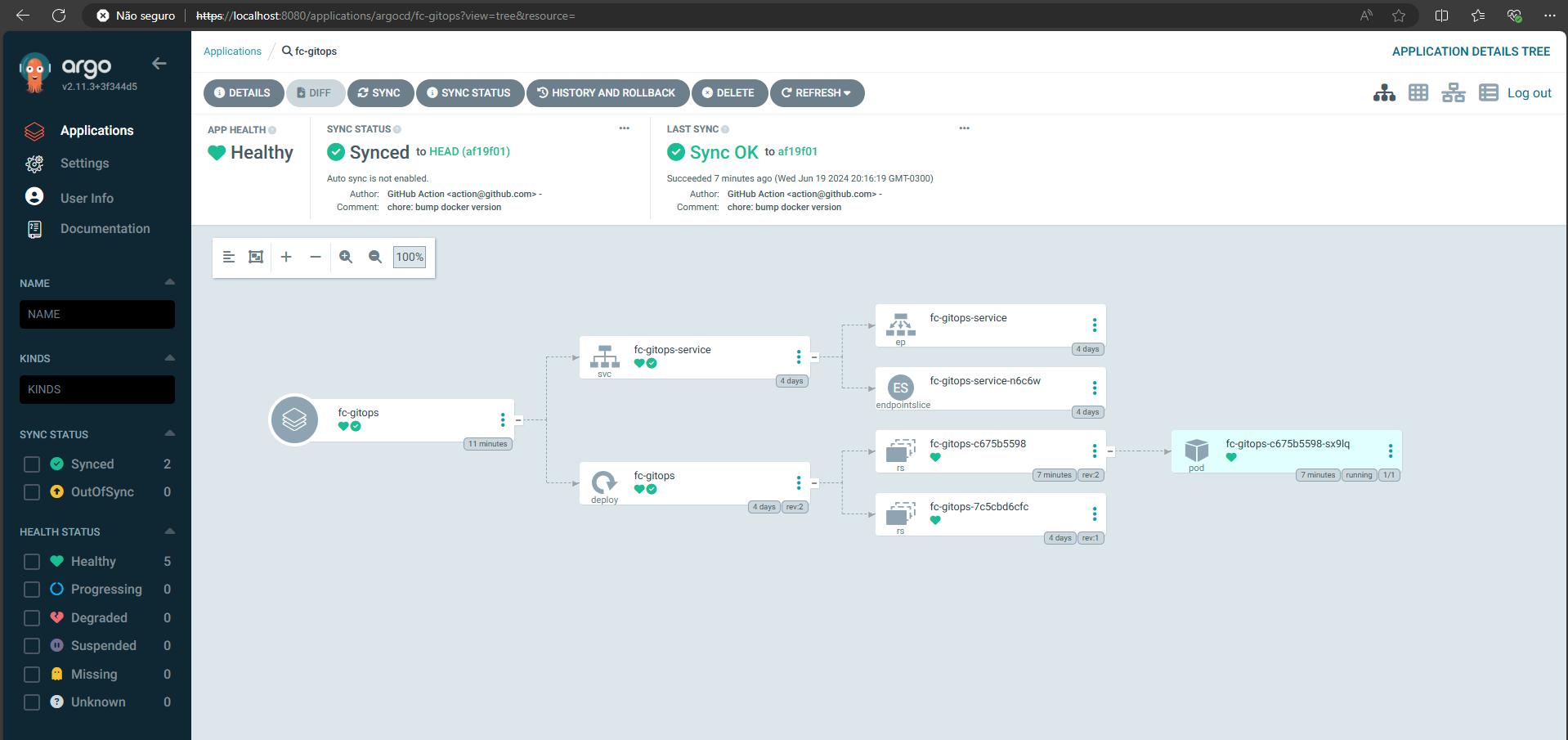
This repository contains the source code for the Full Cycle course I took to practice GitOps.
GitOps is a set of practices that use Git repositories as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and applications. It combines the benefits of Git's version control and collaboration features with automated deployment and operations processes.
- Declarative descriptions: use declarative configurations for infrastructure and applications.
- Single source of truth: maintain these configurations in a Git repository.
- Automated synchronization: automatically synchronize the desired state with the actual state.
- Pull-based deployments: pull changes from the Git repository and apply them to the infrastructure.
- Version control and auditability: leverage Git’s versioning to track changes and ensure auditability.
- Consistency and reliability: ensures that the deployed state matches the desired state as defined in Git.
- Enhanced collaboration: facilitates collaboration through Git’s branching and pull request model.
- Improved security: centralizes control over changes, reducing the risk of unauthorized modifications.
- Faster recovery: allows for quick rollback to previous states in case of issues.
- Audit and compliance: provides a clear history of changes, aiding compliance and audits.
- Scalability: simplifies scaling operations across multiple environments and clusters.
- Define desired state: use declarative files to describe the desired state of your infrastructure and applications.
- Create or update infrastructure: commit and push changes to the Git repository.
- Automated deployment: use automation tools to apply changes from the Git repository to the actual environment.
- Monitor and correct: continuously monitor the environment and correct any drift from the desired state.
Argo CD is a declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes. Application definitions, configurations, and environments should be declarative and version-controlled. Application deployment and lifecycle management should be automated, auditable, and easy to understand.
GitOps leverages the strengths of Git for version control and collaboration to manage infrastructure and application deployments. By treating Git as the single source of truth and using automation to ensure the actual state matches the desired state, GitOps enhances consistency, reliability, and security in software operations.
name: GitOps Pipeline
on:
push:
branches: [develop, main]
env:
DOCKERHUB_USERNAME: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
DOCKERHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_TOKEN }}
jobs:
build:
name: Build and Push Docker Image
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
contents: write
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Docker meta
id: meta
uses: docker/metadata-action@v5
with:
images: dalloglio/fc-gitops
tags: type=sha,prefix={{branch}}-
- name: Set up QEMU
uses: docker/setup-qemu-action@v3
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
- name: Login to Docker Hub
uses: docker/login-action@v3
with:
username: ${{ env.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
password: ${{ env.DOCKERHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Build and Push
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
with:
push: true
tags: ${{ steps.meta.outputs.tags }}
labels: ${{ steps.meta.outputs.labels }}
- name: Set up Kustomize
uses: imranismail/setup-kustomize@v1
with:
kustomize-version: 3.6.1
- name: Update Kubernetes resources
env:
DOCKERHUB_USERNAME: ${{ env.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
run: |
cd k8s
kustomize edit set image fc-gitops=$DOCKERHUB_USERNAME/fc-gitops:$DOCKER_METADATA_OUTPUT_VERSION
- name: Git Commit
run: |
git config --local user.email "[email protected]"
git config --local user.name "GitHub Action"
git commit -am "chore: bump docker version"
- name: Git Push
uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
with:
github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
repository: dalloglio/fc-gitops
branch: ${{ github.ref }}-
Build and push docker image:
- The workflow builds a new Docker image for the
fc-gitopsapplication using the latest code from the repository. - This image is then pushed to Docker Hub with tags and labels generated by the
docker/metadata-action.
- The workflow builds a new Docker image for the
-
Update Kubernetes manifests:
- After the Docker image is built and pushed, the workflow updates the
k8s/kustomization.ymlfile to use the new image version. - This update is done using Kustomize, which allows for declarative management of Kubernetes resources.
- After the Docker image is built and pushed, the workflow updates the
-
Deploy updated application:
- The updated
kustomization.ymlfile includes references to the new Docker image. - When committed and pushed back to the repository, this triggers a deployment pipeline (typically handled by a GitOps tool like Argo CD) to automatically apply the changes to the Kubernetes cluster.
- The Kubernetes cluster then updates the running application to use the new Docker image, ensuring that the latest version of the application is deployed.
- The updated
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: fc-gitops
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: fc-gitops
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: fc-gitops
spec:
containers:
- name: fc-gitops
image: fc-gitops:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 3000- Deployment: manages the application pods, ensuring the specified number of replicas are running and updated.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: fc-gitops-service
spec:
selector:
app: fc-gitops
ports:
- port: 3000
targetPort: 3000- Service: exposes the application internally within the cluster, allowing it to be accessed by other services.
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
- deployment.yml
- service.yml
images:
- name: fc-gitops
newName: dalloglio/fc-gitops
newTag: develop-2db3540- Kustomization: provides a way to customize the resources, such as updating the container image without directly modifying the YAML files.
This GitHub Actions workflow automates the process of building, pushing, and deploying updates to the fc-gitops application. By leveraging Docker, Kubernetes, and GitOps principles, it ensures that the application is always running the latest code from the repository with minimal manual intervention.