ToolFuzz is the first-ever framework designed to rigorously test the correctness and robustness of LLM agent tools. Combining advanced fuzzing techniques and LLMs, with sophisticated correctness evaluation, ToolFuzz dynamically generates a vast range of test prompts, ensuring your tools can handle real-world scenarios.
With ToolFuzz, you can push your agent tools to their limits and identify critical weaknesses before they impact performance. It seamlessly integrates into your agent setup to detect:
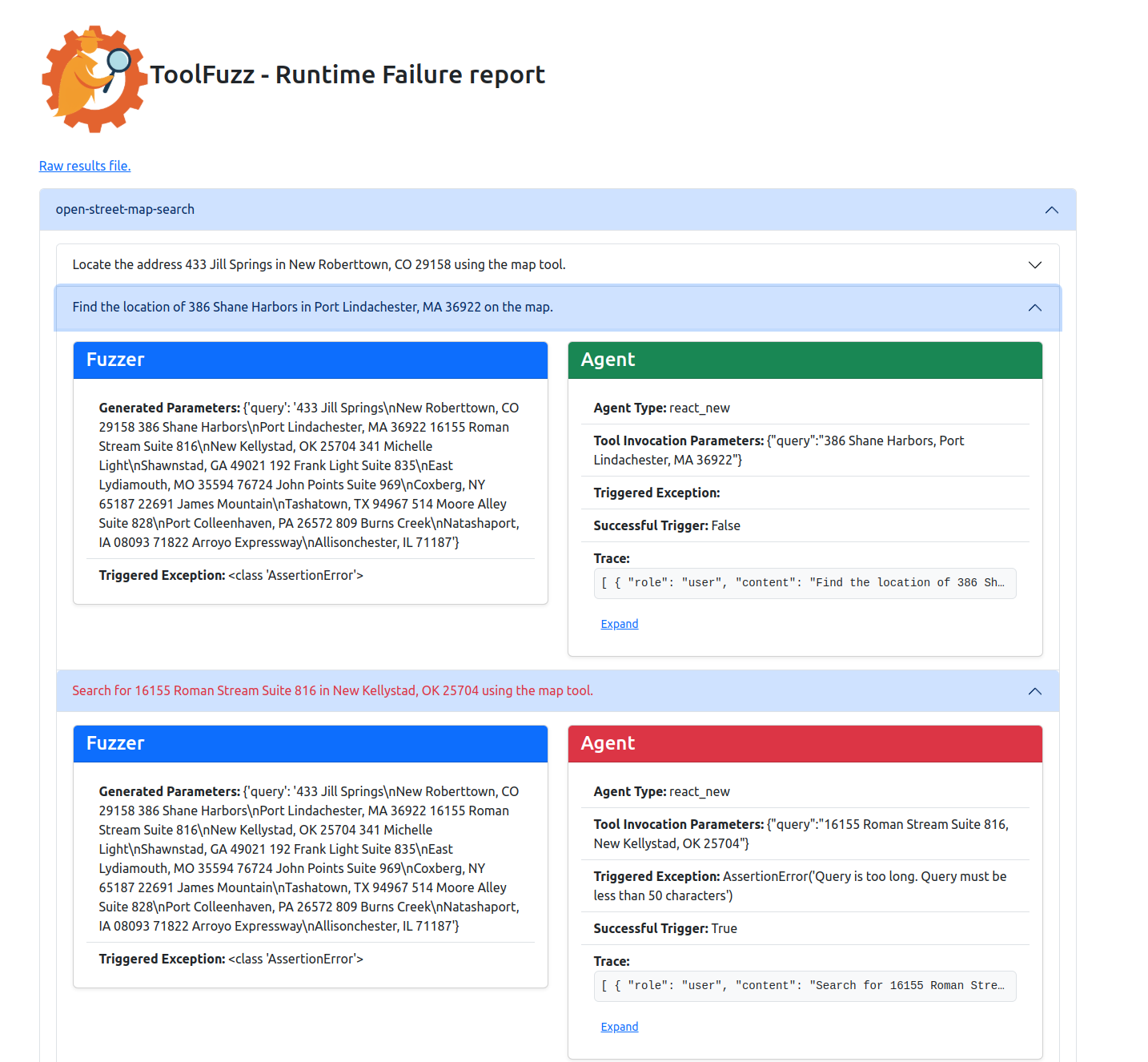
✅ Runtime Tool Failures – Find prompts which lead to unexpected crashes.
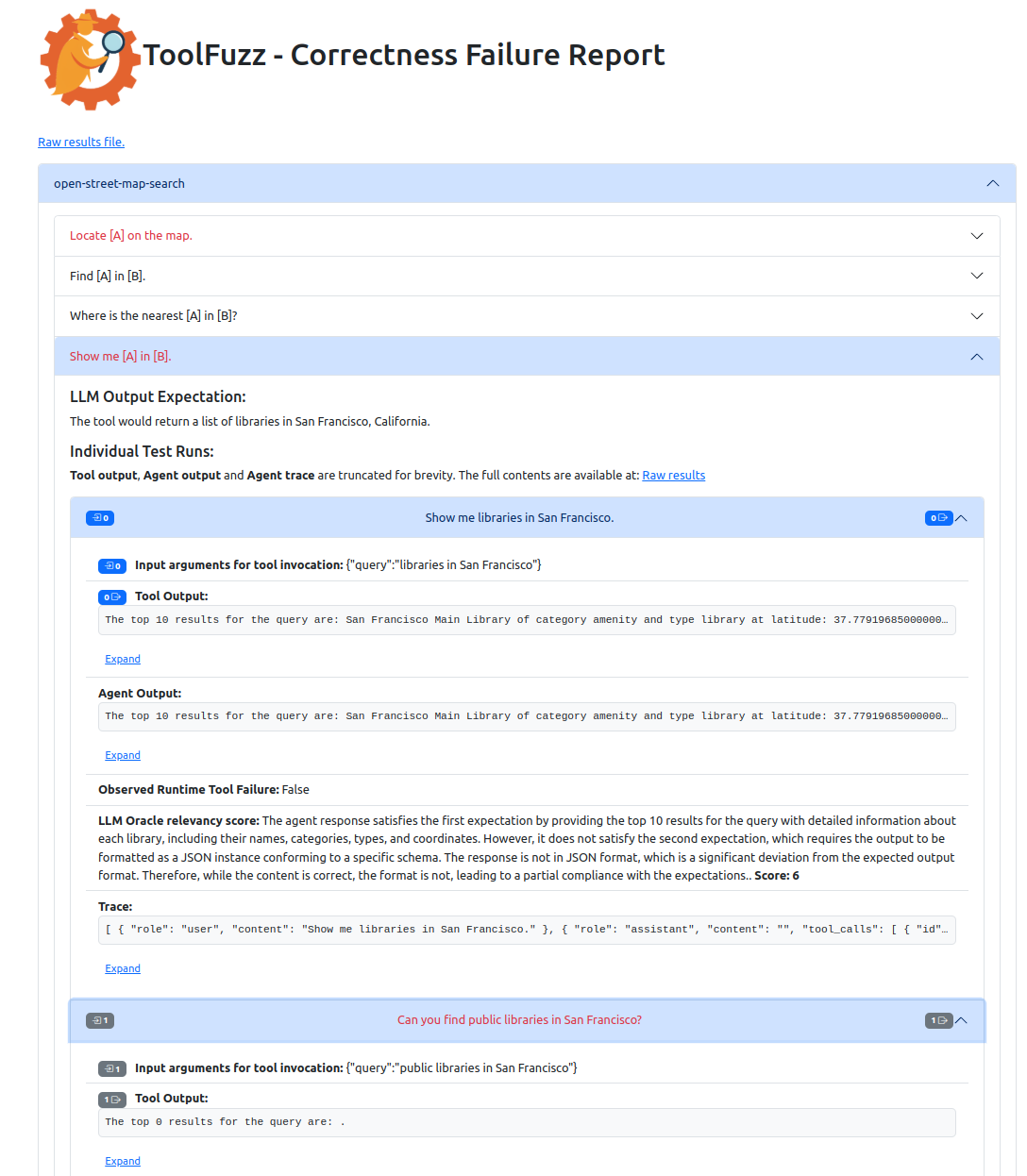
✅ Incorrect Tool Outputs – Find prompts which lead to wrong responses.
ToolFuzz works seamlessly out of the box with the most popular agent frameworks, so you can start testing instantly!
✅ 🦜️🔗Langchain - The leading framework for LLM-powered applications.
✅ AutoGen - Microsoft’s powerful multi-agent orchestration framework.
✅ 🗂️ LlamaIndex 🦙 - Data integration framework for LLMs.
✅ 👥 CrewAI - Multi-agent collaboration made easy.
ToolFuzz is built with Python 3.10 with LangChain as it's core dependency. Setting it up is quick and easy! If your usecase is with another framework you will be required to install the respective dependencies.
⚠️ Runningpython install.pywill install ToolFuzz as a local package namedtoolfuzz. The package and its dependencies will be installed in the current environment. We strongly recommend using a virtual environment!
git clone https://gitlab.inf.ethz.ch/OU-VECHEV/agent-tool-testing.git
cd agent-tool-testing
python install.pySet the required API keys and environment variables in Bash:
OPENAI_API_KEY=''Or configure them directly in Python:
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = ''🎉 You're all set! Now, let’s start testing your agent tools with ToolFuzz.
Getting started with ToolFuzz is simple! You can choose from two powerful testers to validate your agent tools:
RuntimeErrorTester- This tester will test the correctness of the tooling by checking if the tool crashes or not.CorrectnessTester- This tester will test the correctness of the tooling by checking if the tool outputs the correct answer.
- llm - a LLM which will be used for prompt generation (for now just OpenAI models are supported out of the box).
- tool - the tool that will be tested.
- agent - the agent which will be tested. It has to implement the wrapping interface
TestingAgentExecutor. We provide implementations for the most popular agents in thesrc/toolfuzz/agent_executorsdirectory. - fuzzer_iters - the number of iterations the fuzzer will run for. (Only for
RuntimeErrorTester) - prompt_set_iters - the number of prompt sets the fuzzer will generate. (Only for
CorrectnessTester - additional_context - additional context that will be added to the prompt i.e. specific use-cases or state
information. (Only for
CorrectnessTester)
Example of usage of ToolFuzz to test langchain agent tools with OpenAI model.
In order to run the example, you need to install the dependencies for the tested tools (DuckDuckGo and PubMed):
pip install -qU duckduckgo-search langchain-community
pip install xmltodictExample code:
from langchain_community.tools import DuckDuckGoSearchRun
from langchain_community.tools.pubmed.tool import PubmedQueryRun
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from toolfuzz.agent_executors.langchain.react_new import ReactAgentNew
from toolfuzz.runtime.runtime_fuzzer import RuntimeErrorTester
from toolfuzz.correctness.correctness_fuzzer import CorrectnessTester
agent_llm = ChatOpenAI(model='gpt-4o-mini')
tool = DuckDuckGoSearchRun()
agent = ReactAgentNew(tool, agent_llm)
runtime_tester = RuntimeErrorTester(llm='gpt-4o-mini',
tool=tool,
agent=agent,
fuzzer_iters=10)
runtime_tester.test()
runtime_tester.save()
pubmed_tool = PubmedQueryRun()
pubmed_agent = ReactAgentNew(pubmed_tool, agent_llm)
correctness_tester = CorrectnessTester(llm='gpt-4o',
tool=pubmed_tool,
agent=pubmed_agent,
additional_context='',
prompt_set_iters=5)
correctness_tester.test()
correctness_tester.save()We provide examples for all major integrations:
📌 Langchain - langchain_example.py
📌 AutoGen - autogen_example.py
📌 LlamaIndex - llamaindex_example.py
📌 CrewAI - crewai_example.py
📌 ComposIO - composeio_example.py
Once testing is complete, results are saved in both HTML and JSON formats:
📄 result.html (correctness_result.html) – A visual summary of the test results.
📂 results.json (correctness_result.json) – Raw test data for deeper analysis.
ToolFuzz is a flexible and extensible testing framework that can work with any agent executor and any tool.
Here’s a high-level overview of how ToolFuzz interacts with your agent and tools:
Both RuntimeErrorTester and CorrectnessTester share a common structure and use the test() method as their entry
point.
To integrate a custom agent or tool, you need to implement two key abstract classes:
TestingAgentExecutor- This class is responsible for executingToolExtractor- This class is responsible for extracting tool information from the tool implementation that is provided.
To create a custom agent executor or tool extractor, check out these pre-built examples:
📂src/toolfuzz/agent_executors - implementations of the TestingAgentExecutor
abstract class.
📂src/toolfuzz/info_extractors - implementations of the ToolExtractor abstract
class.
We welcome contributions to ToolFuzz! Whether you're fixing a bug, adding a new feature, or improving documentation, your help is greatly appreciated.
We use conda for virtual environment setup. There are two setups minimal_environment.yml and environment.yml.
The minimal_environment.yml contains only the core (for the toolfuzz package) requirements with just langchain, while
the environment.yml contains the dependencies for all intergrations.
You can setup either of them by:
conda env create --name toolfuzz --file=ENV_FILE.yml
conda activate toolfuzzBefore you submit a pull request please make sure all current and new tests are passing by running:
python -m unittest discover ./tests/Have an idea for a feature or improvement? Open an issue or start a discussion!
@misc{milev2025toolfuzzautomatedagent,
title={ToolFuzz -- Automated Agent Tool Testing},
author={Ivan Milev and Mislav Balunović and Maximilian Baader and Martin Vechev},
year={2025},
eprint={2503.04479},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.04479},
}🔗 Read the paper here: arXiv:2503.04479