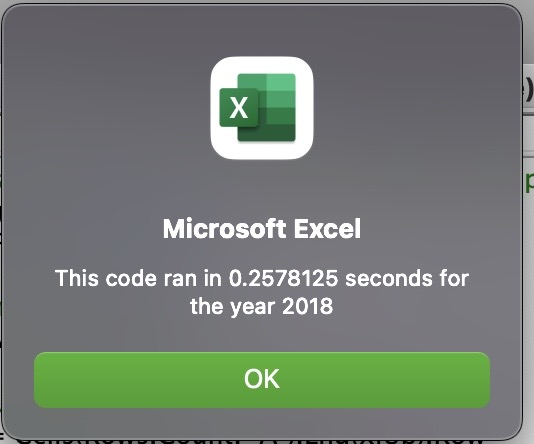
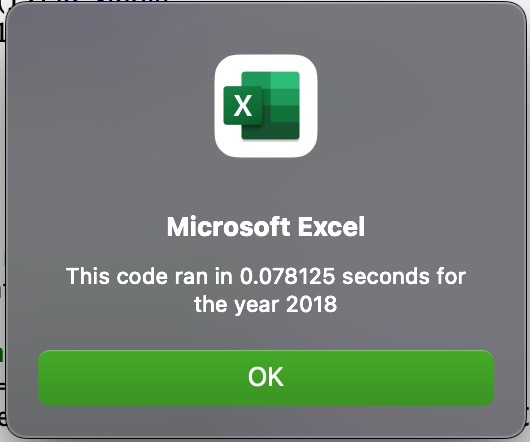
The purpose of this analysis is to compare whether a refactored script that efficiently runs through a loop will significantly affect the runtime of the script. This is done by comparing the runtime between two scripts that have the same output.
The refactored script did not provide any significantly faster runtime than the older script.
Run time for original script: 0.26 seconds
Run time for refactored script: 0.08 seconds
The advantages of refactoring a code is to provide a cleaner and more organized script. By running the loop only once, the time to run the script has been reduced to be less than one third of the original time. Creating more efficient and faster code also future proofs code in case the data grows exponentially.
The disadvantages are the time it takes to fix code that was running correctly already.
The question of whether the advantages outweigh the disadvantages can be answered by first asking if this code is predicted to remain as a core essential tool for the long term, and if there will be future coders who will be working with it with unpredictable data sets and sizes.