The nydus project implements a user space filesystem on top of a container image format that improves over the current OCI image specification, in terms of container launching speed, image space, and network bandwidth efficiency, as well as data integrity.
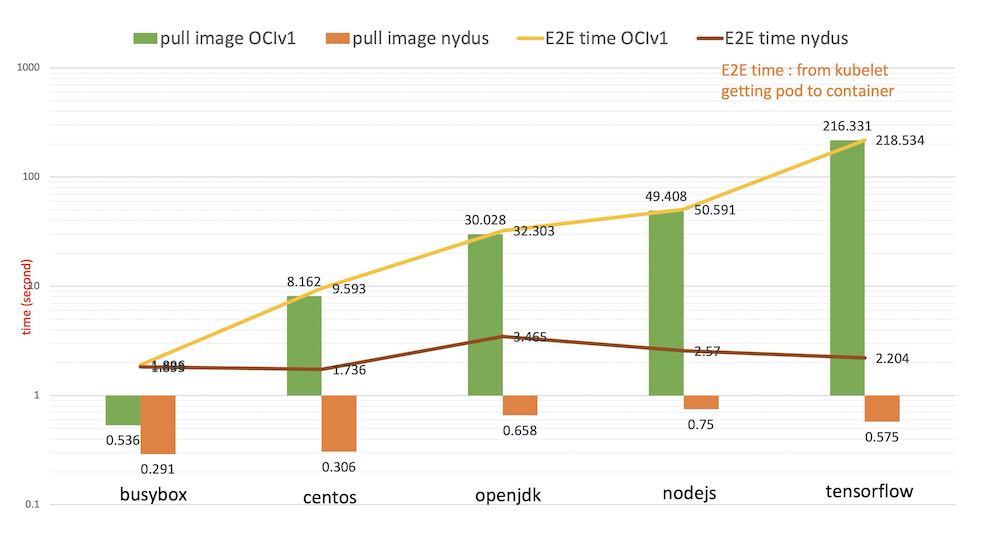
The following benchmarking result shows the performance improvement compared with the OCI image for the container cold startup elapsed time on containerd. As the OCI image size increases, the container startup time of using Nydus image remains very short.
Nydus' key features include:
- Container images may be downloaded on demand in chunks to boost container startup
- Chunk level data de-duplication among layers in a single repository to reduce storage, transport and memory cost
- Flatten image metadata and data to remove all intermediate layers
- Deleted(whiteout) files in certain layer aren't packed into nydus image, therefore, image size may be reduced
- E2E image data integrity check. So security issues like "Supply Chain Attach" can be avoided and detected at runtime
- Compatible with the OCI artifacts spec and distribution spec, so nydus image can be stored in a regular container registry
- Integrated with CNCF incubating project Dragonfly to distribute container images in P2P fashion and mitigate the pressure on container registries
- Different container image storage backends are supported. For example, Registry, NAS, Aliyun/OSS.
- Capable to prefetch data block before user IO hits the block thus to reduce read latency
- Readonly FUSE file system with Linux overlayfs to provide full POSIX compatibility
- Record files access pattern during runtime gathering access trace/log, by which user abnormal behaviors are easily caught
- Access trace based prefetch table
- User IO amplification to reduce the amount of small requests to storage backend.
Currently the repository includes following tools:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| nydusd | Linux FUSE user-space daemon, it processes all fuse messages from host/guest kernel and parses nydus container image to fullfil those requests |
| nydus-image | Convert a single layer of OCI format container image into a nydus format container image generating meta part file and data part file respectively |
| nydusify | It pulls OCI image down and unpack it, invokes nydus-image to convert image and then pushes the converted image back to registry and data storage |
| containerd-nydus-grpc | Works as a containerd remote snapshotter to help setup container rootfs with nydus images |
| nydusctl | Nydusd CLI client, query daemon's working status/metrics and configure it |
| ctr-remote | An enhanced containerd CLI tool enable nydus support with containerd ctr |
| nydus-docker-graphdriver | Works as a docker remote graph driver to control how images and containers are stored and managed |
To try nydus image service:
- Convert an original OCI image to nydus image and store it somewhere like Docker/Registry, NAS or Aliyun/OSS. This can be directly done by
nydusify. Normal users don't have to get involved withnydus-image. - Get
nydus-snapshotter(containerd-nydus-grpc) installed locally and configured properly. Or installnydus-docker-graphdriverplugin. - Operate container in legacy approaches. For example,
docker,nerdctl,CRIandctr
# build debug binary
make
# build release binary
make release
# build static binary with docker
make docker-staticFor more details on how to lazily start a container with nydus-snapshotter and nydus image on Kubernetes nodes or locally use nerdctl rather than CRI, please refer to Nydus Setup
Build Nydus image from directory source: Nydus Image Builder.
Convert OCI image to Nydus image: Nydusify.
Nydus supports containerd. To run containers with nydus images and containerd, please build and install the nydus snapshotter. It is a containerd remote snapshotter and handles nydus image format when necessary. When running without nydus images, it is identical to the containerd's builtin overlayfs snapshotter.
To build and setup nydus-snapshotter for containerd, please refer to Nydus Snapshotter
Normally, users do not need to start nydusd by hand. It is started by nydus-snapshotter or nydus-docker-graphdriver when a container rootfs is prepared.
Run Nydusd Daemon to serve Nydus image: Nydusd.
Docker graph driver is also accompanied, it helps to start container from nydus image. For more particular instructions, please refer to
Browse the documentation to learn more. Here are some topics you may be interested in:
- A Nydus Tutorial for Beginners
- Our talk on Open Infra Summit 2020: Toward Next Generation Container Image
- Nydus Design Doc
Welcome to share your use cases and contribute to Nydus project. You can reach the community via Dingtalk and Slack
Any bug report, feature requirement, and technique discussion and cooperation are welcomed and expected!