Learn more about modpoll usage at documentation site.
The initial idea of creating this tool is to help myself debugging new devices during site survey. A site survey usually has limited time and space, working on-site also piles up some pressures. At that time, a portable swiss-knife toolkit is our best friend.
This program can be easily deployed to Raspberry Pi or similar embedded devices, polling data from modbus devices, users can choose to log data locally or publish to a MQTT broker for further debugging.
The MQTT broker can be setup on the same Raspberry Pi or on the cloud. Once data successfully published, users can subscribe to a specific MQTT topic to view the data via a smart phone at your fingertip.
Moreover, you can also run this program continuously on a server as a Modbus-MQTT gateway, i.e. polling from local Modbus devices and forwarding data to a centralized cloud service.
In fact, modpoll helps to bridge between the traditional fieldbus world and the new IoT world.
This program is designed to be a standalone tool, it works out-of-the-box on Linux/macOS/Windows.
If you are looing for a modbus python library, please consider the following great open source projects, pymodbus or minimalmodbus
- Support Modbus RTU/TCP/UDP devices
- Show polling data for local debugging, like a typical modpoll tool
- Publish polling data to MQTT broker for remote debugging, especially on smart phone
- Export polling data to local storage for further investigation
- Provide docker solution for continuous data polling use case
This program tested on python 3.8+, the package is available in the Python Package Index, users can easily install it using pip or pipx.
Python3 is supported by most popular platforms, e.g. Linux/macOS/Windows, on which you can install modpoll using pip tool,
pip install modpollUpgrade the tool via the following command,
pip install -U modpollIt is recommended to use pipx for installing modpoll on Windows, refer to here for more information about pipx.
Once pipx installed, you can run the following command in a Command Prompt termial.
pipx install modpollUpgrade the tool via the following command,
pipx upgrade modpollAs the name tells, modpoll is a tool for communicating with Modbus devices, so ideally it makes more sense if you have a real Modbus device on hand for the following test, but it is OK if you don't, we provide a virtual Modbus TCP device deployed at modsim.topmaker.net:502 for your quick testing purpose.
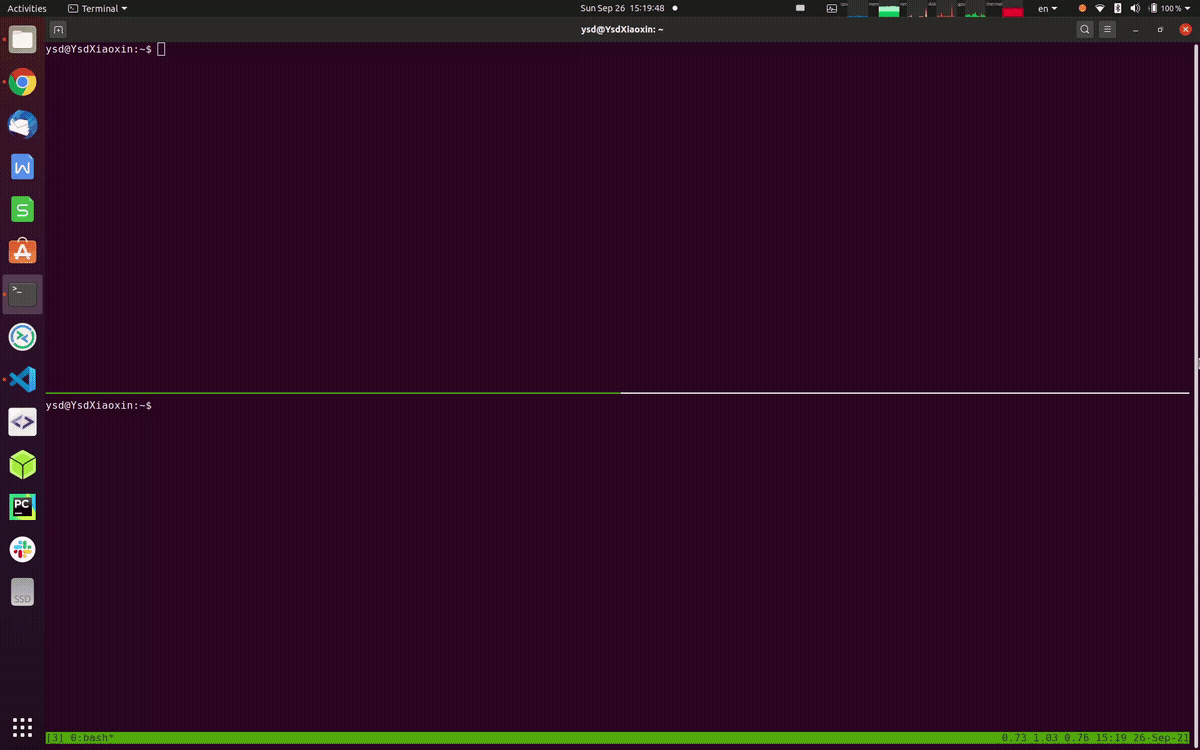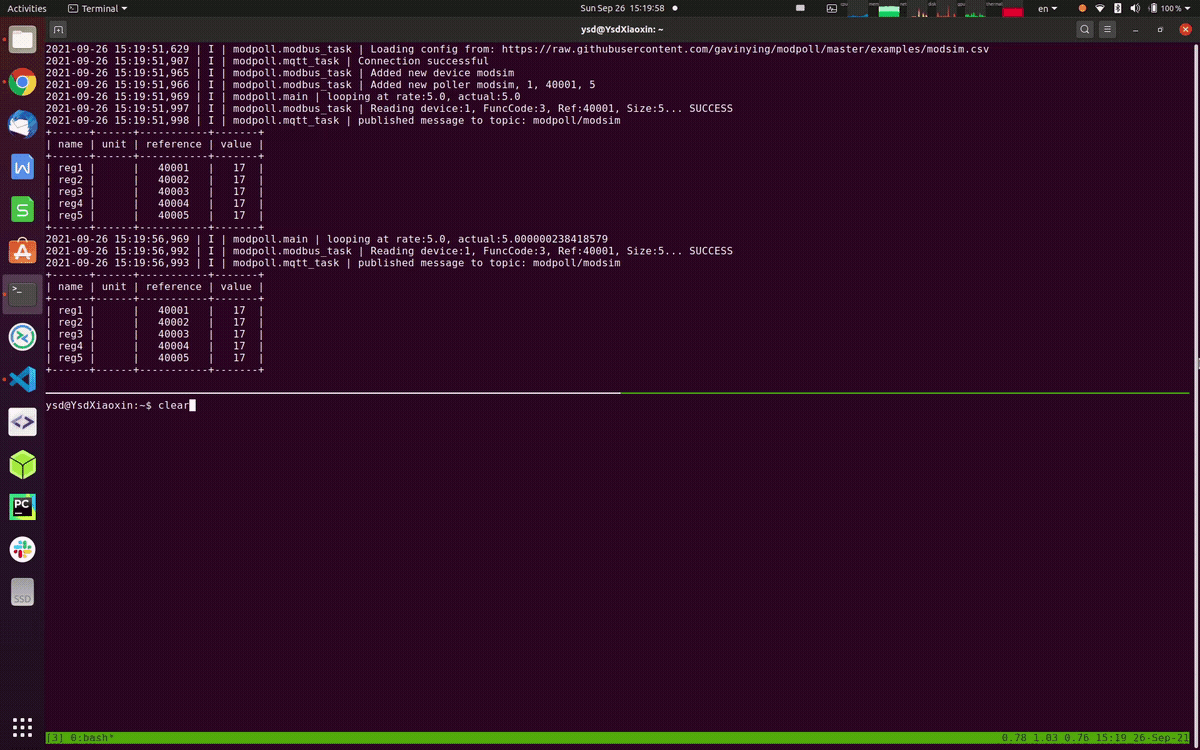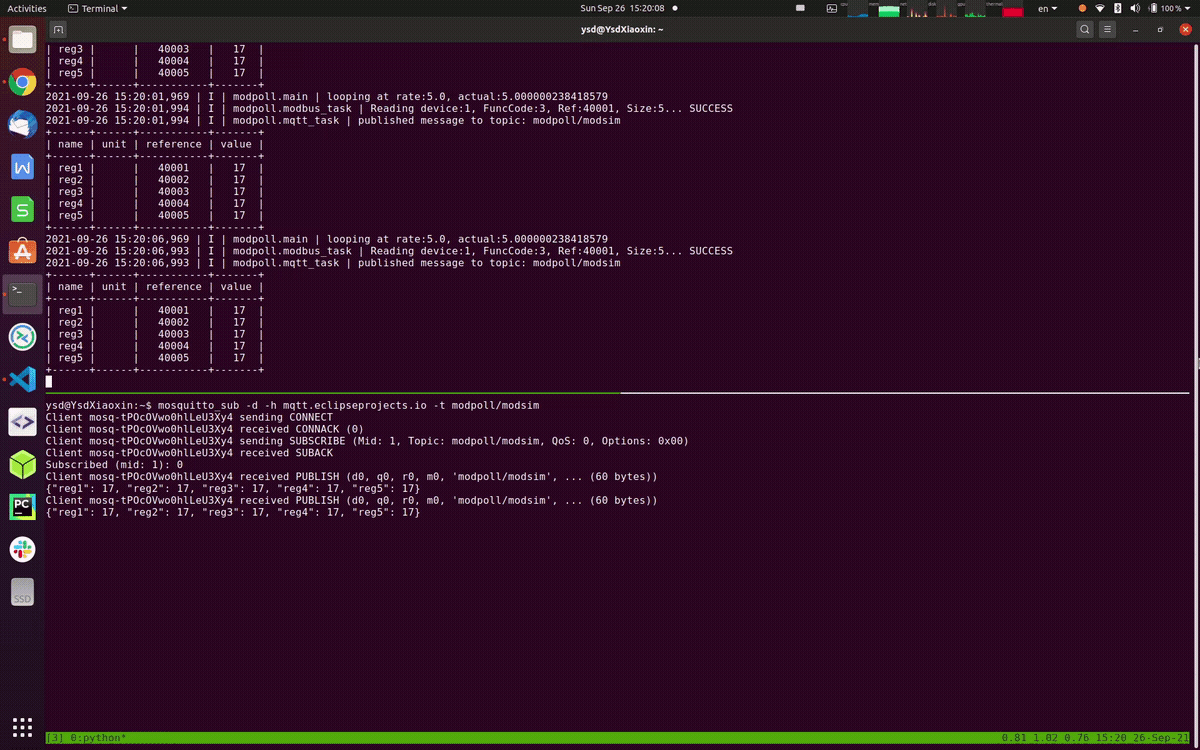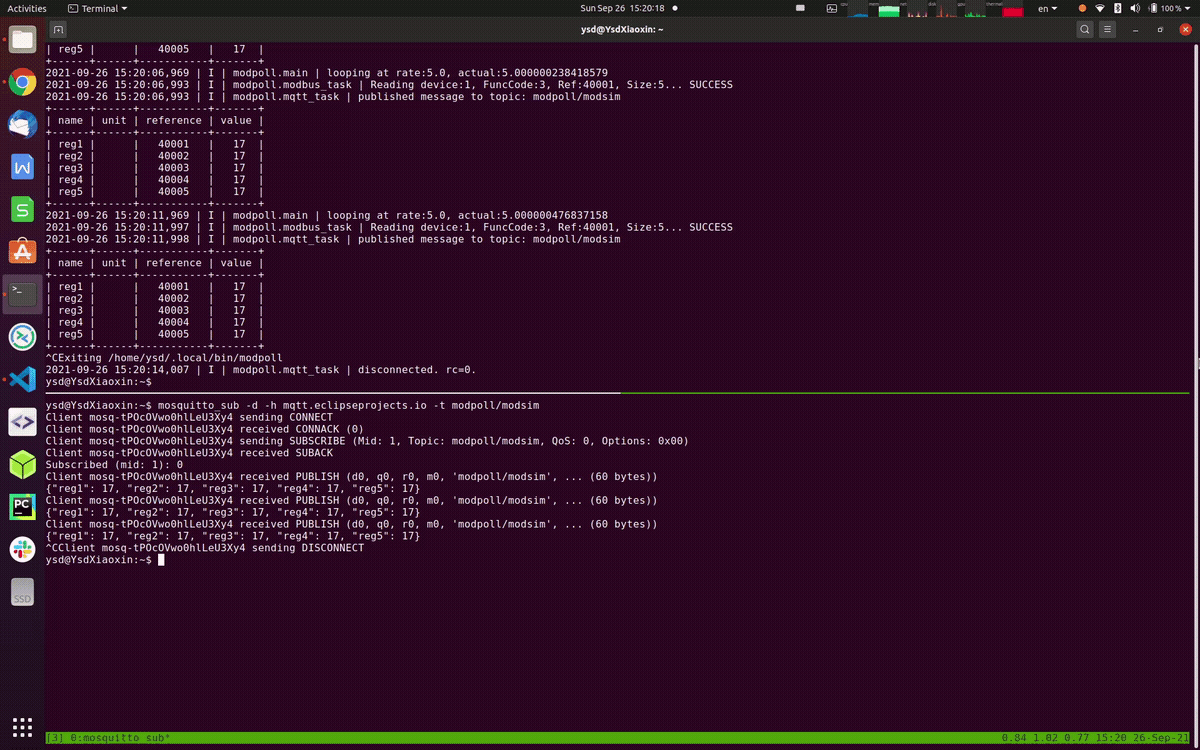
Let's start expoloring modpoll with modsim device, run the following command to get a first glimpse,
modpoll --tcp modsim.topmaker.net --config https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gavinying/modpoll/master/examples/modsim.csvthe modsim code is also available here
The reason we can magically poll data from the online device modsim is because we have already provided the Modbus configure file for modsim device as following,
device,modsim001,1,,
poll,holding_register,40000,20,BE_BE
ref,value1,40000,uint16,rw
ref,value2,40001,uint16,rw
ref,value3,40002,uint16,rw
ref,value4,40003,uint16,rw
ref,value5,40004,int16,rw
ref,value6,40005,int16,rw
ref,value7,40006,int16,rw
ref,value8,40007,int16,rw
ref,value9,40008,uint32,rw
ref,value10,40010,uint32,rw
ref,value11,40012,int32,rw
ref,value12,40014,int32,rw
ref,value13,40016,float32,rw
ref,value14,40018,float32,rw
poll,coil,0,24,BE_BE
ref,coil1-8,0,bool,rw
ref,coil9-16,8,bool,rw
This configuration tells modpoll to do the following for each poll,
- Read
20holding registers (register address:40000-40019) and parse data accordingly; - Read
24coils (coil address:0-23) and parse data accordingly;
Normally, you need to customize a Modbus configuration file for your own device before running modpoll tool, which defines the optimal polling patterns and register mappings according to device vendor's documents.
The configuration can be either a local file or a remote public URL resource.
Refer to the documentation site for more details.
If you are blocked by company firewall for online device or prefer a local test, you can launch your own device simulator by running modsim locally,
docker run -p 5020:5020 helloysd/modsimIt will create a virtual Modbus TCP device running at localhost:5020, and then you can poll it using modpoll tool,
modpoll --tcp localhost --tcp-port 5020 --config https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gavinying/modpoll/master/examples/modsim.csvUse
sudobefore the docker command if you want to use the standard port502.
sudo docker run -p 502:5020 helloysd/modsim
modpoll --tcp localhost --config https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gavinying/modpoll/master/examples/modsim.csvThis is a useful function of this new modpoll tool, which provides a simple way to publish collected modbus data to MQTT broker, so users can view data from a smart phone via a MQTT client.
The following example uses a public MQTT broker mqtt.eclipseprojects.io for test purpose. You can also setup your own MQTT broker locally using mosquitto.
modpoll --tcp modsim.topmaker.net --config https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gavinying/modpoll/master/examples/modsim.csv --mqtt-host mqtt.eclipseprojects.ioWith successful data polling and publishing, you can subscribe the topic modpoll/modsim on the same MQTT broker mqtt.eclipseprojects.io to view the collected data.
The MQTT topic uses
<mqtt_topic_prefix>/<deviceid>pattern, <mqtt_topic_prefix> is provided by--mqtt-topic-prefixargument, the default value ismodpoll/and is provided by the Modbus configure file.
The modpoll tool will subscribe to the topic <mqtt_topic_prefix>/<deviceid>/set once it successfully connected to MQTT broker, user can write device register(s) via MQTT publish,
-
To write a single holding register (address at
40001){ "object_type": "holding_register", "address": 40001, "value": 12 } -
To write multiple holding registers (address starting from
40001){ "object_type": "holding_register", "address": 40001, "value": [12, 13, 14, 15] }
A docker image has been provided for user to directly run the program without local installation,
docker run helloysd/modpollIt shows the version of the program by default.
Similar to the above modsim test, we can poll the first 5 holding registers with docker run,
docker run helloysd/modpoll modpoll --tcp modsim.topmaker.net --config https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gavinying/modpoll/master/examples/modsim.csvIf you want to load a local configure file, you need to mount a local folder onto container volume,
for example, if the child folder examples contains the config file modsim.csv, we can use it via the following command,
docker run -v $(pwd)/examples:/app/examples helloysd/modpoll modpoll --tcp modsim.topmaker.net --config /app/examples/modsim.csv-
Connect to Modbus TCP device
modpoll --tcp 192.168.1.10 --config examples/modsim.csv
-
Connect to Modbus RTU device
modpoll --rtu /dev/ttyUSB0 --rtu-baud 9600 --config contrib/eniwise/scpms6.csv
-
Connect to Modbus TCP device and publish data to MQTT broker
modpoll --tcp modsim.topmaker.net --tcp-port 5020 --config examples/modsim.csv --mqtt-host mqtt.eclipseprojects.io
-
Connect to Modbus TCP device and export data to local csv file
modpoll --tcp modsim.topmaker.net --tcp-port 5020 --config examples/modsim.csv --export data.csv
Refer to the documentation site for more details about the configuration and examples.
The implementation of this project is heavily inspired by the following two projects:
- https://github.com/owagner/modbus2mqtt (MIT license)
- https://github.com/mbs38/spicierModbus2mqtt (MIT license)
Thanks to Max Brueggemann and Oliver Wagner for their great work.
MIT © helloysd