Build a Traffic Sign Recognition Project
-
Number of training examples = 34799 (67.1%)
-
Number of validation examples = 4410 (8.5%)
-
Number of testing examples = 12630 (24.4%)
-
Image data shape/type = (
33x32x3)uint8 -
Number of classes = 43
The dataset includes additional information about the original sizes of the images before being resized to 32x32, as well as the coordinates in the original images that delimit the sign. This extra information is not used in this project.
Random images samples from each one of the classes/labels, the sign is usually located in the center of the image with no cropping. The images have different levels of exposure, some of them are almost completely dark.
Below is the distribution of the classes in the dataset, it's visible that some classes are more predominant in the dataset (up to a factor of 10)
The images were converted to grayscale after applying histogram equalization to uniform exposure levels across images.
On the first row are displayed the original images, bottom is the result after preprocessing:
The implemented model is heavily based on LeNet 5, with the addition of three dropout layers to prevent overfitting.
| Layer | Description |
|---|---|
| Input | 32x32x1 gray scale image |
| Convolution 5x5 | 1x1 stride, valid padding, outputs 28x28x6 |
| RELU | |
| Max pooling | 2x2 stride, outputs 14x14x6 |
| Convolution 5x5 | 1x1 stride, valid padding, outputs 10x10x16 |
| RELU | |
| Max pooling | 2x2 stride, outputs 5x5x16 |
| Flatten | outputs 400 |
| Dropout | |
| Fully connected | outputs 120 |
| RELU | |
| Dropout | |
| Fully connected | outputs 84 |
| RELU | |
| Dropout | |
| Fully connected | outputs 43 |
| Softmax |
The Adam-Optimizer is used with the training operation of reducing cross-entropy.
Hyperparameters:
- Batch Size :
128 - Learning rate:
0.001 - Dropout probability:
50% - Epochs:
30
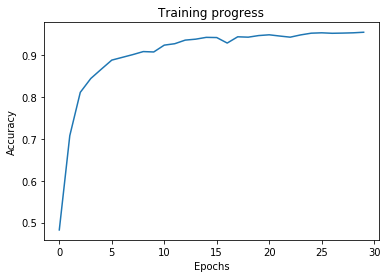
The default parameters used for LeNet 5 are already sufficient to get good accuracy over the training set. Only additional dropout layers were added to further increase the accuracy. Some experimentation was done by feeding RGB images to the model instead of grayscale, but the accuracy values were very similar.
The test accuracy obtained is around 94%
A set of eight photos were obtained through a google images search, and cropped more or less accordingly to the data set, but not exactly. The images have different resolutions and sizes so a resizing to 32x32 was performed using cv2.resize. The result after the resize is shown below:
Some images are purposely difficult like the stop signal in the bottom left corner, which is an attempt to fool the A.I. of autonomous driving vehicles by putting black and white stickers on top.
The model predicted correctly 4 out of 8 images resulting in 50% accuracy rate which is a value much lower than the one from the test set.
The results also vary (from 3 to 6 correct images) just by re-running the training, the softmax probabilities can also be completely different from run to run (for a given particular image), which is kind of unexpected.
The priority signal and the simple stop are the only ones that are correctly identified with a high certainty.
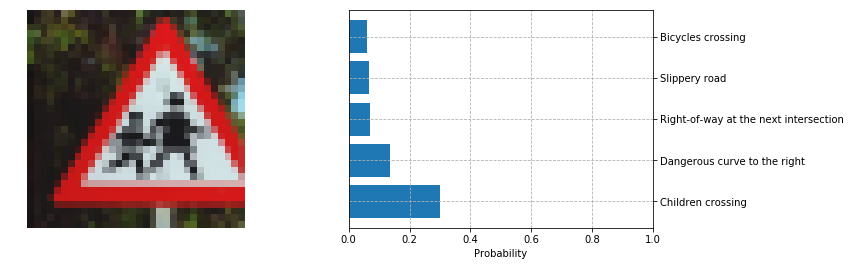
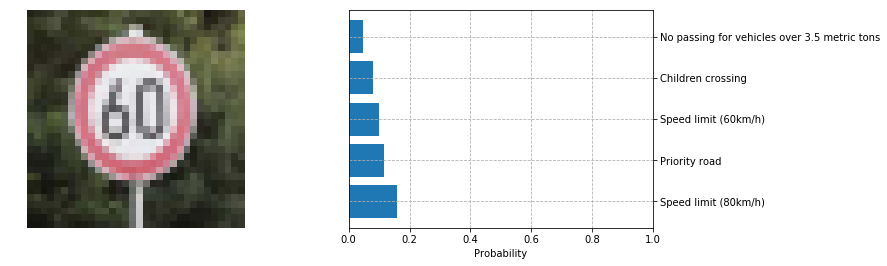
The following ones are sometimes correctly predicted with low certainty:
However looking at the second/third highest softmax classes they are often of similar shape (60 sign classified as 80, roundabout and priority road both have arrows, and so on).
-
Augmenting the training set might help improve model certainty. Common data augmentation techniques include rotation, translation, zoom, flips, inserting jitter, and/or color perturbation. Tensorflow v2 seems to already have embedded tools for this purpose.
-
Perform error analysis to identify which image characteristics the model has a harder time to classify.
-
Visualization of layers in the neural network, as suggested in the project, to get more insight on how the model works. Also exploring Tensorboard could be useful.