Red Hat OpenShift on IBM Cloud is an extension of the IBM Cloud Kubernetes Service, where IBM manages an OpenShift Container Platform for you.
Tekton Pipelines is an open source framework used for creating cloud-native continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines that run on Kubernetes. Tekton Pipelines was built specifically for container environments, supports the software lifecycle, and uses a serverless approach.
In this tutorial, you will become familiar with CI/CD pipelines and webhooks on Red Hat OpenShift 4.3 and Kubernetes 1.17 and higher using Tekton Pipelines.
Before you begin this tutorial, please complete the following steps:
- Register for an IBM Cloud account.
- Create a free Kubernetes v1.17 cluster on IBM Cloud.
- Create an OpenShift 4.3 cluster on IBM Cloud.
- Install and configure the IBM Cloud CLI.
- Configure the standard IBM Cloud Container Registry by creating in Dallas region (
us.icr.io) a namespace called:tekton-pipeline
Optional: Download Visual Studio Code IDE for editing the Node.js project.
Optional: Download tkn command line for easy command line interation with Tekton
Now that you’ve set up your environment, please note that IBM Cloud offers a free Kubernetes 1.17 cluster for one month for testing purposes. You will also receive a free IBM Cloud Image Registry with 512MB of storage and 5GB of pull traffic each month.
It should take you approximately 1 hour to provision the OpenShift / K8s cluster and to perform this tutorial.
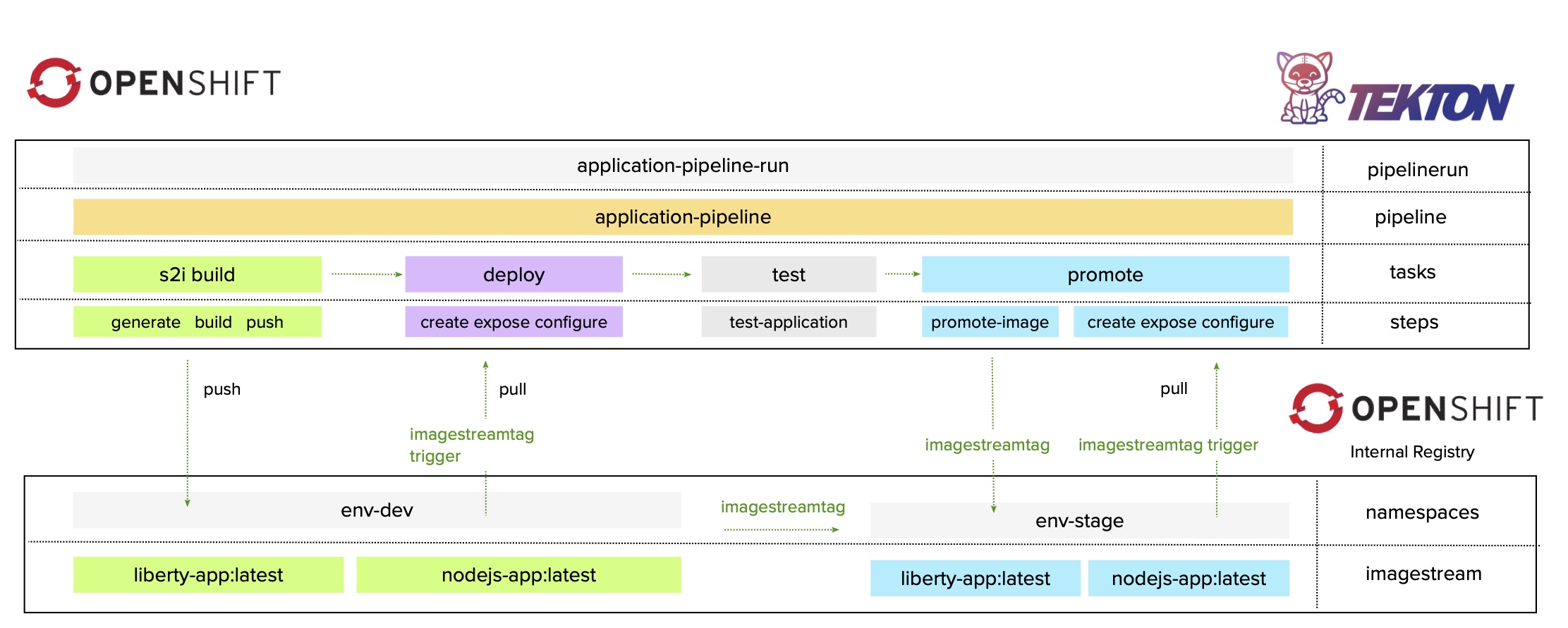
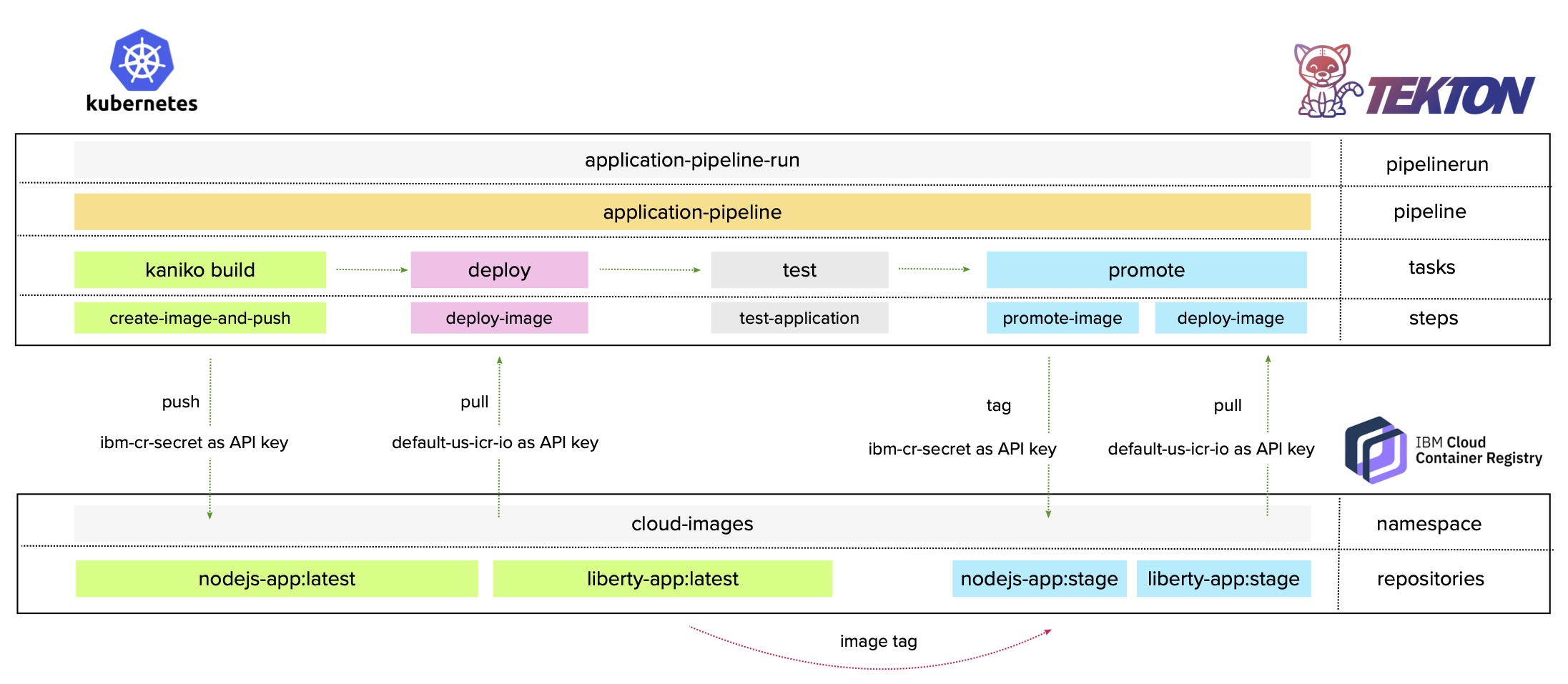
Before you get started, it’s important to understand how the application image is built. Using Tekton Pipelines involves building the application image inside the OpenShift/Kubernetes cluster. When using OpenShift, you use the standard S2I Build task and for Kubernetes you use the Kaniko Build task.
It’s also important to know what each Git folder contains:
-
nodejsis the context root of the Node.js application, based on Red Hat DO101 Demo application. -
tekton-openshiftcontains the OpenShift Pipeline implementation and YAML resources. -
tekton-kubernetescontains the Kubernetes Pipeline implementation and YAML resources. -
tekton-triggerscontains the Tekton Triggers implementation for creating a Git webhook to OpenShift/Kubernetes.
If you’d like to use Visual Studio Code to edit and run the Node.js application locally, you can. From the repo root folder run:
npm install .
node ./nodejs/bin/www/
curl http://localhost:8080/nodejs
OpenShift Pipelines is a cloud-native, continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) solution based on Kubernetes resources. It uses Tekton building blocks to automate deployments across multiple platforms by abstracting away the underlying implementation details. Tekton introduces a number of standard Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) for defining CI/CD pipelines that are portable across Kubernetes distributions.
More information can be found here: https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.4/pipelines/understanding-openshift-pipelines.html
- Install the OpenShift Pipelines Operator.
Follow the OpenShift documentation on how to install the OpenShift Pipelines Operator from either WebConsole or CLI:
After successful installation, you will have all related Tekton building blocks created in pipeline project.
- Create
env-ci,env-devandenv-stageprojects. Inenv-ci, you will store the CI/CD pipeline and all pipeline resources. Inenv-devandenv-stage, you will deploy the application through image promotion.
oc new-project env-ci
oc new-project env-dev
oc new-project env-stage
- Create ImageStream
nodejs-tektonfor storing the NodeJ.js image inenv-devandenv-stageprojects:
oc create is nodejs-tekton -n env-dev
oc create is nodejs-tekton -n env-stage
- Allow the
pipelineServiceAccount to make deploys on otherenv-devandenv-stageprojects:
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user privileged system:serviceaccount:env-ci:pipeline -n env-ci
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user privileged system:serviceaccount:env-ci:pipeline -n env-dev
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user privileged system:serviceaccount:env-ci:pipeline -n env-stage
oc adm policy add-role-to-user edit system:serviceaccount:env-ci:pipeline -n env-ci
oc adm policy add-role-to-user edit system:serviceaccount:env-ci:pipeline -n env-dev
oc adm policy add-role-to-user edit system:serviceaccount:env-ci:pipeline -n env-stage
- Clone the Git project:
git clone https://github.com/vladsancira/nodejs-tekton.git
cd nodejs-tekton
- Create Tekton resources, tasks, and a pipeline:
oc create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-openshift/resources.yaml -n env-ci
oc create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-openshift/task-build-s2i.yaml -n env-ci
oc create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-openshift/task-deploy.yaml -n env-ci
oc create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-openshift/task-test.yaml -n env-ci
oc create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-openshift/task-promote.yaml -n env-ci
oc create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-openshift/pipeline.yaml -n env-ci
- Create an application secret which will be mounted as an environment variable inside the Node.js pod:
oc create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-openshift/secrets.yaml -n env-dev
oc create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-openshift/secrets.yaml -n env-stage
- Execute the
Pipelineeither by usingtkncommand line or via OpenShift Pipelines UI :
tkn t ls -n env-ci
tkn p ls -n env-ci
tkn p start nodejs-pipeline -n env-ci
- List
PipelineRunfrom CI environment :
tkn pr ls -n env-ci
NAME STARTED DURATION STATUS
nodejs-pipeline-run-4fe564430272f1ea78cad 15 hours ago 2 minutes Succeeded
The Tekton Pipelines project provides k8s-style resources for declaring CI/CD-style pipelines.
More information can be found here : https://github.com/tektoncd/pipeline
- Clone the Git project:
git clone https://github.com/vladsancira/nodejs-tekton.git
cd nodejs-tekton
- Install Tekton Pipelines in the default
tekton-pipelinesnamespace:
kubectl apply --filename https://storage.googleapis.com/tekton-releases/pipeline/latest/release.yaml
kubectl get pods --namespace tekton-pipelines
- Create new
env-stage,env-devandenv-cinamespaces. Inenv-ci, you will store the CI/CD pipeline and all pipeline resources. Inenv-devandenv-stagenamespaces, you will deploy the application via image promotion.
kubectl create namespace env-stage
kubectl create namespace env-dev
kubectl create namespace env-ci
- Create an API key for the IBM Cloud Registry and export the PullImage secret from the
defaultnamespace. The API key is used for pushing images into the IBM Cloud Registry. When creating a Kubernetes cluster, an IBM Cloud Registry pull secret will be created in thedefaultnamespace (for all regions) that is used for pulling images from the IBM Cloud Registry.
ibmcloud iam api-key-create MyKey -d "this is my API key" --file key_file.json
cat key_file.json | grep apikey
kubectl create secret generic ibm-cr-secret -n env-ci --type="kubernetes.io/basic-auth" --from-literal=username=iamapikey --from-literal=password=<API_KEY>
kubectl annotate secret ibm-cr-secret -n env-ci tekton.dev/docker-0=us.icr.io
kubectl get secret default-us-icr-io --export -o yaml > default-us-icr-io.yaml
kubectl create -f default-us-icr-io.yaml -n env-dev
kubectl create -f default-us-icr-io.yaml -n env-stage
- Create a new ServiceAccount to enable the pipeline to run and deploy to
env-devnamespace. You will specify this ServiceAccount in the pipeline definition. Also, you will bind a custom Role to this ServiceAccount that will enable it to create, delete, or edit resources inenv-devandenv-stagenamespaces.
kubectl apply -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-kubernetes/service-account.yaml -n env-ci
kubectl apply -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-kubernetes/service-account-binding.yaml -n env-dev
kubectl apply -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-kubernetes/service-account-binding.yaml -n env-stage
- Create the Tekton
Resources,Task, andPipeline:
kubectl create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-kubernetes/resources.yaml -n env-ci
kubectl create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-kubernetes/task-build-kaniko.yaml -n env-ci
kubectl create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-kubernetes/task-deploy.yaml -n env-ci
kubectl create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-kubernetes/task-test.yaml -n env-ci
kubectl create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-kubernetes/task-promote.yaml -n env-ci
kubectl create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-kubernetes/pipeline.yaml -n env-ci
- Create an application
Secretwhich will be mounted as an environment variable inside the Node.js pod:
kubectl apply -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-kubernetes/secrets.yaml -n env-dev
kubectl apply -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-kubernetes/secrets.yaml -n env-stage
- Execute the pipeline via
PipelineRunviakubectlor viatkncommand:
kubectl create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-kubernetes/pipeline-run.yaml -n env-ci
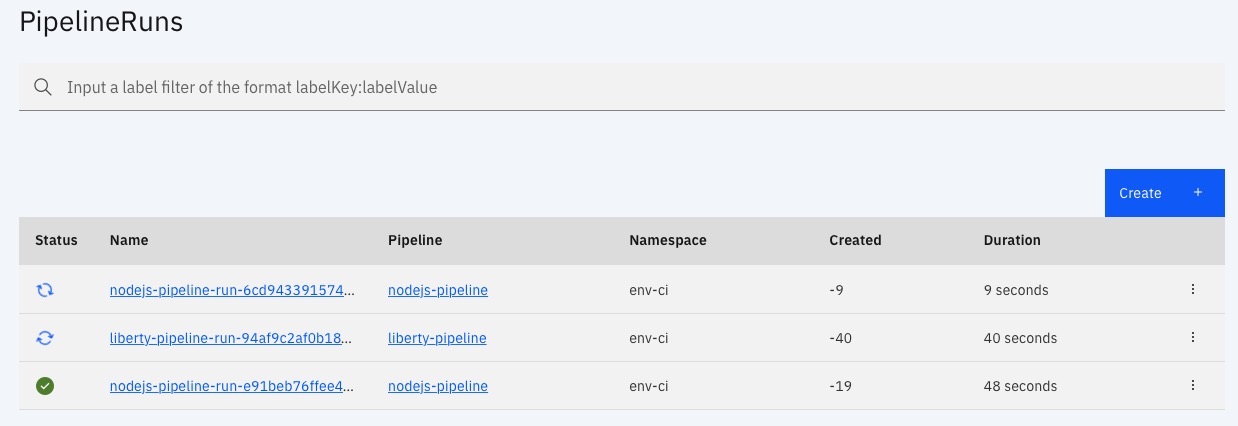
kubectl get pipelinerun -n env-ci
NAME SUCCEEDED REASON STARTTIME COMPLETIONTIME
nodejs-pipeline-run-4fe564430272f1e True Succeeded 15h 15h
tkn p start nodejs-pipeline -n env-ci
tkn pr ls -n env-ci
NAME STARTED DURATION STATUS
nodejs-pipeline-run-4fe564430272f1ea78 15 hours ago 2 minutes Succeeded
- Check the Node.JS application pods and logs from both environments:
kubectl get pods -n env-dev
kubectl get pods -n env-stage
kubectl logs nodejs-app-76fcdc6759-pjxs7 -f -n env-dev
- View the Node.JS application UI:
Retrieve the Kubernetes cluster EXTERNAL-IP using following command:
kubectl get nodes -o wide
Then open following URL in a Browser to view the Node.JS application UI :
- from
DEVenvironment:http://<EXTERNAL-IP>:32426/nodejs - from
STAGEenvironment:http://<EXTERNAL-IP>:32526/nodejs
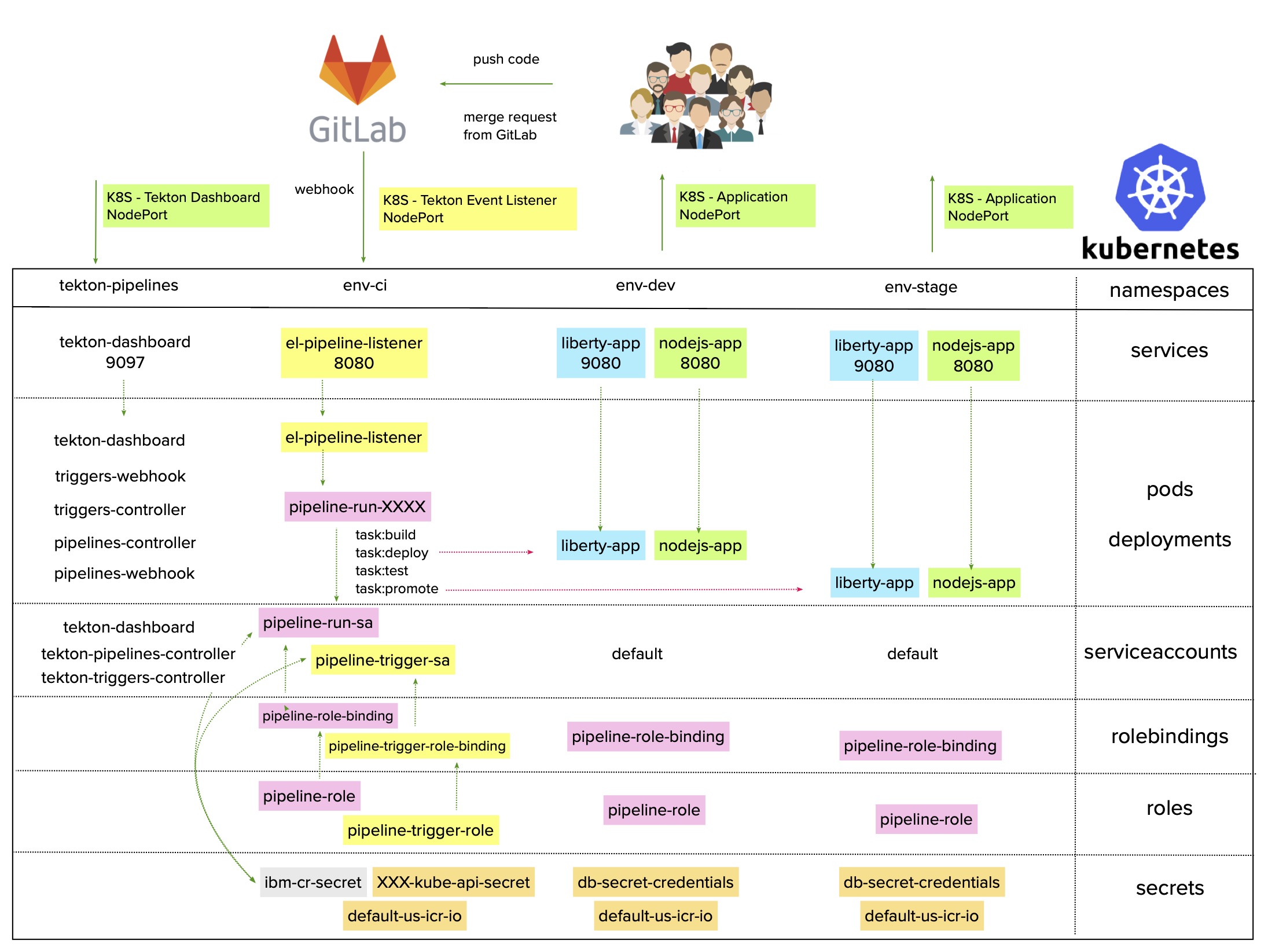
To create a webhook from Git to your Tekton Pipeline, you need to install Tekton Triggers in your Kubernetes cluster.
Tekton Triggers is a Kubernetes custom resource definition (CRD) controller that allows you to extract information from events payloads to create Kubernetes resources. Remember, you can use the Tekton Dashboard as a web console for viewing all your Tekton resources.
On OpenShift 4.3, Tekton Triggers is already installed as part of the OpenShift Pipelines Operator, in the openshift-pipelines project (namespace). However, the Tekton Dashboard is not. Instead, you can use the OpenShift Web Console.
The mechanism for triggering builds through webhooks is the same and involves creating an EventListener and exposing that EventListener Service to outside. The EventListener handles external events and receives a Git payload. This payload is parsed through the TriggerBinding resource for certain information, like gitrevision or gitrepositoryurl. These variables are then sent to the TriggerTemplate resource that calls the Tekton Pipeline via a PipelineRun definition (with optional arguments).
- Create
TriggerTemplate,TriggerBindingand EventListener pipelines:
oc create -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-triggers/webhook-event-listener-openshift.yaml -n env-ci
- Create a
Routefor theEventListenerservice:
oc expose svc/el-nodejs-pipeline-listener -n env-ci
oc get route -n env-ci
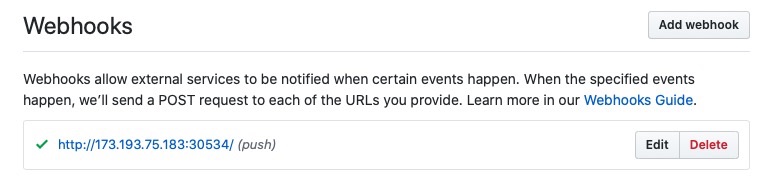
- Add the
Routeto Git webhook and then preform a push.
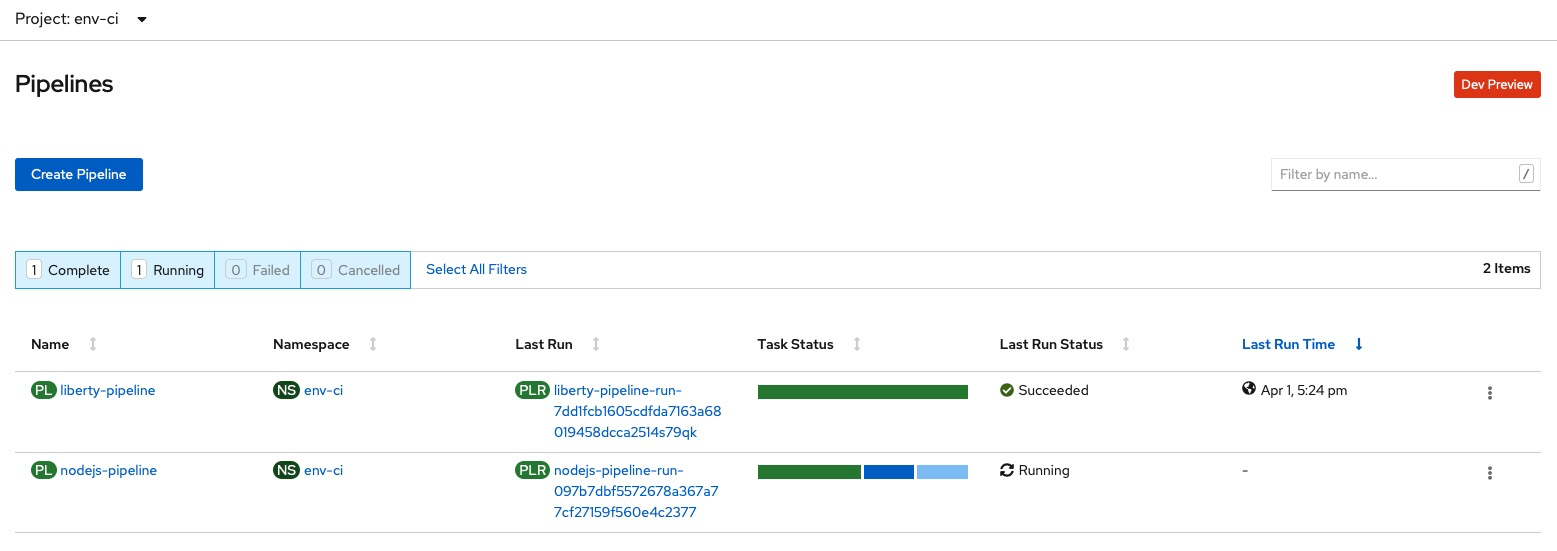
Finally, the new PipelineRun will be triggered automatically and visible in the pipelines console ci-env project.
- Install the Tekton Dashboard and Tekton Triggers:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/tektoncd/dashboard/releases/download/v0.6.1.2/tekton-dashboard-release.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://storage.googleapis.com/tekton-releases/triggers/latest/release.yaml
kubectl apply -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-triggers/tekton-dashboard.yaml -n tekton-pipelines
- Create a new
ServiceAccount,RoleandRoleBinding. In Kubernetes, this new ServiceAccount will be used for running theEventListenerand starting thePipelineRunvia theTriggerTemplate. The actual pipeline will still run as the ServiceAccount defined in it.
kubectl apply -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-triggers/webhook-service-account.yaml -n env-ci
- Create
TriggerTemplate,TriggerBindingand EventListener pipelines. By default, the EventListener service type is ClusterIP. However, you need to set it to NodePort so it can be triggered from outside the cluster.
kubectl apply -f ci-cd-pipeline/tekton-triggers/webhook-event-listener-kubernetes.yaml -n env-ci
- Retrieve
el-nodejs-pipeline-listenerPORT and cluster EXTERNAL-IP:
kubectl get svc el-nodejs-pipeline-listener -n env-ci
kubectl get nodes -o wide
- Add 'http://<EXTERNAL_IP>:<EVENT_LISTNER_PORT>' to GitHib as the webhook. Then perform a push.
- Open the Tekton dashboard,
http://<EXTERNAL-IP>:32428/#/pipelineruns, to make sure your changes were successful. Your output should look like the following:
Congratulations! You have successfully created a cloud-native CI/CD Tekton Pipeline for building and deploying a Node.js application in an OpenShift/Kubernetes cluster. If you’d like to continue using Tekton and Red Hat OpenShift, try another tutorial where you can learn how to Build a Tekton Pipeline to deploy a mobile app back end to OpenShift 4.