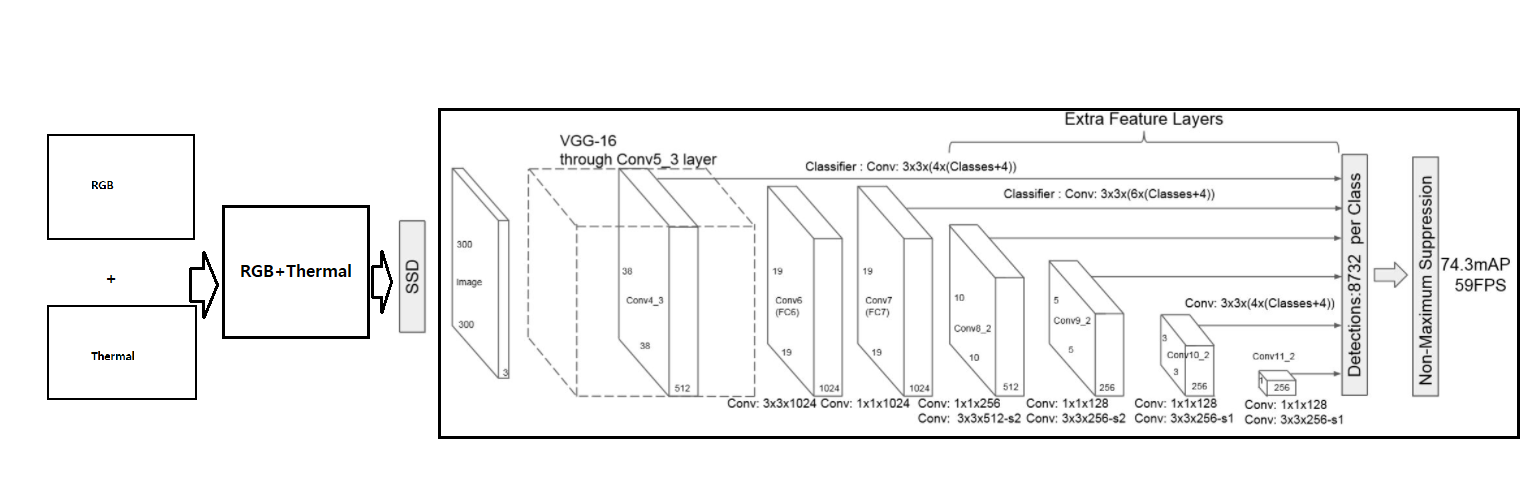
SSD[2] (Object detection Model) Implementation on Kaist pedestrian multispectral dataset[1]
- To understand SSD model
- To apply SSD model to Kaist Pedestrain dataset.
- phtometric disortation(randomly adjusts 4-disortation methods(Brightness,contrast,saturation,Hue) with a 50% chance)
- Brightness , contrast,saturation : [0.5, 1.5] (random distribution : Uniform)
- Zoom out (with 50% chance of occurrence)
- Crop the image (50%)
- Flip (50%)
Resize Normalization
- baseline0
initialized with pretrained SSD weights (pre-trained on VOC dataset)
SSD300 trained on VOC - baseline1 You can download here
optimizer : SGD(lr=0.001)
loss : MultiBoxLoss (same as original paper[2])
=======
- Make kaist dataset be small size (for working on colab)
- split(train,val,test)
- tr,val, test (155, 52, 69)
- Dataset&DataLoader
- SSD model
- train
- diverse optimizers; AdamP[3], Madgrad[4]
- augmentation in object detection
- Few shot learning in small dataset
- Continual Learning (cl)
- problem : Catastrophic Forgetting , Semantic Draft
- Categorization of CL Approach
- Regularization
- EWC (Elastic Weight Consolidation)[7]
- Structure
- Progressive Networks[8]
- Memory
- DGR (Deep Generative Replay)[9]
- Mixed above
- Dynamically Expandable Network[10]
😁 when i have a time, I wanna think of this topic deeply.
- the ways of solving Class Imbalance problems (In this paper , used Hard Negative method for solving this problem)
- Online Hard Example Mining [6]
- Focal loss[5]
origin : https://soonminhwang.github.io/rgbt-ped-detection/
download : https://gofile.me/4ce0I/uRhsZ8nnF
github : https://github.com/luzhang16/AR-CNN
download : https://drive.google.com/open?id=1FLkoJQOGt4PqRtr0j6namAaehrdt_A45
baseline0 : https://github.com/amdegroot/ssd.pytorch/tree/5b0b77faa955c1917b0c710d770739ba8fbff9b7 (it has many bugs)
baseline1 : https://github.com/sgrvinod/a-PyTorch-Tutorial-to-Object-Detection
object detection framework : https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection
#reference
- [1] S. Hwang, J. Park, N. Kim, Y. Choi, and I. S. Kweon, “Multispectral Pedestrian Detection: Benchmark Dataset and Baseline.” Accessed: May 07, 2021. [Online]. Available: http://rcv.kaist.ac.kr/multispectral-pedestrian/.
- [2] W. Liu et al., “SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector.” Accessed: May 07, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://github.com/weiliu89/caffe/tree/ssd.
- [3] B. Heo et al., “ADAMP: SLOWING DOWN THE SLOWDOWN FOR MO-MENTUM OPTIMIZERS ON SCALE-INVARIANT WEIGHTS Equal contribution * , Works done at Naver AI Lab †.” Accessed: May 07, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://github.com/clovaai/adamp.
- [4] A. Defazio and S. Jelassi, “Adaptivity without Compromise: A Momentumized, Adaptive, Dual Averaged Gradient Method for Stochastic Optimization,” pp. 1–31, 2021, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2101.11075.
- [5] T.-Y. Lin, P. Goyal, R. Girshick, K. He, and P. Dollár, “Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection.” Accessed: May 11, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://github.com/facebookresearch/Detectron.
- [6] A. Shrivastava, A. Gupta, and R. Girshick, “Training Region-based Object Detectors with Online Hard Example Mining.”
- [7] J. Kirkpatrick et al., “Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in neural networks,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., vol. 114, no. 13, pp. 3521–3526, Mar. 2017, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611835114.
- [8] A. A. Rusu et al., “Progressive Neural Networks,” Jun. 2016, Accessed: May 15, 2021. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1606.04671.
- [9] H. Shin, J. K. Lee, J. Kim, and J. Kim, “Continual Learning with Deep Generative Replay,” Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst., vol. 2017-December, pp. 2991–3000, May 2017, Accessed: May 15, 2021. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1705.08690.
- [10] J. Yoon, E. Yang, J. Lee, and S. J. Hwang, “Lifelong Learning with Dynamically Expandable Networks,” arXiv, Aug. 2017, Accessed: May 15, 2021. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1708.01547.