This application is used to predict resistome(s) from protein or nucleotide data based on homology and SNP models. The application uses reference data from the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database (CARD).
RGI analyses can be performed via the CARD website RGI portal, via use of a Galaxy wrapper for the Galaxy platform, or alternatively you can Install RGI from Conda or Run RGI from Docker (see below). The instructions below discuss use of RGI at the command line, following a general overview of how RGI works for genomes, genome assemblies, proteomes, and metagenomic sequencing.
CARD reference sequences and significance cut-offs are under constant curation - as CARD curation evolves, the results of RGI evolve.
Contents
- The Resistance Gene Identifier (RGI)
- Overview of RGI
- Installation
- RGI Usage Documentation
If DNA sequences are submitted, RGI first predicts complete open reading frames (ORFs) using Prodigal (ignoring those less than 30 bp) and analyzes the predicted protein sequences. This includes a secondary correction by RGI if Prodigal undercalls the correct start codon to ensure complete AMR genes are predicted. However, if Prodigal fails to predict an AMR ORF, this will produce a false negative result.
Short contigs, small plasmids, low quality assemblies, or merged metagenomic reads should be analyzed using Prodigal's algorithms for low quality/coverage assemblies (i.e. contigs <20,000 bp) and inclusion of partial gene prediction. If the low sequence quality option is selected, RGI uses Prodigal anonymous mode for open reading frame prediction, supporting calls of partial AMR genes from short or low quality contigs.
If protein sequences are submitted, RGI skips ORF prediction and uses the protein sequences directly.
The RGI currently supports CARD's protein homolog models (use of BLASTP or DIAMOND bitscore cut-offs to detect functional homologs of AMR genes), protein variant models (for accurate differentiation between susceptible intrinsic genes and intrinsic genes that have acquired mutations conferring AMR, based on CARD's curated SNP matrices), rRNA mutation models (for detection of drug resistant rRNA target sequences), and protein over-expression models (which detect efflux subunits associated AMR, but also highlights mutations conferring over-expression when present).
| Example | AMR Gene |
|---|---|
| Protein Homolog Model | NDM-1 |
| Protein Variant Model | Acinetobacter baumannii gyrA conferring resistance to fluoroquinolones |
| rRNA Mutation Model | Campylobacter jejuni 23S rRNA with mutation conferring resistance to erythromycin |
| Protein Over-Expression Model | MexR |
The RGI analyzes genome or proteome sequences under three paradigms: Perfect, Strict, and Loose (a.k.a. Discovery). The Perfect algorithm is most often applied to clinical surveillance as it detects perfect matches to the curated reference sequences and mutations in the CARD. In contrast, the Strict algorithm detects previously unknown variants of known AMR genes, including secondary screen for key mutations, using detection models with CARD's curated similarity cut-offs to ensure the detected variant is likely a functional AMR gene. The Loose algorithm works outside of the detection model cut-offs to provide detection of new, emergent threats and more distant homologs of AMR genes, but will also catalog homologous sequences and spurious partial hits that may not have a role in AMR. Combined with phenotypic screening, the Loose algorithm allows researchers to hone in on new AMR genes.
By default, all Loose hits of 95% identity or better are automatically listed as Strict, regardless of alignment length (see --exclude_nudge).
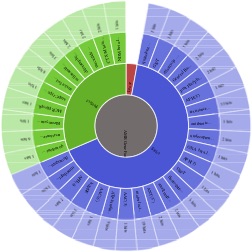
All results are organized via the Antibiotic Resistance Ontology classification: AMR Gene Family, Drug Class, and Resistance Mechanism. JSON files created at the command line can be Uploaded at the CARD Website for visualization.
Example visualization of Escherichia coli EC160090 (GenBank MCNL01)
Note on metagenomic assemblies or merged metagenomic reads: this is a computationally expensive approach, since each merged read or contig set may contain partial ORFs, requiring RGI to perform large amounts of BLAST/DIAMOND analyses against CARD reference proteins. While not generally recommended, this does allow analysis of metagenomic sequences in protein space, overcoming issues of high-stringency read mapping relative to nucleotide reference databases (see below).
RGI can align short DNA sequences in FASTQ format using Bowtie2 , BWA , and KMA against CARD's protein homolog models (support for SNP screening models will be added to future versions). FASTQ sequences can be aligned to the 'canonical' curated CARD reference sequences (i.e. sequences available in GenBank with clear experimental evidence of elevated MIC in a peer-reviewed journal available in PubMED) or additionally to the in silico predicted allelic variants available in CARD's Resistomes & Variants data set. The latter is highly recommended as the allelic diversity for AMR genes is greatly unrepresented in the published literature, hampering high-stringency read mapping (i.e. AMR genes are often only characterized for a single pathogen). Inclusion of CARD's Resistomes & Variants allows read mapping to predicted allelic variants and AMR gene homologs for a wide variety of pathogens, incorporation of CARD's Prevalence Data for easier interpretation of predicted AMR genes, and ultimately use of k-mer classifiers for prediction of pathogen-of-origin for FASTQ reads predicted to encode AMR genes (see below).
CARD's Resistomes & Variants and Prevalence Data (nicknamed WildCARD) were generated using the RGI to analyze molecular sequence data available in NCBI Genomes for pathogens of interest (see Sampling Table). For each of these pathogens, complete chromosome sequences, complete plasmid sequences, and whole genome shotgun (WGS) assemblies were analyzed individually by RGI. RGI results were then aggregated to calculate prevalence statistics for distribution of AMR genes among pathogens and plasmids, predicted resistomes, and to produce a catalog of predicted AMR alleles. These data were predicted under RGI's Perfect and Strict paradigms (see above), the former tracking perfect matches at the amino acid level to the curated reference sequences and mutations in the CARD, while the latter predicts previously unknown variants of known AMR genes, including secondary screen for key mutations. The reported results are entirely dependant upon the curated AMR detection models in CARD, the algorithms available in RGI, the pathogens sampled, and the sequence data available at NCBI at their time of generation.
CARD's Resistomes & Variants and Prevalence Data (see above) provides a data set of AMR alleles and their distribution among pathogens and plasmids. CARD's k-mer classifiers sub-sample these sequences to identify k-mers (default length 61 bp) that are uniquely found within AMR alleles of individual pathogen species, pathogen genera, pathogen-restricted plasmids, or promiscuous plasmids. CARD's k-mer classifiers can then be used to predict pathogen-of-origin for hits found by RGI for genomes, genome assemblies, metagenomic contigs, or metagenomic reads.
CARD's k-mer classifiers assume the data submitted for analysis has been predicted to encode AMR genes, via RGI or another AMR bioinformatic tool. The k-mer data set was generated from and is intended exclusively for AMR sequence space. As above, the reported results are entirely dependant upon the curated AMR detection models in CARD, the algorithms available in RGI, and the pathogens & sequences sampled during generation of CARD's Resistomes & Variants and Prevalence Data.
Use or reproduction of these materials, in whole or in part, by any commercial organization whether or not for non-commercial (including research) or commercial purposes is prohibited, except with written permission of McMaster University. Commercial uses are offered only pursuant to a written license and user fee. To obtain permission and begin the licensing process, see the CARD website.
Alcock et al. 2020. CARD 2020: antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 48, Issue D1, Pages D517-525 [PMID 31665441]
Please log an issue on github issue.
You can email the CARD curators or developers directly at [email protected], via Twitter at @arpcard.
Recommended installation method for most users is via conda or docker. This will handle dependency management and ensure installation of the correct version of RGI's external dependencies e.g., BLAST, DIAMOND.
Install conda on your system if not already available ().
Search for RGI package and show available versions:
$ conda search --channel bioconda --channel conda-forge --channel defaults rgi
Create a new conda environment
$ conda create --name rgi --channel bioconda --channel conda-forge --channel defaults rgi
Install RGI package:
$ conda install --channel bioconda --channel conda-forge --channel defaults rgi
Install RGI specific version:
$ conda install --channel bioconda --channel conda-forge --channel defaults rgi=5.1.1
Remove RGI package:
$ conda remove rgi
RGI is available via dockerhub or biocontainers full installed with all databases appropriately loaded.
Install docker on your system if not already available
Pull the Docker container from dockerhub (built from Dockerfile in repository) or biocontainers (built from conda package).
docker pull finlaymaguire/rgi:latest
Or
docker pull quay.io/biocontainers/rgi:5.1.1--py_0
RGI can be executed from the containers as follows:
docker run -v $PWD:/data finlaymaguire/rgi -hOr
docker run -v $PWD:/data quay.io/biocontainers/rgi:5.1.1--py_0 -h
The following conda command will install all RGI dependencies (listed below):
git clone https://github.com/arpcard/rgi
conda env create -f conda_env.yml
conda activate rgi- Python 3.6
- NCBI BLAST 2.9.0
- zlib
- Prodigal 2.6.3
- DIAMOND 0.8.36
- Biopython 1.78
- filetype 1.0.0+
- pytest 3.0.0+
- pandas 0.15.0+
- Matplotlib 2.1.2+
- seaborn 0.8.1+
- pyfaidx 0.5.4.1+
- pyahocorasick 1.1.7+
- OligoArrayAux 3.8
- samtools 1.9
- bamtools 2.5.1
- bedtools 2.27.1
- Jellyfish 2.2.10
- Bowtie2 2.3.4.3
- BWA 0.7.17 (r1188)
- KMA 1.3.4
pip install git+https://github.com/arpcard/rgi.gitor
python setup.py build
python setup.py test
python setup.py installcd tests
pytest -v -rxsThe following command will bring up RGI's main help menu:
rgi --help usage: rgi <command> [<args>]
commands are:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Database
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
auto_load Automatically loads CARD database, annotations and k-mer database
load Loads CARD database, annotations and k-mer database
clean Removes BLAST databases and temporary files
database Information on installed card database
galaxy Galaxy project wrapper
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Genomic
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
main Runs rgi application
tab Creates a Tab-delimited from rgi results
parser Creates categorical JSON files RGI wheel visualization
heatmap Heatmap for multiple analysis
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Metagenomic
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
bwt Align reads to CARD and in silico predicted allelic variants (beta)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Baits validation
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
tm Baits Melting Temperature
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Annotations
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
card_annotation Create fasta files with annotations from card.json
wildcard_annotation Create fasta files with annotations from variants
baits_annotation Create fasta files with annotations from baits (experimental)
remove_duplicates Removes duplicate sequences (experimental)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Pathogen of origin
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
kmer_build Build AMR specific k-mers database used for pathogen of origin (beta)
kmer_query Query sequences against AMR k-mers database to predict pathogen of origin (beta)
Resistance Gene Identifier - <version_number>
positional arguments:
command Subcommand to run
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Use the Resistance Gene Identifier to predict resistome(s) from protein or
nucleotide data based on homology and SNP models. Check
https://card.mcmaster.ca/download for software and data updates. Receive email
notification of monthly CARD updates via the CARD Mailing List
(https://mailman.mcmaster.ca/mailman/listinfo/card-l)Help screens for subcommands can be accessed using the -h argument, e.g.
rgi load -hRequired CARD Reference Data
To start analyses, first acquire the latest AMR reference data from CARD. CARD data can be installed at the system level or at the local level:
Obtain CARD data:
wget https://card.mcmaster.ca/latest/data tar -xvf data ./card.json
Local or working directory:
rgi load --card_json /path/to/card.json --local
System wide:
rgi load --card_json /path/to/card.json
Additional Reference Data for Metagenomics Analyses
Metagenomics analyses may additionally require CARD's Resistomes & Variants data, which can also be installed at the system level or at the local level once the CARD data has been loaded.
Additional CARD data pre-processing for metagenomics using a local or working directory (note that the filename card_database_v3.0.1.fasta depends on the version of CARD data downloaded, please adjust accordingly):
rgi card_annotation -i /path/to/card.json > card_annotation.log 2>&1 rgi load -i /path/to/card.json --card_annotation card_database_v3.0.1.fasta --local
System wide additional CARD data pre-processing for metagenomics (note that the filename card_database_v3.0.1.fasta depends on the version of CARD data downloaded, please adjust accordingly):
rgi card_annotation -i /path/to/card.json > card_annotation.log 2>&1 rgi load -i /path/to/card.json --card_annotation card_database_v3.0.1.fasta
Obtain WildCARD data:
wget -O wildcard_data.tar.bz2 https://card.mcmaster.ca/latest/variants mkdir -p wildcard tar -xjf wildcard_data.tar.bz2 -C wildcard gunzip wildcard/*.gz
Local or working directory (note that the filenames wildcard_database_v3.0.2.fasta and card_database_v3.0.1.fasta depend on the version of CARD data downloaded, please adjust accordingly):
rgi wildcard_annotation -i wildcard --card_json /path/to/card.json \ -v version_number > wildcard_annotation.log 2>&1 rgi load --wildcard_annotation wildcard_database_v3.0.2.fasta \ --wildcard_index /path/to/wildcard/index-for-model-sequences.txt \ --card_annotation card_database_v3.0.1.fasta --local
System wide (note that the filenames wildcard_database_v3.0.2.fasta and card_database_v3.0.1.fasta depend on the version of CARD data downloaded, please adjust accordingly):
rgi wildcard_annotation -i wildcard --card_json /path/to/card.json \ -v version_number > wildcard_annotation.log 2>&1 rgi load --wildcard_annotation wildcard_database_v3.0.2.fasta \ --wildcard_index /path/to/wildcard/index-for-model-sequences.txt \ --card_annotation card_database_v3.0.1.fasta
Additional Reference Data for K-mer Pathogen-of-Origin Analyses
Complete all the above steps for Required CARD Reference Data and Additional Reference Data for Metagenomics Analyses, then load the k-mer reference data:
Local or working directory (example uses the pre-compiled 61 bp k-mers):
rgi load --kmer_database /path/to/wildcard/61_kmer_db.json \ --amr_kmers /path/to/wildcard/all_amr_61mers.txt --kmer_size 61 \ --local --debug > kmer_load.61.log 2>&1
System wide (example uses the pre-compiled 61 bp k-mers):
rgi load --kmer_database /path/to/wildcard/61_kmer_db.json \ --amr_kmers /path/to/wildcard/all_amr_61mers.txt --kmer_size 61 \ --debug > kmer_load.61.log 2>&1
Local or working directory:
rgi database --version --local
System wide :
rgi database --version
Local or working directory:
rgi clean --local
System wide:
rgi clean
rgi main -husage: rgi main [-h] -i INPUT_SEQUENCE -o OUTPUT_FILE [-t {contig,protein}]
[-a {DIAMOND,BLAST}] [-n THREADS] [--include_loose] [--local]
[--clean] [--debug] [--low_quality]
[-d {wgs,plasmid,chromosome,NA}] [-v] [--split_prodigal_jobs]
Resistance Gene Identifier - 4.2.2 - Main
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INPUT_SEQUENCE, --input_sequence INPUT_SEQUENCE
input file must be in either FASTA (contig and
protein) or gzip format! e.g myFile.fasta,
myFasta.fasta.gz
-o OUTPUT_FILE, --output_file OUTPUT_FILE
output folder and base filename
-t {contig,protein}, --input_type {contig,protein}
specify data input type (default = contig)
-a {DIAMOND,BLAST}, --alignment_tool {DIAMOND,BLAST}
specify alignment tool (default = BLAST)
-n THREADS, --num_threads THREADS
number of threads (CPUs) to use in the BLAST search
(default=32)
--include_loose include loose hits in addition to strict and perfect
hits
--exclude_nudge exclude hits nudged from loose to strict hits
--local use local database (default: uses database in
executable directory)
--clean removes temporary files
--debug debug mode
--low_quality use for short contigs to predict partial genes
-d {wgs,plasmid,chromosome,NA}, --data {wgs,plasmid,chromosome,NA}
specify a data-type (default = NA)
-v, --version prints software version number
--split_prodigal_jobs
run multiple prodigal jobs simultaneously for contigs
in a fasta fileBy default, all Loose RGI hits of 95% identity or better are automatically listed as Strict, regardless of alignment length, unless the --exclude_nudge flag is used.
You must Load CARD Reference Data for these commands to work. These examples use a local database, exclude "--local" flag to use a system wide reference database.
Generate Perfect or Strict hits for a genome assembly or genome sequence:
rgi main --input_sequence /path/to/nucleotide_input.fasta \ --output_file /path/to/output_file --input_type contig --local --clean
Include Loose hits:
rgi main --input_sequence /path/to/nucleotide_input.fasta \ --output_file /path/to/output_file --input_type contig --local \ --include_loose --clean
Include Loose hits, but not nudging Loose hits of 95% identity or better to Strict:
rgi main --input_sequence /path/to/nucleotide_input.fasta \ --output_file /path/to/output_file --input_type contig --local \ --include_loose --exclude_nudge --clean
Short or low quality contigs with partial gene prediction, including Loose hits:
rgi main --input_sequence /path/to/nucleotide_input.fasta \ --output_file /path/to/output_file --input_type contig --local \ --low_quality --include_loose --clean
Short or low quality contigs with partial gene prediction, including Loose hits, but not nudging Loose hits of 95% identity or better to Strict:
rgi main --input_sequence /path/to/nucleotide_input.fasta \ --output_file /path/to/output_file --input_type contig --local \ --low_quality --include_loose --exclude_nudge --clean
High-performance (e.g. 40 processors) generation of Perfect and Strict hits for high quality genome assembly contigs:
rgi main --input_sequence /path/to/nucleotide_input.fasta \ --output_file /path/to/output_file --input_type contig --local \ --alignment_tool DIAMOND --num_threads 40 --split_prodigal_jobs --clean
You must Load CARD Reference Data for these commands to work. These examples use a local database, exclude "--local" flag to use a system wide reference database.
Generate Perfect or Strict hits for a set of protein sequences:
rgi main --input_sequence /path/to/protein_input.fasta \ --output_file /path/to/output_file --input_type protein --local --clean
Include Loose hits:
rgi main --input_sequence /path/to/protein_input.fasta \ --output_file /path/to/output_file --input_type protein --local \ --include_loose --clean
Include Loose hits, but not nudging Loose hits of 95% identity or better to Strict:
rgi main --input_sequence /path/to/protein_input.fasta \ --output_file /path/to/output_file --input_type protein --local \ --include_loose --exclude_nudge --clean
High-performance (e.g. 40 processors) generation of Perfect and Strict hits:
rgi main --input_sequence /path/to/protein_input.fasta \ --output_file /path/to/output_file --input_type protein --local \ --alignment_tool DIAMOND --num_threads 40 --clean
System wide and writing log files for each input file. Note: add code below to script.sh then run with ./script.sh /path/to/input_files.
#!/bin/bash DIR=`find . -mindepth 1 -type d` for D in $DIR; do NAME=$(basename $D); parallel --no-notice --progress -j+0 'rgi main -i {} -o {.} -n 16 -a diamond --clean --debug > {.}.log 2>&1' ::: $NAME/*.{fa,fasta}; done
| Field | Contents |
|---|---|
| ORF_ID | Open Reading Frame identifier (internal to RGI) |
| Contig | Source Sequence |
| Start | Start co-ordinate of ORF |
| Stop | End co-ordinate of ORF |
| Orientation | Strand of ORF |
| Cut_Off | RGI Detection Paradigm (Perfect, Strict, Loose) |
| Pass_Bitscore | Strict detection model bitscore cut-off |
| Best_Hit_Bitscore | Bitscore value of match to top hit in CARD |
| Best_Hit_ARO | ARO term of top hit in CARD |
| Best_Identities | Percent identity of match to top hit in CARD |
| ARO | ARO accession of match to top hit in CARD |
| Model_type | CARD detection model type |
| SNPs_in_Best_Hit_ARO | Mutations observed in the ARO term of top hit in CARD (if applicable) |
| Other_SNPs | Mutations observed in ARO terms of other hits indicated by model id (if applicable) |
| Drug Class | ARO Categorization |
| Resistance Mechanism | ARO Categorization |
| AMR Gene Family | ARO Categorization |
| Predicted_DNA | ORF predicted nucleotide sequence |
| Predicted_Protein | ORF predicted protein sequence |
| CARD_Protein_Sequence | Protein sequence of top hit in CARD |
| Percentage Length of Reference Sequence | (length of ORF protein / length of CARD reference protein) |
| ID | HSP identifier (internal to RGI) |
| Model_id | CARD detection model id |
| Nudged | TRUE = Hit nudged from Loose to Strict |
| Note | Reason for nudge or other notes |
rgi heatmap -husage: rgi heatmap [-h] -i INPUT
[-cat {drug_class,resistance_mechanism,gene_family}] [-f]
[-o OUTPUT] [-clus {samples,genes,both}]
[-d {plain,fill,text}] [--debug]
Creates a heatmap when given multiple RGI results.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INPUT, --input INPUT
Directory containing the RGI .json files (REQUIRED)
-cat {drug_class,resistance_mechanism,gene_family}, --category {drug_class,resistance_mechanism,gene_family}
The option to organize resistance genes based on a
category.
-f, --frequency Represent samples based on resistance profile.
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
Name for the output EPS and PNG files. The number of
files run will automatically be appended to the end of
the file name. (default=RGI_heatmap)
-clus {samples,genes,both}, --cluster {samples,genes,both}
Option to use SciPy's hiearchical clustering algorithm
to cluster rows (AMR genes) or columns (samples).
-d {plain,fill,text}, --display {plain,fill,text}
Specify display options for categories
(deafult=plain).
--debug debug modeRGI heatmap produces EPS and PNG image files. An example where rows are organized by AMR Gene Family and columns clustered by similarity of resistome is shown above.
Generate a heat map from pre-compiled RGI main JSON files, samples and AMR genes organized alphabetically:
rgi heatmap --input /path/to/rgi_results_json_files_directory/ \ --output /path/to/output_file
Generate a heat map from pre-compiled RGI main JSON files, samples clustered by similarity of resistome and AMR genes organized by AMR gene family:
rgi heatmap --input /path/to/rgi_results_json_files_directory/ \ --output /path/to/output_file -cat gene_family -clus samples
Generate a heat map from pre-compiled RGI main JSON files, samples clustered by similarity of resistome and AMR genes organized by Drug Class:
rgi heatmap --input /path/to/rgi_results_json_files_directory/ \ --output /path/to/output_file -cat drug_class -clus samples
Generate a heat map from pre-compiled RGI main JSON files, samples clustered by similarity of resistome and AMR genes organized by distribution among samples:
rgi heatmap --input /path/to/rgi_results_json_files_directory/ \ --output /path/to/output_file -clus both
Generate a heat map from pre-compiled RGI main JSON files, samples clustered by similarity of resistome (with histogram used for abundance of identical resistomes) and AMR genes organized by distribution among samples:
rgi heatmap --input /path/to/rgi_results_json_files_directory/ \ --output /path/to/output_file -clus both -f
This is an unpublished algorithm undergoing beta-testing.
rgi bwt -husage: rgi bwt [-h] -1 READ_ONE [-2 READ_TWO] [-a {bowtie2,bwa}] [-n THREADS]
-o OUTPUT_FILE [--debug] [--local] [--include_wildcard]
[--include_baits] [--mapq MAPQ] [--mapped MAPPED]
[--coverage COVERAGE]
Aligns metagenomic reads to CARD and wildCARD reference using bowtie or bwa
and provide reports.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-1 READ_ONE, --read_one READ_ONE
raw read one (qc and trimmied)
-2 READ_TWO, --read_two READ_TWO
raw read two (qc and trimmied)
-a {bowtie2,bwa,kma}, --aligner {bowtie2,bwa,kma}
aligner
-n THREADS, --threads THREADS
number of threads (CPUs) to use (default=32)
-o OUTPUT_FILE, --output_file OUTPUT_FILE
name of output filename(s)
--debug debug mode
--clean removes temporary files
--local use local database (default: uses database in
executable directory)
--include_wildcard include wildcard
--include_baits include baits
--mapq MAPQ filter reads based on MAPQ score
--mapped MAPPED filter reads based on mapped reads
--coverage COVERAGE filter reads based on coverage of reference sequenceNote: the mapq, mapped, and coverage filters are planned features and do not yet work (but values are reported for manual filtering). Support for AMR bait capture methods (--include_baits) is forthcoming.
BWA usage within RGI bwt:
bwa mem -M -t {threads} {index_directory} {read_one} > {output_sam_file}
Bowtie2 usage within RGI bwt:
bowtie2 --very-sensitive-local --threads {threads} -x {index_directory} \ -U {unpaired_reads} -S {output_sam_file}
You must Load CARD Reference Data for these commands to work. These examples use a local database, exclude "--local" flag to use a system wide reference database.
RGI will take FASTQ files as provided, be sure to include linker and quality trimming, plus sorting or any other needed pre-processing prior to using RGI.
Align forward and reverse FASTQ reads using Bowtie2 using 8 processors against 'canonical' CARD only:
rgi bwt --read_one /path/to/fastq/R1.fastq.gz \ --read_two /path/to/fastq/R2.fastq.gz --aligner bowtie2 \ --output_file output_prefix --threads 8 --local
Align forward and reverse FASTQ reads using Bowtie2 using 8 processors against 'canonical' CARD plus CARD's Resistomes & Variants:
rgi bwt --read_one /path/to/fastq/R1.fastq.gz \ --read_two /path/to/fastq/R2.fastq.gz --aligner bowtie2 \ --output_file output_prefix --threads 8 --include_wildcard --local
RGI bwt aligns FASTQ reads to the AMR alleles used as reference sequences, with results provided for allele mapping and summarized at the AMR gene level (i.e. summing allele level results by gene). Five tab-delimited files are produced:
| File | Contents |
|---|---|
| output_prefix.allele_mapping_data.txt | RGI bwt read mapping results at allele level |
| output_prefix.gene_mapping_data.txt | RGI bwt read mapping results at gene level |
| output_prefix.artifacts_mapping_stats.txt | Statistics for read mapping artifacts |
| output_prefix.overall_mapping_stats.txt | Statistics for overall read mapping results |
| output_prefix.reference_mapping_stats.txt | Statistics for reference matches |
| Field | Contents |
|---|---|
| Reference Sequence | Reference allele to which reads have been mapped |
| ARO Term | ARO Term |
| ARO Accession | ARO Accession |
| Reference Model Type | CARD detection model type |
| Reference DB | Reference allele is from either CARD or WildCARD |
| Reference Allele Source | See below |
| Resistomes & Variants: Observed in Genome(s) | Has this allele sequence been observed in a CARD Prevalence genome sequence? |
| Resistomes & Variants: Observed in Plasmid(s) | Has this allele sequence been observed in a CARD Prevalence plasmid sequence? |
| Resistomes & Variants: Observed Pathogen(s) | CARD Prevalence pathogens bearing this allele sequence. If Reference DB is CARD, pathogen used as the reference in the CARD detection model will be shown. Use k-mers to verify pathogen-of-origin. |
| Completely Mapped Reads | Number of reads mapped completely to allele |
| Mapped Reads with Flanking Sequence | Number of reads mapped incompletely to allele |
| All Mapped Reads | Sum of previous two columns |
| Percent Coverage | Percent of reference allele covered by reads |
| Length Coverage (bp) | Base pairs of reference allele covered by reads |
| Average MAPQ (Completely Mapped Reads) | Average MAPQ value |
| Mate Pair Linkage | For mate pair sequencing, if a sister read maps to a different AMR gene, this is listed |
| Reference Length | Length (bp) of reference allele |
| AMR Gene Family | ARO Categorization |
| Drug Class | ARO Categorization |
| Resistance Mechanism | ARO Categorization |
| Depth | Depth of coverage (reported only when using kma) |
| SNPs | Single nucleotide polymorphisms observed from mapped reads (reported only when using kma) |
| Consensus Sequence DNA | Nucleotide Consensus Sequence using mapped reads (reported only when using kma) |
| Consensus Sequence Protein | Protein Consensus Sequence translated from DNA (reported only when using kma) |
Reference Allele Source:
Entries with CARD Curation are aligned to a reference allele from a published, characterized AMR gene, i.e. 'canonical CARD', and thus encode a 100% match to the reference protein sequence. Otherwise, entries will be reported as in silico allele predictions based on either Perfect or Strict RGI hits in CARD's Resistomes & Variants, with percent identity to the CARD reference protein reported. Hits with low values should be used with caution, as CARD's Resistomes & Variants has predicted a low identity AMR homolog.
| Field | Contents |
|---|---|
| ARO Term | ARO Term |
| ARO Accession | ARO Accession |
| Reference Model Type | CARD detection model type |
| Reference DB | Reference allele(s) are from CARD and/or WildCARD |
| Alleles with Mapped Reads | # of alleles for this AMR gene with mapped reads |
| Reference Allele(s) Identity to CARD Reference Protein | See below |
| Resistomes & Variants: Observed in Genome(s) | Have these allele sequences been observed in a CARD Prevalence genome sequence? |
| Resistomes & Variants: Observed in Plasmid(s) | Have these allele sequences been observed in a CARD Prevalence plasmid sequence? |
| Resistomes & Variants: Observed Pathogen(s) | CARD Prevalence pathogens bearing this allele sequence. If Reference DB is CARD, pathogen used as the reference in the CARD detection model will be shown. Use k-mers to verify pathogen-of-origin. |
| Completely Mapped Reads | Number of reads mapped completely to these alleles |
| Mapped Reads with Flanking Sequence | Number of reads mapped incompletely to these alleles |
| All Mapped Reads | Sum of previous two columns |
| Average Percent Coverage | Average % of reference allele(s) covered by reads |
| Average Length Coverage (bp) | Average bp of reference allele(s) covered by reads |
| Average MAPQ (Completely Mapped Reads) | Statistics for reference matches |
| Number of Mapped Baits | not yet supported |
| Number of Mapped Baits with Reads | not yet supported |
| Average Number of reads per Bait | not yet supported |
| Number of reads per Bait Coefficient of Variation (%) | not yet supported |
| Number of reads mapping to baits and mapping to complete gene | not yet supported |
| Number of reads mapping to baits and mapping to complete gene (%) | not yet supported |
| Mate Pair Linkage (# reads) | For mate pair sequencing, if a sister read maps to a different AMR gene, this is listed (# reads supporting linkage in parentheses) |
| Reference Length | Length (bp) of reference sequences |
| AMR Gene Family | ARO Categorization |
| Drug Class | ARO Categorization |
| Resistance Mechanism | ARO Categorization |
Reference Allele(s) Identity to CARD Reference Protein:
Gives range of Reference Allele Source values reported in the RGI bwt read mapping results at allele level, indicating the range of percent identity at the amino acid level of the encoded proteins to the corresponding CARD reference sequence. Hits with low values should be used with caution, as CARD's Resistomes & Variants has predicted a low identity AMR homolog.
Order of operations
## Running jobs on computecanada using serial farm method
- `rgi bwt` was used as example.
### step 1:
- update make_table_dat.sh to construct arguments for commands
### step 2:
- update eval command in job_script.sh to match your tool and also load appropriate modules
### step 3:
- create table.dat using script make_table_dat.sh with inputs files in all_samples directory
./make_table_dat.sh ./all_samples/ > table.dat
### step 4:
- submit multiple jobs using for_loop.sh
### Resource:
- https://docs.computecanada.ca/wiki/Running_jobs#Serial_jobUpdate the make_table_dat.sh
DIR=`find . -mindepth 1 -type d`
for D in $DIR; do
directory=$(basename $D);
for file in $directory/*; do
filename=$(basename $file);
if [[ $filename = *"_pass_1.fastq.gz"* ]]; then
read1=$(basename $filename);
base=(${read1//_pass_1.fastq.gz/ });
#echo "--read_one $(pwd)/$directory/${base}_pass_1.fastq.gz --read_two $(pwd)/$directory/${base}_pass_2.fastq.gz -o $(pwd)/$directory/${base} -n 16 --aligner bowtie2 --debug"
echo "--read_one $(pwd)/$directory/${base}_pass_1.fastq.gz --read_two $(pwd)/$directory/${base}_pass_2.fastq.gz -o $(pwd)/$directory/${base}_wild -n 8 --aligner bowtie2 --debug --include_wildcard"
fi
done
doneThis block of code is used to generate the arguments for serial farming. In this example, rgi bwt is used, however depending on the job you are running you may update it according to your specifications.
Update the job_script.sh to match used tool
#SBATCH --account=def-mcarthur
#SBATCH --time=120
#SBATCH --job-name=rgi_bwt
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=8
#SBATCH --mem-per-cpu=2048M
#SBATCH [email protected]
#SBATCH --mail-type=ALL
# Extracing the $I_FOR-th line from file $TABLE:
LINE=`sed -n ${I_FOR}p "$TABLE"`
# Echoing the command (optional), with the case number prepended:
#echo "$I_FOR; $LINE"
# load modules
module load nixpkgs/16.09 python/3.6.3 gcc/5.4.0 blast+/2.6.0 prodigal diamond/0.8.36 bowtie2 samtools bamtools bedtools bwa
# execute command
#eval "$LINE"
#echo "rgi bwt $LINE"
eval "rgi bwt $LINE"Update this block of code according to which tool you want to use. In this example, rgi bwt is shown, however for your use-case, you may update it accordingly.
Creating the table.dat
To create the table.dat, use the script made before named make_table_dat.sh along with the path to the directory containing all your inputs as an argument. Output to table.dat.
./make_table_dat.sh ./all_samples/ > table.datSubmit multiple jobs using for_loop.sh
This script is used once all the previous steps are completed. This script allows you to submit multiple jobs into Compute Canada for rgi.
# Simplest case - using for loop to submit a serial farm
# The input file table.dat contains individual cases - one case per line
export TABLE=table.dat
# Total number of cases (= number of jobs to submit):
N_cases=$(cat "$TABLE" | wc -l)
# Submitting one job per case using the for loop:
for ((i=1; i<=$N_cases; i++))
do
# Using environment variable I_FOR to communicate the case number to individual jobs:
export I_FOR=$i
sbatch job_script.sh
doneResources
More information on serial farming on Compute Canada can be found here.
This is an unpublished algorithm undergoing beta-testing.
You must Load CARD Reference Data for these commands to work. These examples use a local database, exclude "--local" flag to use a system wide reference database. Examples also use the pre-compiled 61 bp k-mers available at the CARD website's Resistomes & Variants download.
As outlined above, CARD's Resistomes & Variants and Prevalence Data provide a data set of AMR alleles and their distribution among pathogens and plasmids. CARD's k-mer classifiers sub-sample these sequences to identify k-mers that are uniquely found within AMR alleles of individual pathogen species, pathogen genera, pathogen-restricted plasmids, or promiscuous plasmids. The default k-mer length is 61 bp (based on unpublished analyses), available as downloadable, pre-compiled k-mer sets at the CARD website.
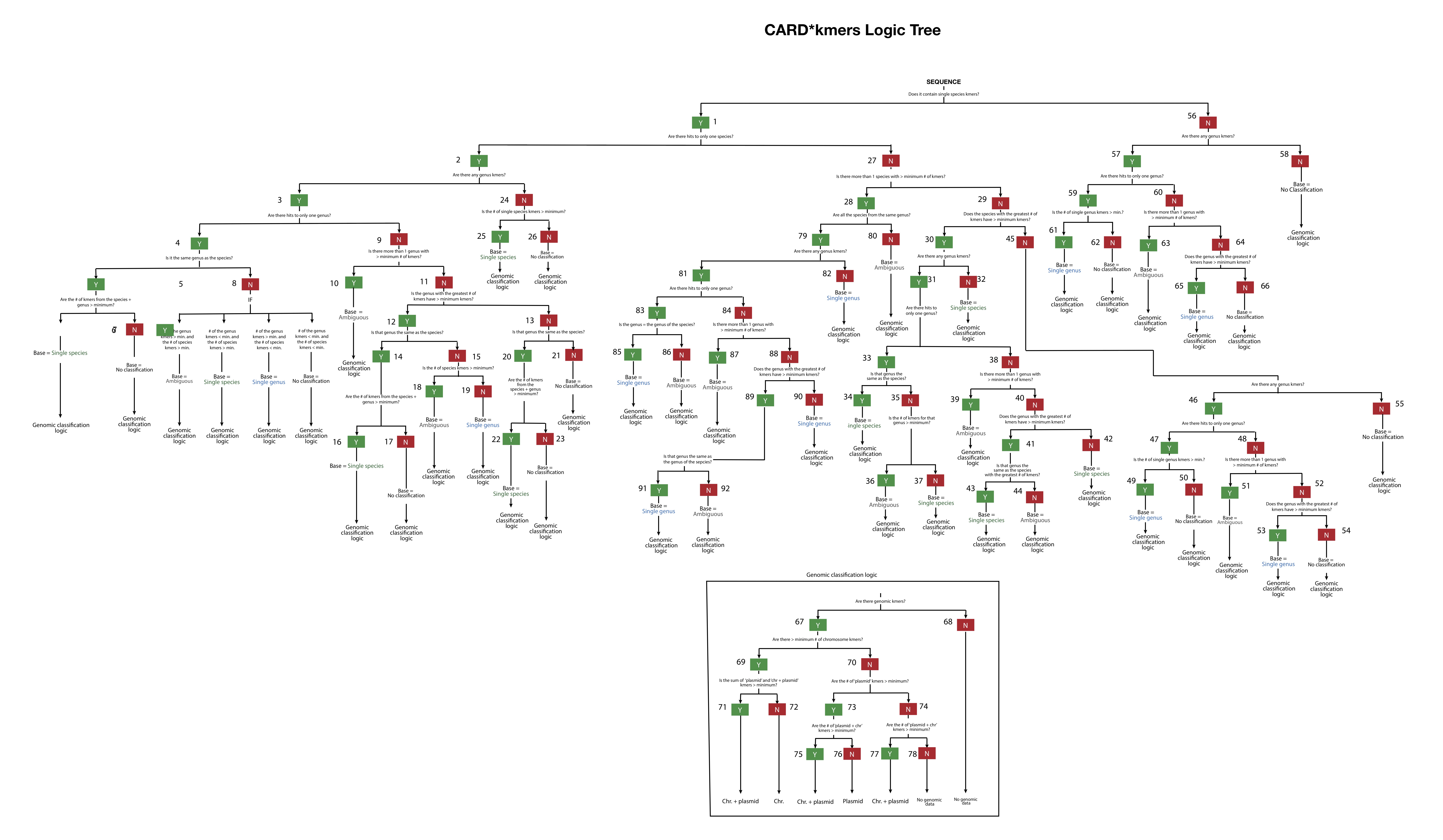
CARD's k-mer classifiers assume the data submitted for analysis has been predicted to encode AMR genes, via RGI or another AMR bioinformatic tool. The k-mer data set was generated from and is intended exclusively for AMR sequence space. To be considered for a taxonomic prediction, individual sequences (e.g. FASTA, RGI predicted ORF, metagenomic read) must pass the --minimum coverage value (default of 10, i.e. the number of k-mers in a sequence that that need to match a single category, for both taxonomic and genomic classifications, in order for a classification to be made for that sequence). Subsequent classification is based on the following logic tree:
rgi kmer_query -husage: rgi [-h] -i INPUT [--bwt] [--rgi] [--fasta] -k K [-m MIN] [-n THREADS]
-o OUTPUT [--local] [--debug]
Tests sequences using CARD*k-mers
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INPUT, --input INPUT
Input file (bam file from RGI*BWT, json file of RGI
results, fasta file of sequences)
--bwt Specify if the input file for analysis is a bam file
generated from RGI*BWT
--rgi Specify if the input file is a RGI results json file
--fasta Specify if the input file is a fasta file of sequences
-k K, --kmer_size K length of k
-m MIN, --minimum MIN
Minimum number of kmers in the called category for the
classification to be made (default=10).
-n THREADS, --threads THREADS
number of threads (CPUs) to use (default=32)
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
Output file name.
--local use local database (default: uses database in
executable directory)
--debug debug modeCARD k-mer Classifier analysis of an individual FASTA file (e.g. using 8 processors, minimum k-mer coverage of 10):
rgi kmer_query --fasta --kmer_size 61 --threads 8 --minimum 10 \
--input /path/to/nucleotide_input.fasta --output /path/to/output_file --localCARD k-mer Classifier analysis of Genome or Assembly DNA Sequences RGI main results (e.g. using 8 processors, minimum k-mer coverage of 10):
rgi kmer_query --rgi --kmer_size 61 --threads 8 --minimum 10 \
--input /path/to/rgi_main.json --output /path/to/output_file --localCARD k-mer Classifier analysis of Metagenomics RGI btw results (e.g. using 8 processors, minimum k-mer coverage of 10):
rgi kmer_query --bwt --kmer_size 61 --threads 8 --minimum 10 \
--input /path/to/rgi_bwt.bam --output /path/to/output_file --localCARD k-mer classifier output differs between genome/gene and metagenomic data:
| Field | Contents |
|---|---|
| Sequence | Sequence defline in the FASTA file |
| Total # kmers | Total # k-mers in the sequence |
| # of AMR kmers | Total # AMR k-mers in the sequence |
| CARD kmer Prediction | Taxonomic prediction, with indication if the k-mers are known exclusively from chromosomes, exclusively from plasmids, or can be found in either chromosomes or plasmids |
| Taxonomic kmers | Number of k-mer hits broken down by taxonomy |
| Genomic kmers | Number of k-mer hits exclusive to chromosomes, exclusively to plasmids, or found in either chromosomes or plasmids |
| Field | Contents |
|---|---|
| ORF_ID | Open Reading Frame identifier (from RGI results) |
| Contig | Source Sequence (from RGI results) |
| Cut_Off | RGI Detection Paradigm (from RGI results) |
| CARD kmer Prediction | Taxonomic prediction, with indication if the k-mers are known exclusively from chromosomes, exclusively from plasmids, or can be found in either chromosomes or plasmids |
| Taxonomic kmers | Number of k-mer hits broken down by taxonomy |
| Genomic kmers | Number of k-mer hits exclusive to chromosomes, exclusively to plasmids, or found in either chromosomes or plasmids |
As with RGI bwt analysis, output is produced at both the allele and gene level:
| Field | Contents |
|---|---|
| Reference Sequence / ARO term | Reference allele or gene ARO term to which reads have been mapped |
| Mapped reads with kmer DB hits | Number of reads classified |
| CARD kmer Prediction | Number of reads classified for each allele or gene, with indication if the k-mers are known exclusively from chromosomes, exclusively from plasmids, or can be found in either |
| Subsequent fields | Detected k-mers within the context of the k-mer logic tree |
This is an unpublished algorithm undergoing beta-testing.
You must Load CARD Reference Data for these commands to work.
As outlined above, CARD's Resistomes & Variants and Prevalence Data provide a data set of AMR alleles and their distribution among pathogens and plasmids. CARD's k-mer classifiers sub-sample these sequences to identify k-mers that are uniquely found within AMR alleles of individual pathogen species, pathogen genera, pathogen-restricted plasmids, or promiscuous plasmids. The default k-mer length is 61 bp (based on unpublished analyses), available as downloadable, pre-compiled k-mer sets at the CARD website, but users can also use RGI to create k-mers of any length.
rgi kmer_build -husage: rgi [-h] [-i INPUT_DIRECTORY] -c CARD_FASTA -k K [--skip] [-n THREADS]
[--batch_size BATCH_SIZE]
Builds the kmer sets for CARD*kmers
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INPUT_DIRECTORY, --input_directory INPUT_DIRECTORY
input directory of prevalence data
-c CARD_FASTA, --card CARD_FASTA
fasta file of CARD reference sequences. If missing,
run 'rgi card_annotation' to generate.
-k K k-mer size (e.g., 61)
--skip skips the concatenation and splitting of the CARD*R*V
sequences.
-n THREADS, --threads THREADS
number of threads (CPUs) to use (default=1)
--batch_size BATCH_SIZE
number of kmers to query at a time using pyahocorasick
--the greater the number the more memory usage
(default=100,000)Example generation of 31 bp k-mers using 20 processors (note that the filename card_database_v3.0.1.fasta depends on the version of CARD data downloaded, please adjust accordingly):
rgi kmer_build --input_directory /path/to/wildcard \
--card card_database_v3.0.1.fasta -k 31 --threads 20 --batch_size 100000The --skip flag can be used if you are making k-mers a second time (33 bp in the example below) to avoid re-generating intermediate files (note that the filename card_database_v3.0.1.fasta depends on the version of CARD data downloaded, please adjust accordingly):
rgi kmer_build --input_directory /path/to/wildcard \
--card card_database_v3.0.1.fasta -k 33 --threads 20 --batch_size 100000 --skip