This style guide is different from other you may see, because the focus is centered on readability for print and the web. We created this style guide to keep the code in our tutorials consistent.
Our overarching goals are conciseness, readability and simplicity.
You should also check out out Swift and Objective-C style guides too.
This style-guide is somewhat of a mash-up between the existing Java language style guides, and a tutorial-readability focused Swift style-guide. The language guidance is drawn from the Android contributors style guide and the Google Java Style Guide. Alterations to support additional readability in tutorials were inspired by the raywenderlich.com Swift style guide.
It is possible to get Android Studio to adhere to these style guidelines, via a rather complex sequence of menus. To make it easier, we've provided a coding style that can be imported into Android Studio.
Download auto1_code_style_guide.xml
and place it in ~/Library/Preferences/AndroidStudio1.2/codestyles.
NOTE: You need to update this location with the correct version of Android Studio.
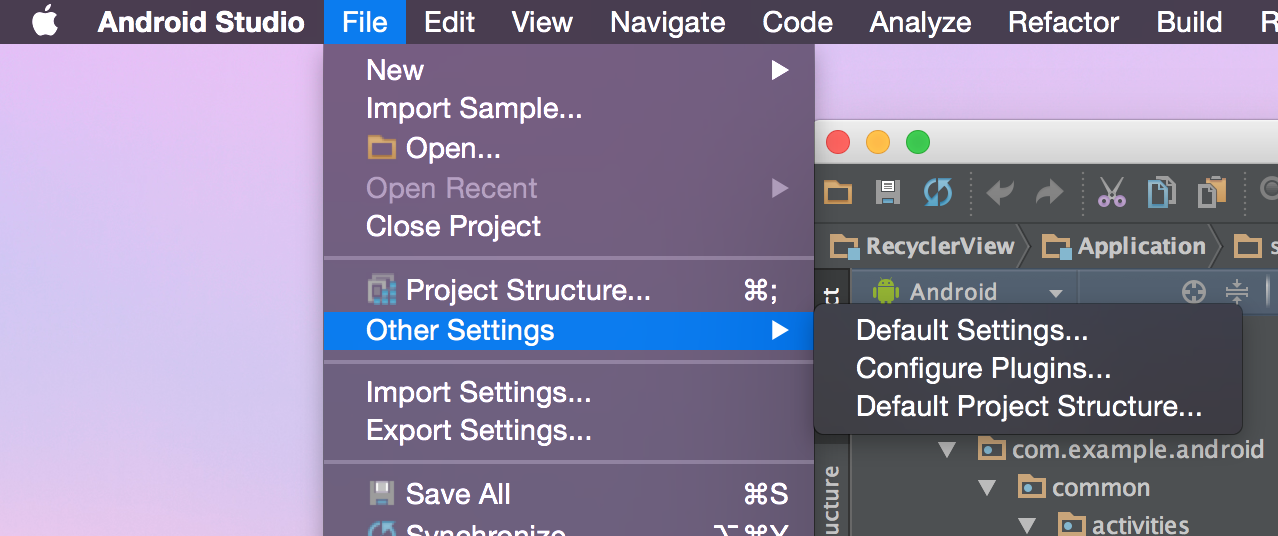
Then, open Android Studio. To set this codestyle as the default, select File > Other Settings > Default Settings...:
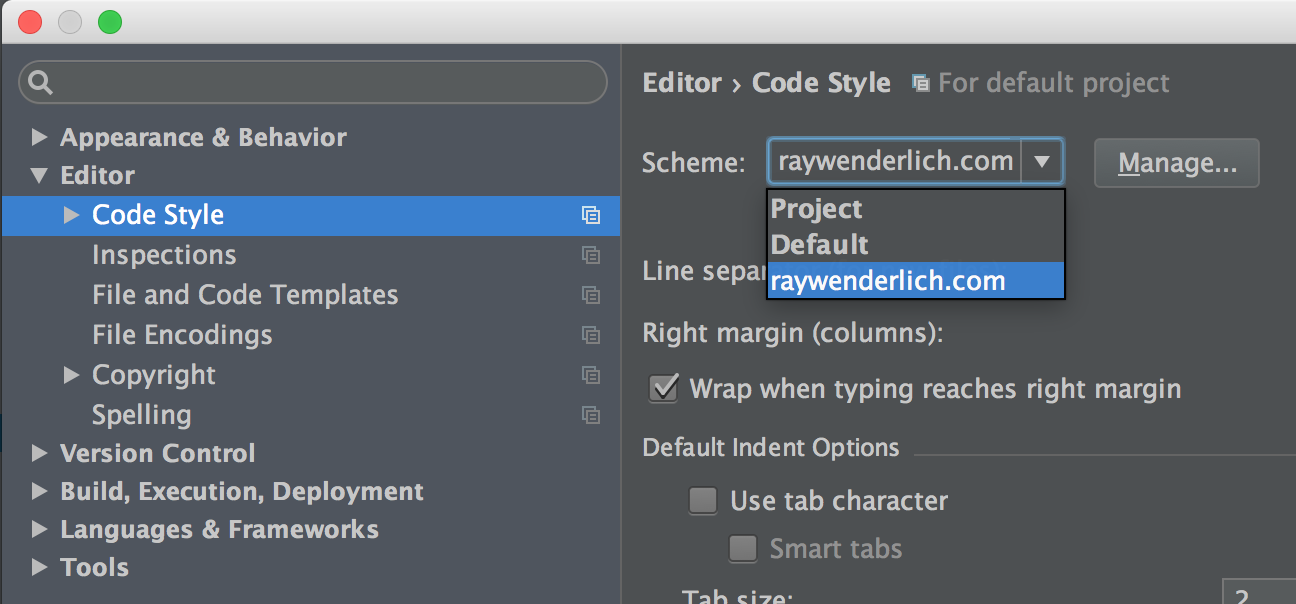
In Editor > Code Style, choose the Scheme to be raywenderlich.com:
From now on, projects you create should follow the correct style guidelines.
- Nomenclature
- Declarations
- Spacing
- Getters & Setters
- Brace Style
- Switch Statements
- Annotations
- XML Guidance
- Language
- Class Content
- Name Conventions
- Copyright Statement
- Smiley Face
- Credit
On the whole, naming should follow Java standards.
Package names are all lower-case, multiple words concatenated together, without hypens or underscores:
BAD:
com.RayWenderlich.funky_widgetGOOD:
com.raywenderlich.funkywidgetWritten in UpperCamelCase. For example RadialSlider.
Written in lowerCamelCase. For example setValue.
Written in lowerCamelCase.
Static fields should be written in uppercase, with an underscore separating words:
public static final int THE_ANSWER = 42;Written in lowerCamelCase.
Single character values to be avoided except for temporary looping variables. Don't use m prefix for class members.
In code, acronyms should be treated as words. For example:
BAD:
XMLHTTPRequest
String URL
findPostByIDGOOD:
XmlHttpRequest
String url
findPostByIdAccess level modifiers should be explicitly defined for classes, methods and member variables.
Prefer single declaration per line.
BAD:
String username, twitterHandle;GOOD:
String username;
String twitterHandle;Exactly one class per source file, although inner classes are encouraged where scoping appropriate.
Enum classes should be avoided where possible, due to a large memory overhead. Static constants are preferred. See http://developer.android.com/training/articles/memory.html#Overhead for further details.
Enum classes without methods may be formatted without line-breaks, as follows:
private enum CompassDirection { EAST, NORTH, WEST, SOUTH }Spacing is especially important in raywenderlich.com code, as code needs to be easily readable as part of the tutorial. Java does not lend itself well to this.
Indentation is using spaces - never tabs.
Indentation for blocks uses 4 spaces:
BAD:
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Log.i(TAG, "index=" + i);
}GOOD:
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Log.i(TAG, "index=" + i);
}Indentation for line wraps should use 4 spaces (not the default 8):
BAD:
CoolUiWidget widget =
someIncrediblyLongExpression(that, reallyWouldNotFit, on, aSingle, line);GOOD:
CoolUiWidget widget =
someIncrediblyLongExpression(that, reallyWouldNotFit, on, aSingle, line);Lines should be no longer than 100 characters long.
There should be exactly one blank line between methods to aid in visual clarity and organization. Whitespace within methods should separate functionality, but having too many sections in a method often means you should refactor into several methods.
For external access to fields in classes, getters and setters are preferred to
direct access of the fields. Fields should rarely be public.
However, it is encouraged to use the field directly when accessing internally (i.e. from inside the class). This is a performance optimization recommended by Google: http://developer.android.com/training/articles/perf-tips.html#GettersSetters
Only trailing closing-braces are awarded their own line. All others appear the same line as preceding code:
BAD:
class MyClass
{
void doSomething()
{
if (someTest)
{
// ...
}
else
{
// ...
}
}
}GOOD:
class MyClass {
void doSomething() {
if (someTest) {
// ...
} else {
// ...
}
}
}Conditional statements are always required to be enclosed with braces, irrespective of the number of lines required.
BAD:
if (someTest)
doSomething();
if (someTest) doSomethingElse();GOOD:
if (someTest) {
doSomething();
}
if (someTest) { doSomethingElse(); }Switch statements fall-through by default, but this can be unintuitive. If you require this behavior, comment it.
Alway include the default case.
BAD:
switch (anInput) {
case 1:
doSomethingForCaseOne();
case 2:
doSomethingForCaseOneOrTwo();
break;
case 3:
doSomethingForCaseOneOrThree();
break;
}GOOD:
switch (anInput) {
case 1:
doSomethingForCaseOne();
// fall through
case 2:
doSomethingForCaseOneOrTwo();
break;
case 3:
doSomethingForCaseOneOrThree();
break;
default:
break;
}Standard annotations should be used - in particular @Override. This should
appear the line before the function declaration.
BAD:
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
}GOOD:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
}Since Android uses XML extensively in addition to Java, we have some rules specific to XML.
View-based XML files should be prefixed with the type of view that they represent.
GOOD:
activity_login.xmlfragment_main_screen.xmlbutton_rounded_edges.xml
BAD:
login.xmlmain_screen.xmlrounded_edges_button.xml
Similarly to Java, indentation should be two characters.
Wherever possible XML resource files should be used:
- Strings =>
res/values/strings.xml - Styles =>
res/values/styles.xml - Colors =>
res/color/colors.xml - Animations =>
res/anim/ - Drawable =>
res/drawable
Where appropriate, XML attributes should appear in the following order:
idattributelayout_*attributes- style attributes such as
gravityortextColor - value attributes such as
textorsrc
Within each of these groups, the attributes should be ordered alphabetically.
Use US English spelling.
BAD:
String colour = "red";GOOD:
String color = "red";-
Max symbol's amount in one row - 100
-
Max raw's amount in one merhod - 40
-
Order of methods: If class contents android methods (lifecycle methods, listeners) it should be oredered first, then will be custom methods.
MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener { @Override public void onCreate() { } @Override public void onDestroy() { } @Override public void onClick(View view) { } private void showMonkey() { } }
layouts : component_name Example : activity_main, dialog_location, item_car
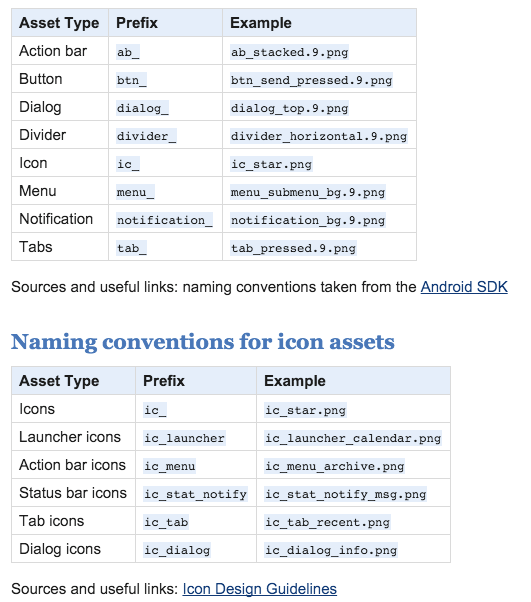
Naming conventions for drawables
File names must contain only lowercase a-z, 0-9, or _.
Drawables for the specific views (ListView, TextView, EditText, ProgressBar, CheckBox etc.) should be named like this views keeping the naming rules, e.g. drawable for CheckBox should be named "checkbox_on_bg.png".
The following copyright statement should be included at the top of every source file:
/*
* Copyright (c) 2015 Razeware LLC
*
* Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
* of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
* in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
* to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
* copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
* furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
*
* The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
* all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
*
* THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
* IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
* AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
* LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
* OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
* THE SOFTWARE.
*/
Smiley faces are a very prominent style feature of the raywenderlich.com site! It is very important to have the correct smile signifying the immense amount of happiness and excitement for the coding topic. The closing square bracket ] is used because it represents the largest smile able to be captured using ASCII art. A closing parenthesis ) creates a half-hearted smile, and thus is not preferred.
Bad:
:)
Good:
:]
This style guide is a collaborative effort from the most stylish raywenderlich.com team members: