Matlab scripts synchronizing data from Enobio EEG device with SMR data from electrophys rig.
There are two scripts intended for regular use.
The 'esSync' script looks at an entire set of EEG data and its corresponding SMR export file, and computes an offset and scale factor to transform the EEG data into the time coords of the 1401 data. The result is a single mat file that is used later when EEG data is to be fetched.
The 'getEEGData' script uses the output from 'esSync' and fetches EEG data from specific time blocks. The time periods are specified in SMR time, and the script converts the SMR time to EEG time, and returns the data. A vector with corresponding time values (converted to SMR time) is also returned.
Background
The 1401 and the Enobio each operate with their own clocks. Since the 1401 is central to our experiments, and all behavior and stimulus-related events are recorded there, analysis will call for data from time periods defined in SMR time units.
During DAQ, the 1401 generates a stream of TTL pulses 1s apart. At the start of DAQ, there is a burst of 3 pulses much closer together - these are intended to identify an anchor point connecting the SMR and the EEG data streams. Once we can connect a specific pulse in each data stream, we can associate all the pulses by simply counting out from the base pulse.
The data are stored in a single folder. That folder will contain a set of EEG data files with extension *.easy, and a mat file exported from the SMR data file.
Algorithm
When designing the experiment, we had hoped that we could use the 3-pulse group to automatically synchronize the SMR and EEG data sets. In practice that cluster is visible to the eye in the EEG data, but not easily resolved when the EEG data is noisy (which is often). So, we abandon hope of automatically identifying the cluster, and intead ask the user to identify where that cluster is, and select the first or second individual pulse in the EEG data. This pulse, and the corresponding pulse in the SMR data, are assumed to be synchronized.
I assume that the clocks are close to synchronized, and that if they're off, any drift in one of the clocks is linear over time. The EEG and SMR data are fitted using a simple linear equation:
tSMR - tSMR,base = K * (tEEG - tEEG,base)
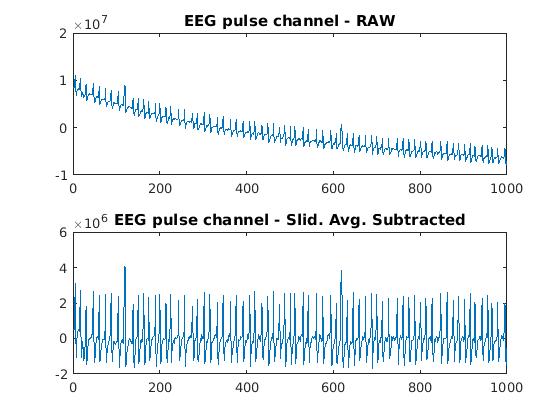
I apply a quick-and-dirty algorithm to locate pulses in the EEG data. First, a sliding average of the EEG data bins is subtracted from each value:
To identify pulses in the resulting data, I collect a list of bins whose value exceeds a given value. The first value used is the max of all bins in the file, and successively lower values are used. At each step, we collect all bins that rise above the threshold. I assume that each pulse will have adjacent bins that rise aboce threshold, so adjacent above-threshold bins are grouped and their average time value is used as the pulse center. Once the centers of all pulses are found for a given threshold level, they are tested for consistency with the assumption that they lie a multiple of 1ms from the base pulse identified by the user. (This is where the assumption that the EEG clock is nearly correct comes into play. The assumption is really that the drift in the relative speed of the EEG clock is such that it will not differ from the SMR clock by more than 1/2 of an EEG clock cycle over the time span of a single EEG data file. In practice this assumption is trivially correct since the EEG data files are approx 20s long.) Once we reach a threshold level where bins inconsistent with these requirements is encountered, the process stops and only the pulses identified at that point are used for this analysis.
Note that it is not critical that ALL pulses be identified. To a good first approximation the scale factor between the clocks is 1 (actually, its 0.001, because the SMR data in the mat file exported are converted to seconds, whereas the Enobio EEG data is marked with a time coordinate in milliseconds. Consequently, the position of the pulses in the sequence recorded in the EEG file can be identified with high confidence. Once a pulse is identified as a particular pulse, for example, the 10th pulse. The time value of the 10th pulse in the SMR data is known, and the value of K can be computed for that pulse. This computation is repeated for each pulse that is identified in the EEG file.
EEG Data
The eeg data is sampled at 500Hz, and each sample is timestamped with an integer clock value (ms). A single DAQ session with the EEG device yields a series of *.easy files, each corresponding to the series of acquisition and stimulation periods used in the NIC configuration. The files follow a naming scheme that looks like this:
<timestamp>_<EEGDatasetName><v2Txt>_Baseline_EEG_Trial_1.easy
<timestamp>_<EEGDatasetName><v2Txt>_Stim_Trial_1.easy
... 2, 3, ...
<timestamp>_<EEGDatasetName><v2Txt>_EEG_Trial_n.easy
<timestamp>_<EEGDatasetName><v2Txt>_Stim_Trial_n.easy
...
<timestamp>_<EEGDatasetName><v2Txt>_Baseline_EEG_End.easy
The "Stim" files above are recorded during stimulation, and during that period the pulses are not recorded (mystery to us, as the pulses are continuous throughout, but the Enobio doesn't register the pulses in these files). So, we're only interested in the "Baseline" files and each of the "EEG_Trial" files.
The easy files are loaded with getEasyFiles:
ezFiles = getEasyFiles(folder, v2Txt);
where
folder is the path to the folder containing the easy files
v2Txt is a string useful when data files have non-standard text in their names (apparently this is true for only one data set, all others follow the convention and this var can be an empty string)
The return value ezFiles is a cell array of filenames, in order, satisfying the filename pattern below. The patterns *<v2Txt>_Baseline_EEG_Trial_1.easy, *<v2Txt>_Baseline_EEG_End.easy, and *<v2Txt>_EEG_Trial_*.easy are used to identify the data files in the EEG data set. There should be only one such data set in the folder!
To run,
blob=esSync('./../data', 'Dr. Zaius_eeg_000_20180126.mat', '_v2'); [allIndices, allK] = esSyncTest(blob);
The struct returned in blob contains the following:
>> blob
blob =
struct with fields:
files: [1×81 struct]
K: 1.0000e-03
tSMRBase: 2.1554
tEEGBase: 1.5170e+12