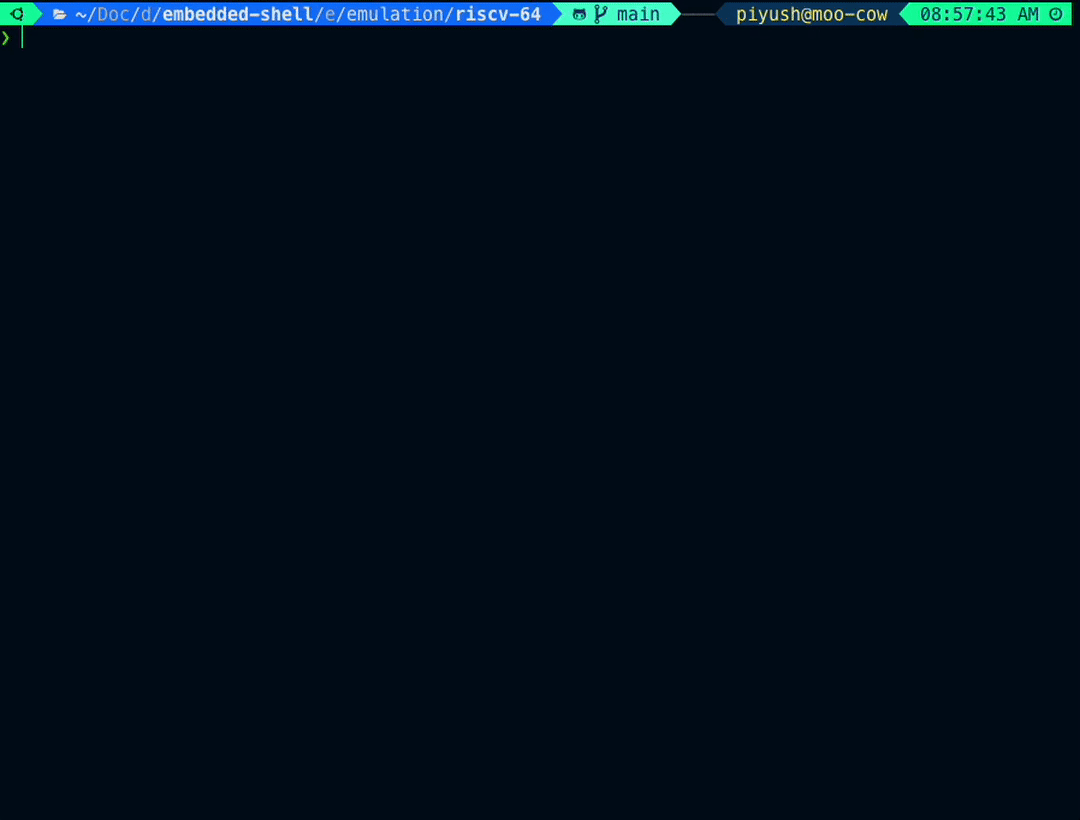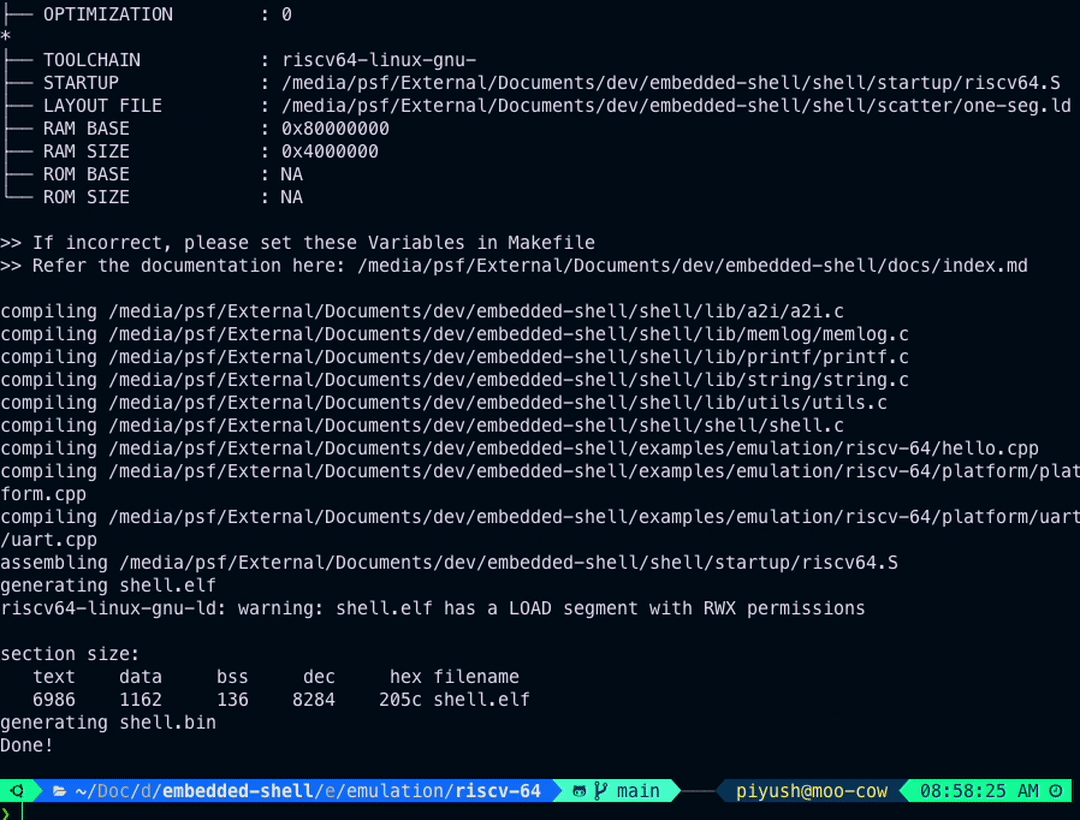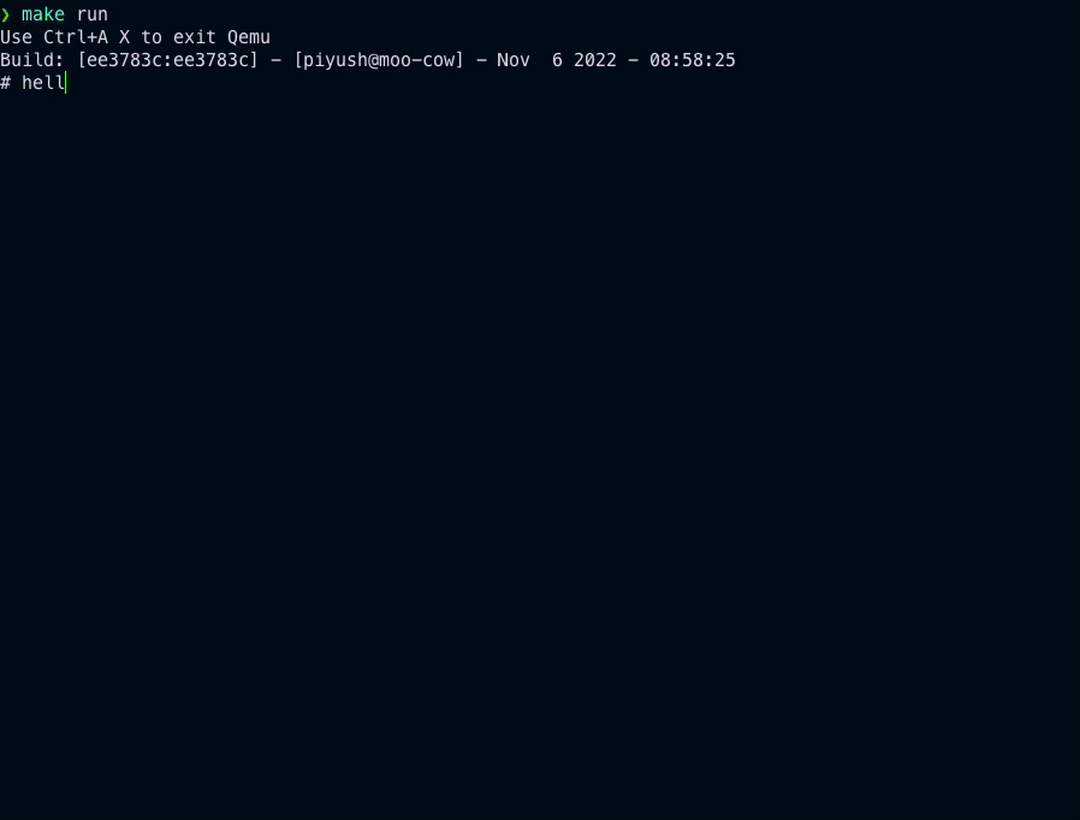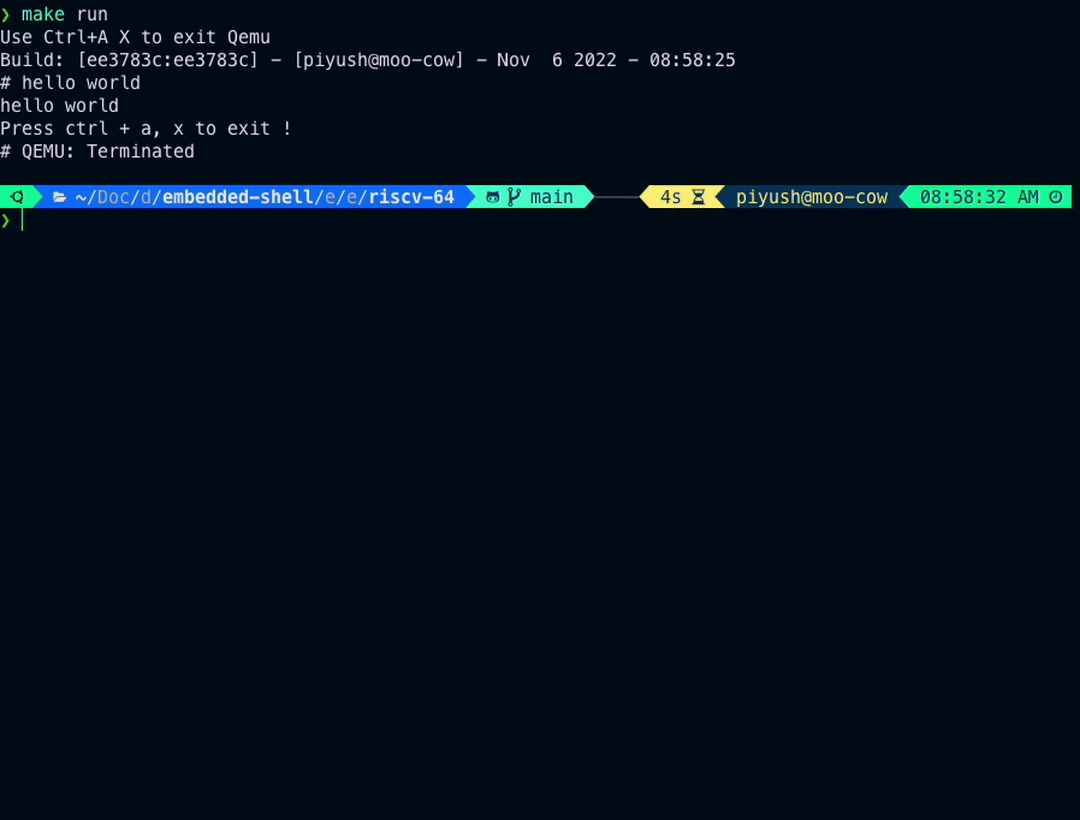
Following is a run of example in examples/emulation/riscv-64
cd examples/emulation/riscv-64
make
make runIf you haven't done the Quick Setup as noted above, you'll need to install following utilities:
sudo apt install -y binutils make binutils-riscv64-linux-gnu gcc-riscv64-linux-gnu g++-riscv64-linux-gnu \
qemu-system-riscv64
wget -P ~ https://git.io/.gdbinit
pip3 install pygments
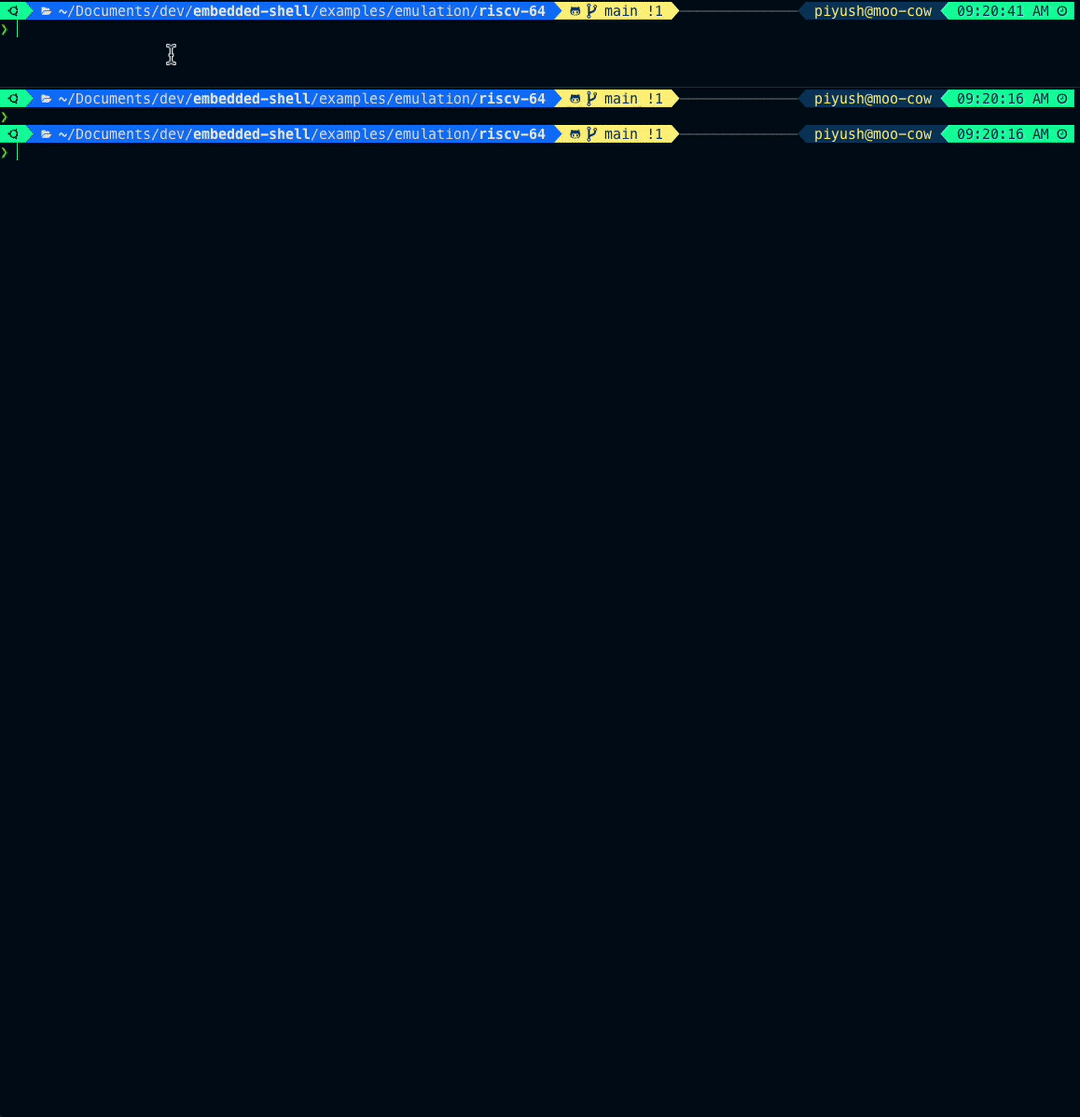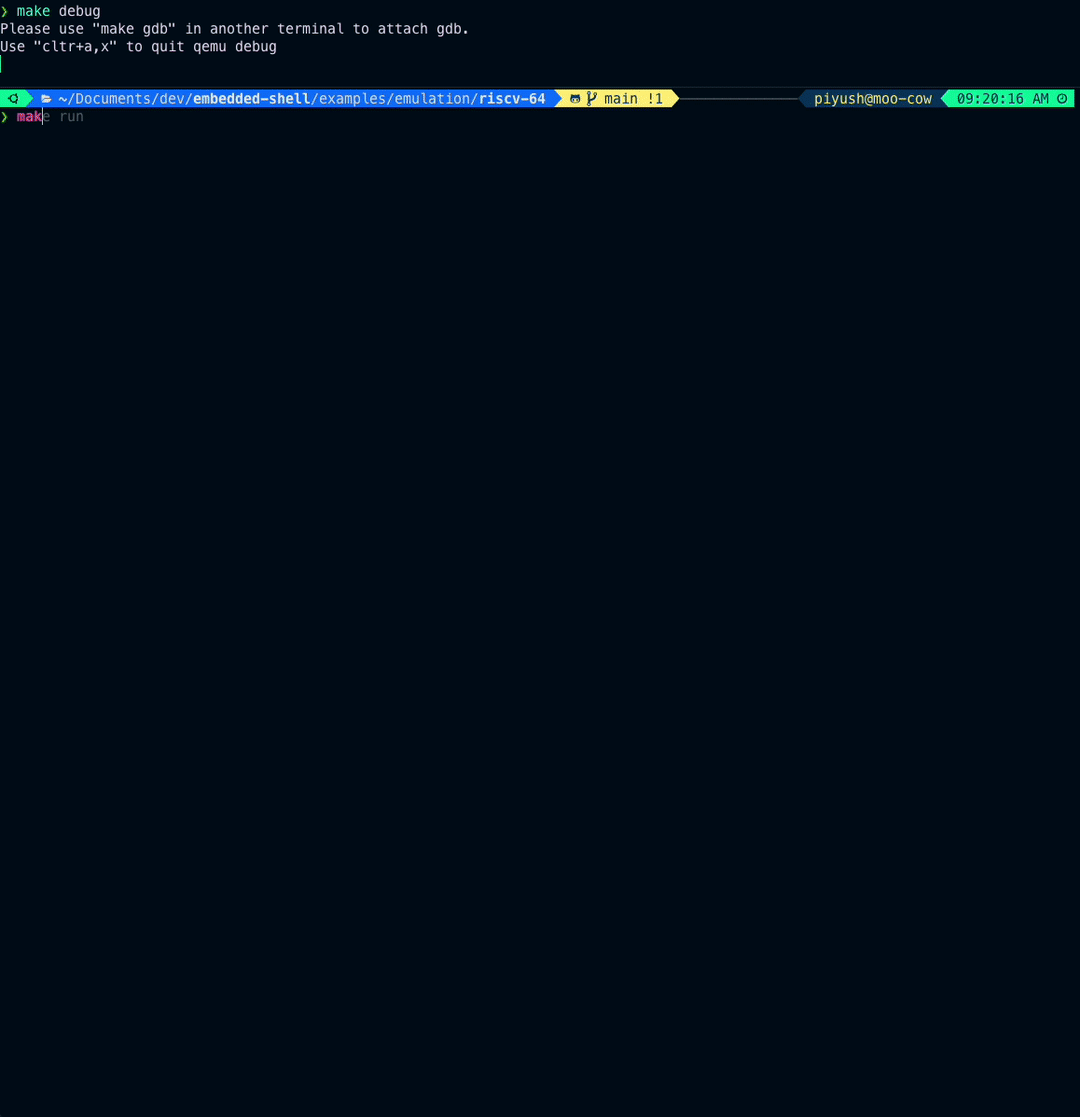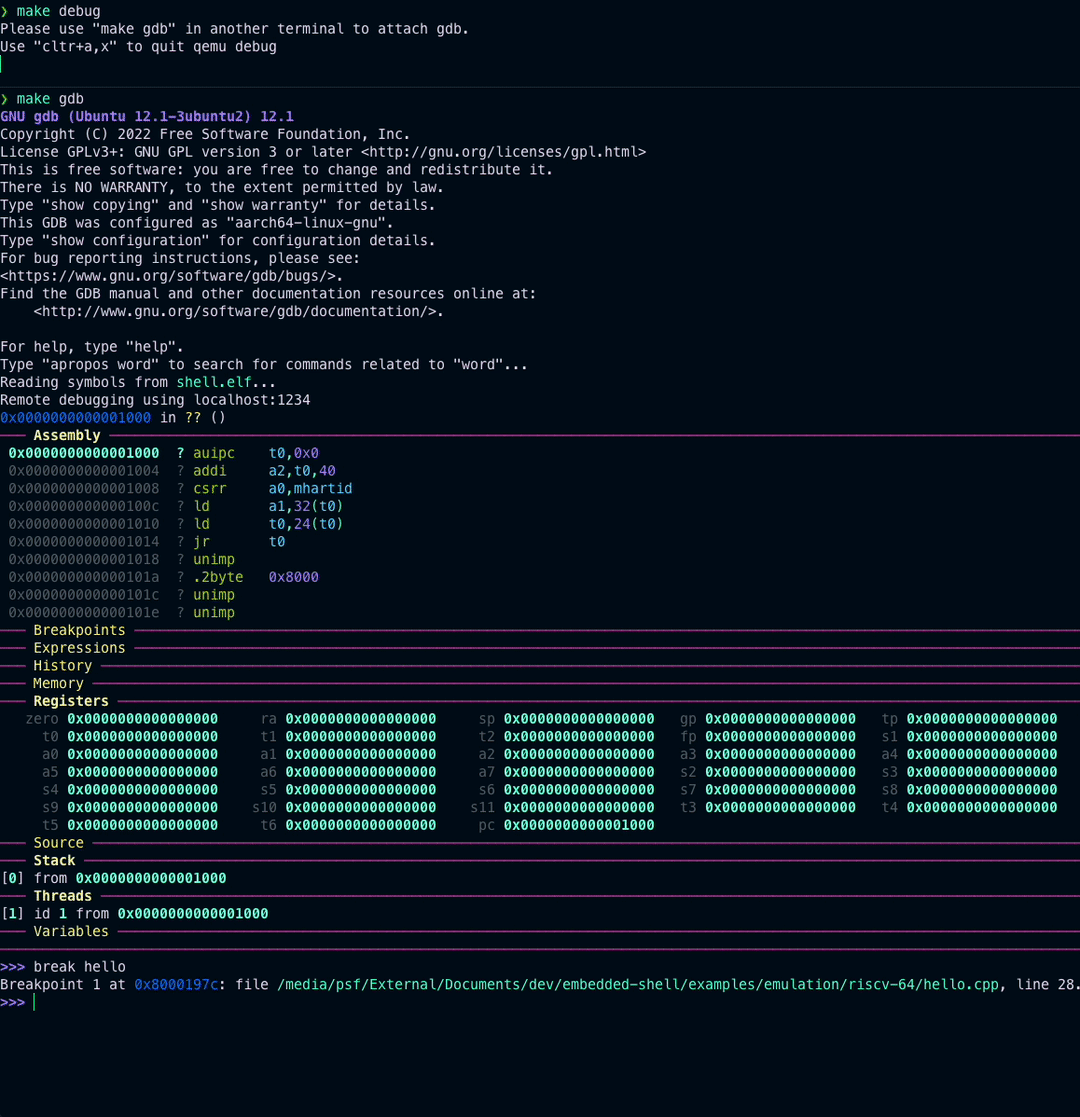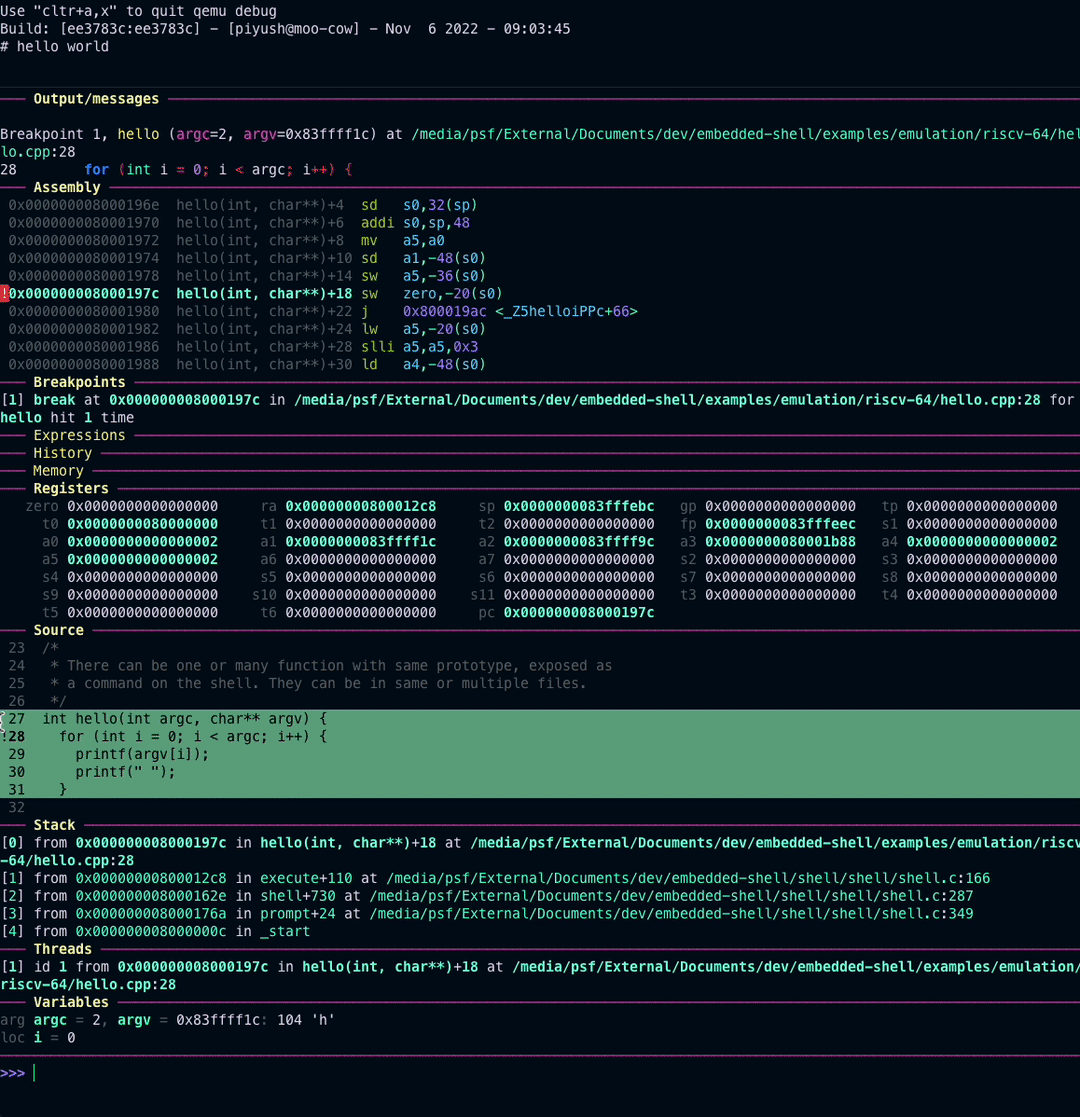
Further, gdb based debugging can also be done by running the following commands in two separate terminals:
make debug
and
make gdb
You should see similar output as in above visual.
- To be able to run all the example and create your own project follow the documentation in docs/.
- It also provides details about the internal workings of shell and how to setup your own project.
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| How shell Works | Explains the working of shell with a flowchart. |
Running examples in example/ |
Guides on getting started with trying examples. Includes topics like - - installing dependences- qemu based targets- physical board based targets- debugging etc |
| Setting up new project | Details on how to start setting up a new project. |
| Platform initialization and uart driver | Details the implementation of the platform_init() and the relation to the uart driver. |
| Uart driver | Describes implementation and constraint on the uart driver. |
| User Linker Scripts | Guides on how a liner script should be written if the user wants to manually set the memory layout and do the code placement. |
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Code of Conduct | Guides on the conduct expected while making contributions. |
| Contributing | Guidelines on how to contribute to the code on GitHub. |
Every file containing source code must include copyright and license information. This is to help well-intentioned people avoid accidental copying that doesn't comply with the license.
Apache header:
Copyright 2021 Google LLC
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.