| Scala version: | 2.10.1 |
| Akka version: | 2.1.2 |
- Overview
- Terminology
- First steps
- Stackable traits
- Sender references
- Channels
- Recovery
- Snapshots
- Behavior changes
- Event series
- Idempotency
- Serialization
- Further examples
- Miscellaneous
- Appendix A: Legend
- Appendix B: Project
- Appendix C: Articles
- Appendix D: Support
The Eventsourced library adds scalable actor state persistence and at-least-once message delivery guarantees to Akka. With Eventsourced, stateful actors
- persist received messages by appending them to a log (journal)
- project received messages to derive current state
- usually hold current state in memory (memory image)
- recover current (or past) state by replaying received messages (during normal application start or after crashes)
- never persist current state directly (except optional state snapshots for recovery time optimization)
In other words, Eventsourced implements a write-ahead log (WAL) that is used to keep track of messages an actor receives and to recover its state by replaying logged messages. Appending messages to a log instead of persisting actor state directly allows for actor state persistence at very high transaction rates and supports efficient replication. In contrast to other WAL-based systems, Eventsourced usually keeps the whole message history in the log and makes usage of state snapshots optional.
Logged messages represent intended changes to an actor's state. Logging changes instead of updating current state is one of the core concept of event sourcing. Eventsourced can be used to implement event sourcing concepts but it is not limited to that. More details about Eventsourced and its relation to event sourcing can be found at How does Eventsourced persist actor state and how is this related to event sourcing.
Eventsourced can also be used to make message exchanges between actors reliable so that they can be resumed after crashes, for example. For that purpose, channels with at-least-once message delivery guarantees are provided. Channels also prevent that output messages, sent by persistent actors, are redundantly delivered during replays which is relevant for message exchanges between these actors and other services.
The core building blocks provided by Eventsourced are processors, channels and journals. These are managed by an Akka extension, the EventsourcingExtension.
A processor is a stateful actor that logs (persists) messages it receives. A stateful actor is turned into a processor by modifying it with the stackable Eventsourced trait during construction. A processor can be used like any other actor.
Messages wrapped inside Message are logged by a processor, unwrapped messages are not logged. Wrapped messages are often referred to as events in this user guide. Wrapped messages can also be commands, as explained in section Application.
Logging behavior is implemented by the Eventsourced trait, a processor's receive method doesn't need to care about that. Acknowledging a successful write to a sender can be done by sending a reply. A processor can also hot-swap its behavior by still keeping its logging functionality.
Processors are registered at an EventsourcingExtension. This extension provides methods to recover processor state by replaying logged messages. Processors can be registered and recovered at any time during an application run.
Eventsourced doesn't impose any restrictions how processors maintain state. A processor can use vars, mutable data structures or STM references, for example.
Channels are used by processors for sending messages to other actors (channel destinations) and receiving replies from them. Channels
- require their destinations to confirm the receipt of messages for providing at-least-once delivery guarantees (explicit ack-retry protocol). Receipt confirmations are written to a log.
- prevent redundant delivery of messages to destinations during processor recovery (replay of messages). Replayed messages with matching receipt confirmations are dropped by the corresponding channels.
A channel itself is an actor that decorates a destination with the aforementioned functionality. Processors usually create channels as child actors for decorating destination actor references.
A processor may also sent messages directly to another actor without using a channel. In this case that actor will redundantly receive messages during processor recovery.
Eventsourced provides three different channel types (more are planned).
- Default channel
- Does not store received messages.
- Re-delivers uncomfirmed messages only during recovery of the sending processor.
- Order of messages as sent by a processor is not preserved in failure cases.
- Reliable channel
- Stores received messages.
- Re-delivers unconfirmed messages based on a configurable re-delivery policy.
- Order of messages as sent by a processor is preserved, even in failure cases.
- Often used to deal with unreliable remote destinations.
- Reliable request-reply channel
- Same as reliable channel but additionally guarantees at-least-once delivery of replies.
- Order of replies not guaranteed to correspond to the order of sent request messages.
Eventsourced channels are not meant to replace any existing messaging system but can be used, for example, to reliably connect processors to such a system, if needed. More generally, they are useful to integrate processors with other services, as described in this article.
A journal is an actor that is used by processors and channels to log messages and receipt confirmations. The quality of service (availability, scalability, ...) provided by a journal depends on the used storage technology. The Journals section below gives an overview of existing journal implementations and their development status.
The Eventsourced library doesn't impose any restrictions on the structure and semantics of Message payloads. Hence, persistent messages can therefore be events as well as commands. The Eventsourced reference application uses both, for example.
Eventsourced fits well into applications that implement the CQRS pattern and follow a domain-driven design (DDD) (see reference application). On the other hand, the library doesn't force applications to do so and allows them to implement event-sourcing (and/or command-sourcing) without CQRS and/or DDD.
For persisting messages, Eventsourced currently provides the following journal implementations:
| Journal | Usage |
|---|---|
| LevelDB journal. A LevelDB and leveldbjni backed journal. Because LevelDB is a native library, this journal requires a special sbt project configuration. It is be used in the following examples. | Production |
| HBase journal. An HBase backed journal supporting high-availability, horizontal read and write scalability, concurrent and non-blocking reads and writes. Details here. | Experimental |
| MongoDB Casbah based journal. A MongoDB backed journal. Details here. Thanks to Duncan DeVore. | Experimental |
| MongoDB Reactive based journal. A MongoDB backed journal. Details here. Thanks to Duncan DeVore. | Experimental |
| DynamoDB journal. A DynamoDB backed journal. Details here. Thanks to Scott Clasen. | Experimental |
| Journal.IO journal. Journal.IO backed journal for testing purposes. Messages are persisted. | Testing |
| In memory journal. An in-memory journal for testing purposes. Messages are not persisted. | Testing |
In the following, the terms persistent actor, event-sourced actor, event-sourced processor and processor are used interchangeably. Furthermore, a Message is often referred to as event message.
This section guides through the minimum steps required to create, use and recover an event-sourced actor and demonstrates the usage of channels. Code from this section is contained in FirstSteps.scala and can be executed from the sbt prompt with
> project eventsourced-examples
> run-nobootcp org.eligosource.eventsourced.guide.FirstSteps
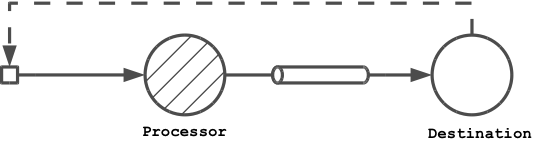
Details about the run-nobootcp task are described here. The legend to the figures used in this and other sections is in Appendix A.
EventsourcingExtension is an Akka extension provided by the Eventsourced library. It is used by applications to
- create and register event-sourced actors (called processors or event processors)
- create and register channels
- recover registered processors and channels from journaled event messages
An EventsourcingExtension is initialized with an ActorSystem and a journal ActorRef.
import java.io.File
import akka.actor._
import org.eligosource.eventsourced.core._
import org.eligosource.eventsourced.journal.leveldb._
val system: ActorSystem = ActorSystem("example")
val journal: ActorRef = Journal(LeveldbJournalProps(new File("target/example-1")))
val extension: EventsourcingExtension = EventsourcingExtension(system, journal)
This example uses a LevelDB based journal but any other journal implementation can be used as well.
Event-sourced actors can be defined as 'plain' actors i.e. they don't need to care about appending received event messages to a journal. For example,
class Processor extends Actor {
var counter = 0
def receive = {
case msg: Message => {
counter = counter + 1
println("[processor] event = %s (%d)" format (msg.event, counter))
}
}
}
is an actor that counts the number of received event Messages. In Eventsourced applications, events are always communicated (transported) via event Messages.
To make Processor an event-sourced actor, it must be modified with the stackable Eventsourced trait during instantiation.
// create and register event-sourced processor
val processor: ActorRef = extension.processorOf(Props(new Processor with Eventsourced { val id = 1 } ))
// recover registered processors by replaying journaled events
extension.recover()
An actor that is modified with Eventsourced writes event Messages to a journal before its receive method is called. The processorOf method registers that actor under a unique id. The processor id is defined by implementing the abstract Eventsourced.id member which must be a positive integer and consistently re-used across applications runs. The recover method recovers the state of processor by replaying all event messages that processor received in previous application runs.
The event-sourced processor can be used like any other actor. Messages of type Message are written to the journal, messages of any other type are directly received by processor without being journaled.
// send event message to processor (will be journaled)
processor ! Message("foo")
A first application run will create an empty journal. Hence, no event messages will be replayed and the processor writes
[processor] event = foo (1)
to stdout. When the application is restarted, however, the processor's state will be recovered by replaying the previously journaled event message. Then, the application sends another event message. You will therefore see
[processor] event = foo (1)
[processor] event = foo (2)
on stdout where the first println is triggered by a replayed event message.
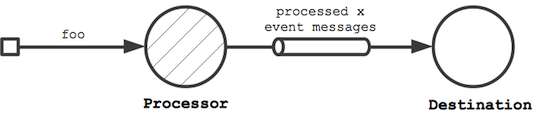
In this step, the event-sourced processor is extended to send out new event messages to a destination. It creates another event message (by making a copy of the received event message) with an updated event field and sends the updated message to destination.
class Processor(destination: ActorRef) extends Actor {
var counter = 0;
def receive = {
case msg: Message => {
counter = counter + 1
// …
destination ! msg.copy(event = "processed %d event messages so far" format counter)
}
}
}
val destination: ActorRef = system.actorOf(Props[Destination])
// instantiate processor by passing the destination as constructor argument
val processor: ActorRef = extension.processorOf(Props(new Processor(destination) with Eventsourced { val id = 1 } ))
extension.recover()
Without any further actions, this would also send event messages to destination during recovery (i.e. during replay of event messages). With every application restart, destination would redundantly receive the whole event message history again and again. This is not acceptable in most cases, such as when destination represents an external service, for example.
To prevent redundant message delivery to destination we need something that remembers which messages have already been successfully delivered. This is exactly the use case for channels. A channel drops all messages that have already been successfully delivered to a destination. We therefore wrap destination by a channel and let the processor communicate with the destination via that channel. This can be done without changing the code of Processor.
val destination: ActorRef = system.actorOf(Props[Destination])
// wrap destination by channel
val channel: ActorRef = extension.channelOf(DefaultChannelProps(1, destination))
// instantiate processor by passing the channel (i.e. wrapped destination) as constructor argument
val processor: ActorRef = extension.processorOf(Props(new Processor(channel) with Eventsourced { val id = 1 } ))
A channel must have a unique id (1 in our example), a positive integer that must be consistently defined across application runs. Here, we create a default channel that is configured with a DefaultChannelProps configuration object. If applications need reliable event message delivery to destinations, they should use a reliable channel that is configured with a ReliableChannelProps configuration object.
Assuming the following definition of a Destination actor
class Destination extends Actor {
def receive = {
case msg: Message => {
println("[destination] event = '%s'" format msg.event)
// confirm receipt of event message from channel
msg.confirm()
}
}
}
and that we're starting again from an empty journal, you should see
[processor] event = foo (1)
[destination] event = 'processed 1 event messages so far'
on stdout during a first application run. When running the application again, you'll see that the event-sourced processor receives the complete event message history but the destination only receives the last event message produced by processor (which corresponds the the single event message sent to processor during the current application run):
[processor] event = foo (1)
[processor] event = foo (2)
[destination] event = 'processed 2 event messages so far'
When receiving event messages from a channel, destinations must confirm the receipt of that message by calling Message.confirm() which asynchronously writes a confirmation (an acknowledgement) to the journal that the message has been successfully delivered. Later, you'll also see how confirmation functionality can be added to destinations with the stackable Confirm trait.
This First steps guide is a rather low-level introduction to the Eventsourced library. More advanced library features are covered in the following sections.
The Eventsourced trait has already been discussed in section First steps. It can be combined with the stackable Receiver, Emitter and/or Confirm traits where the Eventsourced trait must always the last modification i.e.
new MyActor with Receiver with Confirm with Eventsourced
An actor that receives event Messages often wants to pattern-match against the contained event directly instead of the whole event message. This can be achieved by modifying it with the Receiver trait during instantiation.
class MyActor extends Actor {
def receive = {
case event => println("received event %s" format event)
}
}
val myActor = system.actorOf(Props(new MyActor with Receiver))
myActor ! Message("foo")
In the above example, sending Message("foo") to myActor will write received event foo to stdout. The Receiver trait stores the received event message as current event message in a field, extracts the contained event from that message and calls the receive method of MyActor with event as argument. If MyActor wants to have access to the current event message it must be defined with a Receiver self-type and call the message method.
class MyActor extends Actor { this: Receiver =>
def receive = {
case event => {
// obtain current event message
val currentMessage = message
// …
println("received event %s" format event)
}
}
}
The Receiver trait can also be combined with the stackable Eventsourced and/or Confirm traits where Receiver must always be the first modification. For example:
new MyActor with Receiver with Confirm with Eventsourced
Refer to the API docs for further details.
Where a Receiver modification allows actors to pattern-match against incoming events directly instead of whole event Messages, an Emitter introduces a corresponding simplification on the sending (outgoing) side. It allows actors to send (emit) events to channels without having to deal with whole event Messages. An emitter can also lookup channels by name.
class MyActor extends Actor { this: Emitter =>
def receive = {
case event => {
// emit event to channel "myChannel"
emitter("myChannel") sendEvent ("received: %s" format event)
}
}
}
// create register channel under name "myChannel"
extension.channelOf(DefaultChannelProps(1, destination).withName("myChannel"))
val myActor = system.actorOf(Props(new MyActor with Emitter))
Event messages sent by an emitter to a channel are always derived from (i.e. are a copy of) the current event message (an Emitter is also Receiver and maintains a current event message, see also section Receiver). A call to the emitter method with a channel name as argument creates a MessageEmitter object that captures the named channel and the current event message. Calling sendEvent on that object modifies the captured event message with the specified event argument and sends the updated event message to the channel (see also channel usage hints). A MessageEmitter object can also be sent to other actors (or threads) and be used there i.e. a MessageEmitter object is thread-safe. Channels can also be referred to by id when creating a MessageEmitter i.e. there's no need to define a custom channel name:
class MyActor extends Actor { this: Emitter =>
def receive = {
case event => {
// emit event to channel with id 1
emitter(1) sendEvent ("received: %s" format event)
}
}
}
// create register channel
extension.channelOf(DefaultChannelProps(1, destination))
The Emitter trait can also be combined with the stackable Eventsourced and/or Confirm traits where Emitter must always be the first modification. For example:
new MyActor with Emitter with Confirm with Eventsourced
Refer to the API docs for further details.
The receipt of event messages from channels must be confirmed by calling confirm() or confirm(true) on the received event Message. Applications can also negatively confirm an event message receipt by calling confirm(false). This, for example, causes a reliable channel to redeliver the event message.
Instead of calling confirm(true) or confirm(false) explicitly, actors can also be modified with the stackable Confirm trait. This trait calls confirm(true) on the received event message when the modified actor's receive method returns normally and confirm(false) when it throws an exception.
This trait can either be used standalone
new MyActor with Confirm
or in combination with the stackable Receiver, Emitter and/or Eventsourced traits where the Confirm modification must be made after a Receiver or Emitter modification but before an Eventsourced modification. For example:
new MyActor with Receiver with Confirm with Eventsourced
Refer to the API docs for further details.
This section modifies (and simplifies) the example from section First steps by making use of the stackable Receiver, Emitter and Confirm traits. In particular
Processorwill be modified withEmitter(in addition toEventsourced)Destinationwill be modified withReceiverandConfirm
Code from this section is contained in StackableTraits.scala and can be executed from the sbt prompt with
> project eventsourced-examples
> run-nobootcp org.eligosource.eventsourced.guide.StackableTraits
The new definition of Processor
class Processor extends Actor { this: Emitter =>
var counter = 0
def receive = {
case event => {
counter = counter + 1
println("[processor] event = %s (%d)" format (event, counter))
emitter("destination") sendEvent ("processed %d events so far" format counter)
}
}
}
now has a self-type Emitter and pattern-matches against events directly. Instead of passing the channel via the constructor it is now looked-up by name ("destination"). The channel name is specified during channel creation.
extension.channelOf(DefaultChannelProps(1, destination).withName("destination"))
Processor must be instantiated with an additional Emitter modification to conform to the Processor self-type.
val processor: ActorRef = extension.processorOf(Props(new Processor with Emitter with Eventsourced { val id = 1 } ))
The new definition of Destination
class Destination extends Actor {
def receive = {
case event => {
println("[destination] event = '%s'" format event)
}
}
}
pattern-matches against events directly and leaves event message receipt confirmation to the Confirm trait. Destination must be instantiated with a Receiver and a Confirm modification.
val destination: ActorRef = system.actorOf(Props(new Destination with Receiver with Confirm))
The Eventsourced library preserves sender references for all
- message exchanges with actors that are modified with
Eventsourced,Receiver,Emitterand/orConfirmand - message exchanges with destination actors via channels
i.e. event-sourced actor applications can make use of sender references in the same way as plain actor applications. If you know how sender references work with Akka actors, the following will sound familiar to you.
For example, taking the code from section First steps as a starting point, Processor can be extended to reply to message senders as follows.
class Processor(destination: ActorRef) extends Actor {
// …
def receive = {
case msg: Message => {
// …
// reply to sender
sender ! ("done processing event = %s" format msg.event)
}
}
}
Applications can now ask the processor and will get a response asynchronously.
processor ? Message("foo") onSuccess {
case response => println(response)
}
No surprise here. The sender reference in this example represents the future that is returned from the ? method call. But what happens during a replay? During a replay, the sender reference will be deadLetters because Eventsourced processors don't store sender references in the journal. The main reason for this is that applications usually do not want to redundantly reply to senders during replays.
Instead of replying to the sender, the processor can also forward the sender reference to a destination and let the destination reply to the sender. This even works if the destination is wrapped by a channel because a channel simply forwards sender references when delivering event messages to destinations. For that reason, a ReliableChannel needs to store sender references (in contrast to processors). A reliable channel destination can even reply to a sender that was sending an event message in a previous application run (e.g. before the application crashed). If that sender doesn't exist any more after recovery, the reply will go to deadLetters.
class Processor(destination: ActorRef) extends Actor {
var counter = 0
def receive = {
case msg: Message => {
// …
// forward modified event message to destination (together with sender reference)
destination forward msg.copy(event = "processed %d event messages so far" format counter)
}
}
}
class Destination extends Actor {
def receive = {
case msg: Message => {
// …
// reply to sender
sender ! ("done processing event = %s (%d)" format msg.event)
}
}
}
val destination: ActorRef = system.actorOf(Props[Destination])
val channel: ActorRef = extension.channelOf(DefaultChannelProps(1, destination))
val processor: ActorRef = extension.processorOf(Props(new Processor(channel) with Eventsourced { val id = 1 } ))
When using a MessageEmitter (see also section Emitter) applications can choose between methods sendEvent and forwardEvent where sendEvent takes an implicit sender reference as parameter and forwardEvent forwards the current sender reference. They work in the same way as the ! and forward methods on ActorRef, respectively.
Code from this section is contained in SenderReferences.scala and can be executed from the sbt prompt with
> project eventsourced-examples
> run-nobootcp org.eligosource.eventsourced.guide.SenderReferences
A channel is an actor that keeps track of successfully delivered event messages. Channels are used by event-sourced actors (processors) to prevent redundant message delivery to destinations during event message replay. See also section External Updates in Martin Fowler's Event Sourcing article as well as section Channel usage in the First steps guide for an example.
Currently, the library provides two different channel implementations, DefaultChannel and ReliableChannel, and a pattern on top of ReliableChannel, a reliable request-reply channel. These are explained in the following subsections.
A default channel is a transient channel that delivers event messages to a destination actor. When the destination confirms the delivery of an event message by calling either confirm() or confirm(true) on the received Message object, a confirmation (an acknowledgement) is asynchronously written to the journal. During a replay, event messages for which a confirmation exists won't be delivered again to the destination.
Event messages that are negatively confirmed by the destination (via a call to confirm(false) on the received event message) will be re-delivered during the next event message replay. This is also the case for event messages for which no confirmation has been made. Therefore, in cases of negative or missing confirmations, the order of event messages received by a destination from a default channel may differ from the order of event messages produced by an event-sourced processor.
A DefaultChannel is created and registered at an EventsourcingExtension as follows.
val extension: EventsourcingExtension = …
val destination: ActorRef = …
val channelId: Int = …
val channel: ActorRef = extension.channelOf(DefaultChannelProps(channelId, destination))
The channelId must be a positive integer and consistently defined across application runs. The map of registered channels can be obtained via the channels method of EventsourcingExtension which returns a map of type Map[Int, ActorRef] where the mapping key is the channel id. Channels can optionally be registered under a custom name (see also section Emitter).
// …
val channelId: Int = …
val channelName: String = …
val channel: ActorRef = extension.channelOf(DefaultChannelProps(channelId, destination).withName(channelName))
The map of registered named channels can be obtained via the namedChannels method which returns a map of type Map[String, ActorRef] where the mapping key is the channel name.
A reliable channel is a persistent channel that writes event messages to a journal before delivering them to a destination actor. In contrast to a default channel, a reliable channel preserves the order of messages as produced by an event-sourced processor and attempts to re-deliver event messages on destination failures. Therefore, a reliable channel enables applications to recover from temporary destination failures without having to run an event message replay.
If a destination positively confirms the receipt of an event message, the stored message is removed from the channel and the next one is delivered. If a destination negatively confirms the receipt of an event message or if no confirmation is made (i.e. a timeout occurs), a re-delivery attempt is made after a certain redelivery delay. If the maximum number of re-delivery attempts have been made, the channel restarts itself after a certain restart delay and starts again with re-deliveries. If the maximum number of restarts has been reached, the channel stops message delivery and publishes a DeliveryStopped event to the event stream of the actor system this channel belongs to. Applications can then re-activate the channel by calling the deliver(Int) method of EventsourcingExtension with the channel id as argument. Refer to the ReliableChannel API docs for details.
A ReliableChannel is created and registered in the same way as a default channel except that a ReliableChannelProps configuration object is used.
// …
val channel: ActorRef = extension.channelOf(ReliableChannelProps(channelId, destination))
This configuration object additionally allows applications to configure a RedeliveryPolicy for the channel.
A reliable request-reply channel is a pattern implemented on top of a reliable channel. It mediates reliable request-reply interactions between a request sender (usually an Eventsourced processor) and a destination. This channel has the following properties in addition to a plain reliable channel. It
- extracts requests from received
Messages before sending them to the destination. - wraps replies from the destination into a
Messagebefore sending them back to the request sender. - sends a special
DestinationNotRespondingreply to the request sender if the destination doesn't reply within a configurable reply timeout. - sends a special
DestinationFailurereply to the request sender if destination responds withStatus.Failure. - guarantees at-least-once delivery of replies to the request sender (in addition to at-least-once delivery of requests to the destination).
- requires a positive receipt confirmation for a reply to mark a request-reply interaction as successfully completed.
- redelivers requests, and subsequently replies, on missing or negative receipt confirmations.
A reliable request-reply channel is created and registered in the same way as a reliable channel except that a ReliableRequestReplyChannelProps configuration object is used.
// …
import org.eligosource.eventsourced.patterns.reliable.requestreply._
val channel: ActorRef = extension.channelOf(ReliableRequestReplyChannelProps(channelId, destination))
This configuration object additionally allows applications to configure a replyTimeout for replies from the destination. A detailed usage example of a reliable request-reply channel is given in this article.
For channels to work properly, event-sourced processors must copy the processorId and sequenceNr values from a received (and journaled) input event message to output event messages. This is usually done by calling copy() on the received input event message and updating only those fields that are relevant for the application such as event or ack, for example:
class Processor(channel: ActorRef) extends Actor {
def receive = {
case msg: Message => {
// …
channel ! msg.copy(event = …, ack = …)
}
}
}
When using a message emitter, this is done automatically.
Reliable channels and reliable request-reply channels can also be used independently of Eventsourced processors (i.e. standalone). For standalone channel usage, senders must set the Message.processorId of the sent Message to 0 (which is the default value):
val channel = extension.channelOf(ReliableChannelProps(…))
channel ! Message("my event") // processorId == 0
This is equivalent to directly sending the Message.event:
channel ! "my event"
A reliable channel internally wraps a received event into a Message with processorId set to 0. Setting the processorId to 0 causes a reliable channel to skip writing an acknowledgement. An acknowledgement always refers to an event message received by an Eventsourced processor, so there's no need to write one in this case. Another (unrelated) use case for turning off writing acknowledgements is the emission of event message series in context of event-sourced channel usage.
A less reliable alternative to channels is communication via sender references. This means producing event messages to destinations that have been passed to a processor via sender references (along with an input event message). These sender references will be deadLetters during a replay which also prevents redundant delivery. The main difference, however, is that the delivery guarantee changes from at-least-once to at-most-once.
Recovery is a procedure that re-creates the state of event-sourced applications consisting of Eventsourced actors (processors) and channels. Recovery is usually done at application start, either after normal termination or after a crash.
val system: ActorSystem = …
val journal: ActorRef = …
val extension = EventsourcingExtension(system, journal)
// create and register event-sourced processors
extension.processorOf(…)
// …
// create and register channels
extension.channelOf(…)
// …
// recover state of registered processors and activate channels
extension.recover()
// processors and channels are now ready to use
// …
The recover() method first replays journaled event messages to all registered processors. By replaying the event message history, processors can recover state. Processors that emit event messages to one or more channels will also do so during replay. These channels will either ignore (discard) event messages that have already been successfully delivered (i.e. acknowledged) in previous application runs or buffer them for later delivery. After replay, the recover() method triggers the delivery of buffered messages by activating channels.
If channels delivered event messages immediately instead of buffering them, delivered event messages could wrongly interleave with replayed event messages. This could lead to inconsistencies in event message ordering across application runs and therefore to inconsistencies in application state. Therefore, recovery must ensure that buffered event messages are only delivered after all replayed event messages have been added to their corresponding processors' mailboxes. This is especially important for the recovery of processors and channels that are connected to cyclic, directed graphs.
Recovery can be parameterized with replay parameters using the EventsourcingExtension.recover(Seq[ReplayParams]) method (or one of its overloaded definitions). ReplayParams allow fine-grained control over state recovery of individual processors. For each processor to be recovered, an application must create a ReplayParams instance. ReplayParams specify
- whether replay should start from scratch, from a snapshot or from a given sequence number (lower sequence number bound).
- whether replay should end at current state or any state in the past (using an upper sequence number bound)
The following two subsections demonstrate some ReplayParams usage examples. For more details, refer to the API docs of ReplayParams and its companion object. For details about snapshot creation refer to the Snapshots section.
As already explained above
val extension: EventsourcingExtension = …
import extension._
recover()
recovers all processors with no lower and upper sequence number bound i.e. all event messages are replayed. This is equivalent to
recover(replayParams.allFromScratch)
or
recover(processors.keys.map(pid => ReplayParams(pid)).toSeq)
If an application only wants to recover specific processors it should create ReplayParams only for these processors. For example
recover(Seq(ReplayParams(1), ReplayParams(2)))
only recovers processors with ids 1 and 2. Upper and lower sequence number bounds can be specified as well.
recover(Seq(ReplayParams(1, toSequenceNr = 12651L), ReplayParams(2, fromSequenceNr = 10L)))
Here processor 1 will receive replayed event messages with sequence numbers within range 0 and 12615 (inclusive), processor 2 with receive event messages with sequence numbers starting from 10 with no upper sequence number bound.
During snapshot based recovery, a processor receives a SnapshotOffer message before receiving the remaining event messages (if there are any). A processor uses a SnapshotOffer message to restore its state.
class Processor extends Actor {
var state = ...
def receive = {
case so: SnapshotOffer => state = so.snapshot.state
...
}
}
Snapshot based recovery will only send a SnapshotOffer message to a processor if one or more snapshots have been created for that processor before and these snapshots match the criteria in the corresponding ReplayParams. Relevant criteria are toSequenceNr and snapshotFilter. If there are no snapshots for a processor or existing snapshots do not match ReplayParams criteria, event messages will be replayed from scratch i.e. from sequence number 0.
To recover all processors from their latest snapshot
recover(replayParams.allWithSnapshot)
can be used. This is equivalent to
recover(processors.keys.map(pid => ReplayParams(pid, snapshot = true)).toSeq)
Snapshot based recovery can also be made with upper sequence number bound.
recover(Seq(ReplayParams(1, snapshot = true, toSequenceNr = 12651L)))
This recovers processor 1 with the latest snapshot that has a sequence number <= 12561. Remaining event messages (if there are any) are replayed up to sequence number 12561 (inclusive). Applications may also define further constraints on snapshots. For example
import scala.concurrent.duration._
val limit = System.currentTimeMillis - 24.hours.toMillis
recover(Seq(ReplayParams(1, snapshotFilter = snapshotMetadata => snapshotMetadata.timestamp < limit)))
uses the latest snapshot of processor 1 that is older than 24 hours. This is done with a snapshotFilter that filters snapshots based on their timestamp. Snapshot filters operate on SnapshotMetadata.
The recover method waits for replayed messages being sent to all processors (via !) but does not wait for replayed event messages being processed by these processors. However, any new message sent to any registered processor, after recover successfully returned, will be processed after the replayed event messages. Applications that want to wait for processors to complete processing of replayed event messages, should use the awaitProcessing() method of EventsourcingExtension.
val extension: EventsourcingExtension = …
extension.recover()
extension.awaitProcessing()
This can be useful in situations where event-sourced processors maintain state via STM references and the application wants to ensure that the (externally visible) state is fully recovered before accepting new read requests from client applications. By default, the awaitProcessing() method waits for all registered processors to complete processing but applications can also specify a subset of registered processors.
The recover and awaitProcessing methods block the calling thread. This may be convenient in scenarios where a main thread wants to recover the state of an event-sourced application before taking any further actions. In other scenarios, for example, where recovery is done for individual child processors (and channels) inside an actor (see OrderExampleReliable.scala), the non-blocking recovery API should be used:
val extension: EventsourcingExtension = …
val future = for {
_ <- extension.replay(…)
_ <- extension.deliver(…) // optional
_ <- extension.completeProcessing(…) // optional
} yield ()
future onSuccess {
case _ => // event-sourced processors now ready to use …
}
The futures returned by replay, deliver and completeProcessing are monadically composed with a for-comprehension which ensures a sequential execution of the corresponding asynchronous operations. When the composite future completes, the recovered processors and channels are ready to use. More details in the API docs. The replay method can also be parameterized with a ReplayParams sequence (see section Replay parameters).
The behavior of Eventsourced processors may depend on the state of other Eventsourced processors. For example, processor A sends a message to processor B and processor B replies with a message that includes (part of) processor B's state. Depending on the state value included in the reply, processor A may take different actions. To ensure a proper recovery of such a setup, any state-conveying or state-dependent messages exchanged between processors A and B must be of type Message (see also DependentStateRecoverySpec.scala). Exchanging state via non-journaled messages (i.e. messages of type other than Message) can break consistent recovery. This is also the case if an Eventsourced processor maintains state via an externally visible STM reference and another Eventsourced processor directly reads from that reference. Communication between Eventsourced processors is closely related to external queries and external updates.
Snapshots represent processor state at a certain point in time and can dramatically reduce recovery times. Snapshot capturing and saving is triggered by applications. Saving is done in a journal-specific way. At the moment, the following journals support snapshotting:
- HBase journal: saves snapshots to a configurable Hadoop
FileSystem. By default the local filesystem is used. Production deployments should use another filesystem (HDFS, for example). - LevelDB journal: saves snapshots to the local filesystem.
- Journal.IO journal: saves snapshots to the local filesystem.
- In-memory journal: keeps snapshots in-memory only.
Snapshot capturing and saving does not delete entries from the event message history unless explicitly requested by an application.
Applications can create snapshots by sending a processor the SnapshotRequest message.
import org.eligosource.eventsourced.core._
// …
val processor: ActorRef = …
processor ! SnapshotRequest
This will asynchronously capture and save a snapshot of processor's state. The sender will be notified when the snapshot has been successfully saved.
processor ? SnapshotRequest onComplete {
case Success(SnapshotSaved(processorId, sequenceNr, timestamp)) => …
case Failure(e) => …
}
Alternatively, applications may also use the EventsourcingExtension.snapshot method to trigger snapshot creation. For example,
val extension: EventsourcingExtension = ...
extension.snapshot(Set(1, 2)) onComplete {
case Success(snapshotSavedSet) => …
case Failure(_) => …
}
creates snapshots of processors with ids 1 and 2. The returned future (of type Future[Set[SnapshotSaved]]) successfully completes when the snapshots of both processors have been successfully saved.
To participate in snapshot capturing, a processor must process SnapshotRequest messages by calling their process method with its current state as argument:
class Processor extends Actor {
var state = …
def receive = {
case sr: SnapshotRequest => sr.process(state)
…
}
}
Calling process will asynchronously save the state argument together with (generated) snapshot metadata. Creating a new snapshot does not delete older snapshots unless explicitly requested by an application. Hence, there can be n snapshots per processor.
An example that demonstrates snapshot creation and snapshot based recovery is contained in SnapshotExample.scala. It can be executed from the sbt prompt with
> project eventsourced-examples
> run-nobootcp org.eligosource.eventsourced.example.SnapshotExample
Actors that are modified with a stackable Receiver, Emitter and/or Eventsourced trait can change their behavior with the methods become() and unbecome(). These are defined on the Behavior trait from which Receiver, Emitter and Eventsourced inherit.
Actors that change their behavior with become() and unbecome() will keep the functionality introduced by a stackable Receiver, Emitter and/or Eventsourced trait. For example, an actor that is modified with the Eventsourced trait will continue to journal event messages after having changed its behavior with become().
On the other hand, actors that change their behavior with context.become() will loose the functionality introduced by the stackable Receiver, Emitter and/or Eventsourced traits (although the lost behavior can be recovered with context.unbecome()).
When a processor derives more than one output event message from a single input event message and emits those output messages to a single channel, it generates a series of event messages. For an event message series, the event processor should set the ack field for all but the last emitted message to false.
class Processor(channel: ActorRef) extends Actor {
def receive = {
case msg: Message => {
// …
channel ! msg.copy(event = "event 1", ack = false) // 1st message of series
channel ! msg.copy(event = "event 2", ack = false) // 2nd message of series
// …
channel ! msg.copy(event = "event n") // last message of series
}
}
}
Processors that use an emitter do that in the following way.
class Processor extends Actor { this: Emitter =>
def receive = {
case event => {
// …
emitter("channelName") send (msg => msg.copy(event = "event 1", ack = false)) // 1st message of series
emitter("channelName") send (msg => msg.copy(event = "event 2", ack = false)) // 2nd message of series
// …
emitter("channelName") sendEvent "event n"
}
}
}
This ensures that an acknowledgement is only written to the journal after the last message of a series has been successfully
- delivered by a default channel or
- stored by a reliable channel
Destinations, however, should confirm the receipt of every event message, regardless whether it belongs to a series or not.
Under certain failure conditions, channels may deliver event messages to destinations more than once. A typical example is that a destination positively confirms a message receipt but the application crashes shortly before that confirmation can be written to the journal. In this case, the destination will receive the event message again during recovery.
For these (but also other) reasons, channel destinations must be idempotent event message consumers which is an application-level concern. For example, an event message consumer that stores received purchase orders in a map (where the map key is the order id) is likely to be an idempotent consumer because receiving a purchase order only once or several times will lead to the same result: the purchase order is contained in the map only once. An event message consumer that counts the number of received purchase orders is not an idempotent consumer: a re-delivery will lead to a wrong counter value from a business logic perspective. In this case the event message consumer must implement some extra means to detect event message duplicates.
For detecting duplicates, applications should use identifiers with their events. Identifier values should be set by an event-sourced processor before an event is emitted via a channel. Channel destinations (or other downstream consumers) should keep track of identifiers of successfully processed events and compare them to identifiers of newly received events. A newly received event with an already known identifier can be considered as a duplicate (assuming that the emitting processor generates unique identifiers). For generating unique identifiers, processors can use the sequence number of received event messages:
case class MyEvent(details: Any, eventId: Long)
class Processor extends Actor { this: Emitter with Eventsourced =>
def receive = {
case event => {
// get sequence number of current event message
val snr: Long = sequenceNr
val details: Any = …
// …
emitter("channelName") sendEvent MyEvent(details, snr)
}
}
}
Using the sequence number has the advantage that consumers of emitted events only need to remember the identifier of the last successfully consumed event. If the identifier of a newly received event is less than or equal to that of the last consumed event then it is a duplicate and can therefore be ignored.
class Consumer extends Actor {
var lastEventId = 0L
def receive = {
case MyEvent(details, eventId) =>
if (eventId <= lastEventId) {
// duplicate
} else {
// ...
lastEventId = eventId
}
}
}
Consumers that are event-sourced processors can store the event identifier as part of their state which will be recovered during an event message replay. Other consumers must store the identifier somewhere else.
Processors that emit event message series should use an event message index in addition to the sequence number to uniquely identify an emitted event:
case class MyEvent(details: Any, eventId: (Long, Int))
class Processor extends Actor { this: Emitter with Eventsourced =>
def receive = {
case event => {
// get sequence number of current event message
val snr: Long = sequenceNr
val details: Seq[Any] = …
// …
emitter("channelName") send (msg => msg.copy(event = MyEvent(details(0), (snr, 0)), ack = false))
emitter("channelName") send (msg => msg.copy(event = MyEvent(details(1), (snr, 1)), ack = false))
// …
}
}
}
Consumers should then compare the sequence number - index pairs for detecting duplicates.
Applications can configure custom serializers for events of event Messages. Custom serializers are used for both, writing the event to a journal and for remote communication. They can be configured like any other Akka serializer. For example:
akka {
actor {
serializers {
custom = "example.MyEventSerializer"
}
serialization-bindings {
"example.MyEvent" = custom
}
}
}
Here, example.MyEvent is an application-specific event type and example.MyEventSerializer is an application-specific serializer that extends akka.serialization.Serializer
import akka.serialization.Serializer
class CustomEventSerializer extends Serializer {
def identifier = …
def includeManifest = true
def toBinary(o: AnyRef) = …
def fromBinary(bytes: Array[Byte], manifest: Option[Class[_]]) = …
}
Event Messages themselves are serialized with a pre-configured, library-specific serializer. This serializer is automatically used for event Messages when the eventsourced-journal-common-*.jar is on the classpath of an Akka application.
The order management example in this section is taken from Martin Fowler's great LMAX article:
Imagine you are making an order for jelly beans by credit card. A simple retailing system would take your order information, use a credit card validation service to check your credit card number, and then confirm your order - all within a single operation. The thread processing your order would block while waiting for the credit card to be checked, but that block wouldn't be very long for the user, and the server can always run another thread on the processor while it's waiting.
In the LMAX architecture, you would split this operation into two. The first operation would capture the order information and finish by outputting an event (credit card validation requested) to the credit card company. The Business Logic Processor would then carry on processing events for other customers until it received a credit-card-validated event in its input event stream. On processing that event it would carry out the confirmation tasks for that order.
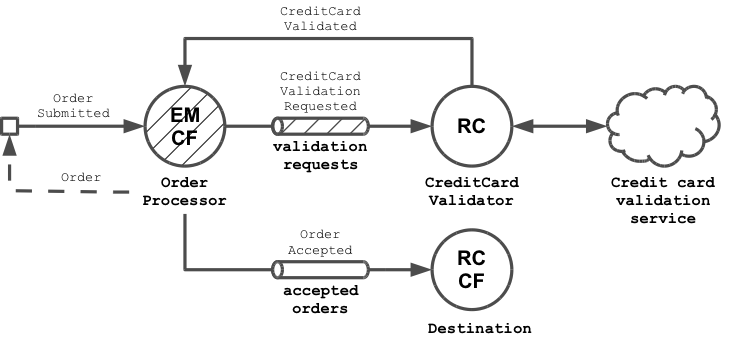
This can be implemented with the Eventsourced library as shown in the following diagram (legend is in Appendix A).
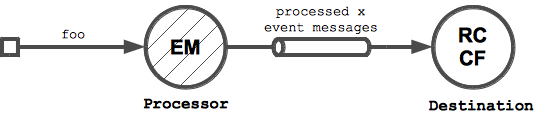
- We implement the mentioned Business Logic Processor processor as event-sourced actor (
OrderProcessor). It processesOrderSubmittedevents by assigning submitted orders an id and storing them in a map (= state ofOrderProcessor). For every submitted order it emits aCreditCardValidationRequestedevent. CreditCardValidationRequestedevents are processed by aCreditCardValidatoractor. It contacts an external credit card validation service and sendsCreditCardValidatedevents back to theOrderProcessorfor every order with a valid credit card number. In the example implementation below, we won't actually use an external service to keep the implementation simple, but for real-world implementations, akka-camel would be a perfect fit here.- On receiving a
CreditCardValidatedevent, the event-sourcedOrderProcessorupdates the status of corresponding order tovalidated = trueand sends anOrderAcceptedevent, containing the updated order, toDestination. It also replies the updated order to the initial sender.
The Order domain object, the domain events and the OrderProcessor are defined as follows:
// domain object
case class Order(id: Int = -1, details: String, validated: Boolean = false, creditCardNumber: String)
// domain events
case class OrderSubmitted(order: Order)
case class OrderAccepted(order: Order)
case class CreditCardValidationRequested(order: Order)
case class CreditCardValidated(orderId: Int)
// event-sourced order processor
class OrderProcessor extends Actor { this: Emitter =>
var orders = Map.empty[Int, Order] // processor state
def receive = {
case OrderSubmitted(order) => {
val id = orders.size
val upd = order.copy(id = id)
orders = orders + (id -> upd)
emitter("validation_requests") forwardEvent CreditCardValidationRequested(upd)
}
case CreditCardValidated(orderId) => {
orders.get(orderId).foreach { order =>
val upd = order.copy(validated = true)
orders = orders + (orderId -> upd)
sender ! upd
emitter("accepted_orders") sendEvent OrderAccepted(upd)
}
}
}
}
The OrderProcessor uses a message emitter to send CreditCardValidationRequested events to CreditCardValidator via the named "validation_requests" channel. The forwardEvent method not only sends the event but also forwards the initial sender reference. Upon receiving a CreditCardValidationRequested event, the CreditCardValidator runs a credit card validation in the background and sends a CreditCardValidated event back to the OrderProcessor
class CreditCardValidator(orderProcessor: ActorRef) extends Actor { this: Receiver =>
def receive = {
case CreditCardValidationRequested(order) => {
val sdr = sender // initial sender
val msg = message // current event message
Future {
// do some credit card validation
// ...
// and send back a successful validation result (preserving the initial sender)
orderProcessor tell (msg.copy(event = CreditCardValidated(order.id)), sdr)
}
}
}
}
The CreditCardValidator again forwards the initial sender reference which finally enables the OrderProcessor to reply to the initial sender when it receives the CreditCardValidated event. The OrderProcessor also sends an OrderAccepted event to Destination via the named "accepted_orders" channel.
class Destination extends Actor {
def receive = {
case event => println("received event %s" format event)
}
}
Next step is to wire the collaborators and to recover them:
val extension: EventsourcingExtension = …
val processor = extension.processorOf(Props(new OrderProcessor with Emitter with Confirm with Eventsourced { val id = 1 }))
val validator = system.actorOf(Props(new CreditCardValidator(processor) with Receiver))
val destination = system.actorOf(Props(new Destination with Receiver with Confirm))
extension.channelOf(ReliableChannelProps(1, validator).withName("validation_requests"))
extension.channelOf(DefaultChannelProps(2, destination).withName("accepted_orders"))
extension.recover()
The named "validation requests" channel is a reliable channel that re-delivers CreditCardValidationRequested events in case of CreditCardValidator failures (for example, when the external credit card validation service is temporarily unavailable). Furthermore, it should be noted that the CreditCardValidator does not confirm event message deliveries (it neither calls confirm() explicitly nor is it modified with the Confirm trait during instantiation). Delivery confirmation will take place when the OrderProcessor successfully processed the CreditCardValidated event.
The Order processor is now ready to receive OrderSubmitted events.
processor ? Message(OrderSubmitted(Order(details = "jelly beans", creditCardNumber = "1234-5678-1234-5678"))) onSuccess {
case order: Order => println("received response %s" format order)
}
Running this example with an empty journal will write
received response Order(0,jelly beans,true,1234-5678-1234-5678)
received event OrderAccepted(Order(0,jelly beans,true,1234-5678-1234-5678))
to stdout. You may observe a different line ordering when running the example. The submitted order was assigned an id of 0 which corresponds to the initial size of the OrderProcessor's orders map. A second application run will first recover the previous application state, so that another order submission will generate an order id of 1.
received response Order(1,jelly beans,true,1234-5678-1234-5678)
received event OrderAccepted(Order(1,jelly beans,true,1234-5678-1234-5678))
The example code is contained in OrderExample.scala and can be executed from the sbt prompt with
> project eventsourced-examples
> run-nobootcp org.eligosource.eventsourced.example.OrderExample
An advanced version of this example, using a reliable request-reply channel, is discussed in Event sourcing and external service integration.
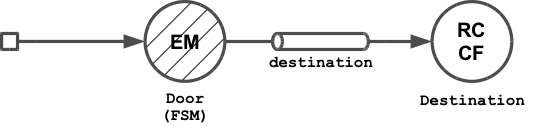
With a change since Akka 2.1, event-sourcing Akka FSMs is now pretty easy. The following state machine example is a Door which can be in one of two states: Open and Closed.
sealed trait DoorState
case object Open extends DoorState
case object Closed extends DoorState
case class DoorMoved(state: DoorState, times: Int)
case class DoorNotMoved(state: DoorState, cmd: String)
case class NotSupported(cmd: Any)
class Door extends Actor with FSM[DoorState, Int] { this: Emitter =>
startWith(Closed, 0)
when(Closed) {
case Event("open", counter) => {
emit(DoorMoved(Open, counter + 1))
goto(Open) using(counter + 1)
}
}
when(Open) {
case Event("close", counter) => {
emit(DoorMoved(Closed, counter + 1))
goto(Closed) using(counter + 1)
}
}
whenUnhandled {
case Event(cmd @ ("open" | "close"), counter) => {
emit(DoorNotMoved(stateName, "cannot %s door" format cmd))
stay
}
case Event(cmd, counter) => {
emit(NotSupported(cmd))
stay
}
}
def emit(event: Any) = emitter("destination") forwardEvent event
}
On state changes, a door emits DoorMoved events to the named "destination" channel. DoorMoved events contain the door's current state and the number of moves so far. On invalid attempts to move a door e.g. trying to open an opened door, a DoorNotMoved event is emitted. The channel destination is an actor that simply prints received events to stdout.
class Destination extends Actor {
def receive = { case event => println("received event %s" format event) }
}
After configuring the application
val system: ActorSystem = …
val extension: EventsourcingExtension = …
val destination = system.actorOf(Props(new Destination with Receiver with Confirm))
extension.channelOf(DefaultChannelProps(1, destination).withName("destination"))
extension.processorOf(Props(new Door with Emitter with Eventsourced { val id = 1 } ))
extension.recover()
val door = extension.processors(1)
we can start sending event messages to door:
door ! Message("open")
door ! Message("close")
This will write
received event DoorMoved(Open,1)
received event DoorMoved(Closed,2)
to stdout. When trying to attempt an invalid state change with
door ! Message("close")
the destination will receive a DoorNotMoved event:
received event DoorNotMoved(Closed,cannot close door)
Restarting the example application will recover the door's state so that
door ! Message("open")
door ! Message("close")
will produce
received event DoorMoved(Open,3)
received event DoorMoved(Closed,4)
The code from this section is contained in slightly modified form in FsmExample.scala.
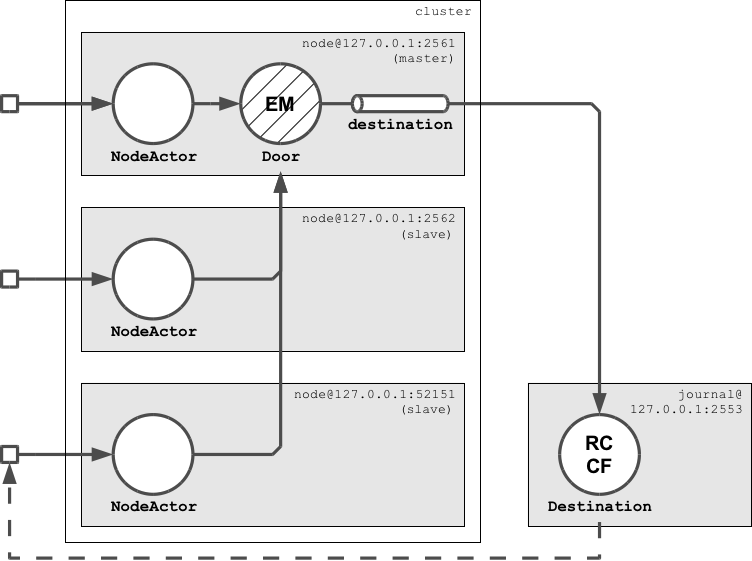
This section makes the Door state machine from the previous example highly-available in an Akka cluster. The Door state machine is a cluster-wide singleton that is managed by NodeActors. There's one NodeActor per cluster node listening to cluster events. If a NodeActor becomes the master (= leader) it creates and recovers a Door instance. The other NodeActors obtain a remote reference to the Door instance on master.
Clients interact with the Door singleton via NodeActors by sending them door commands ("open" or "close"). NodeActors accept commands on any cluster node, not only on master. A NodeActor forwards these commands to the Door as command Messages. Event Messages emitted by the Door are sent to a remote Destination actor via the named "destination" channel. The Destination creates a response from the received events and sends that response back to the initial sender. The application that runs the Destination actor is not part of the cluster but a standalone remote application. It also hosts the journal that is used by the cluster nodes (which is a SPOF in this example but later versions will use a distributed journal).
When the master crashes, another node in the cluster becomes the master and recovers the Door state machine. The remaining slave node renews its remote reference to the Door instance on the new master.
Code from this section is contained in ClusterExample.scala, the configuration files used are journal.conf and cluster.conf. For a more detailed description of the example code, refer to the code comments. To run the distributed example application from sbt, first start the application that hosts the Destination actor and the journal:
> run-main org.eligosource.eventsourced.example.Destination
Then start the first seed node of the cluster
> run-main org.eligosource.eventsourced.example.Node 2561
then the second seed node
> run-main org.eligosource.eventsourced.example.Node 2562
and finally a third cluster node
> run-main org.eligosource.eventsourced.example.Node
The above commands require that you're in the eventsourced-examples project. You can switch to it via
> project eventsourced-examples
Most likely the first seed node will become the master which writes
MASTER: recovered door at akka://[email protected]:2561
to stdout. The other nodes become slaves that write
SLAVE: referenced door at akka://[email protected]:2561
to stdout. All nodes prompt the user to enter a door command:
command (open|close):
We will now enter commands on the last started cluster node (a slave node).
The Door singleton is initially in closed state. Entering open will open it:
command (open|close): open
moved 1 times: door now open
Then close it again:
command (open|close): close
moved 2 times: door now closed
Trying to close a closed door will result in an error:
command (open|close): close
cannot close door: door is closed
Now kill the master node with ctrl^c. This will also destroy the Door singleton. After 1-2 seconds, a new master has been determined by the cluster. The new master is going to recover the event-sourced Door singleton. The slave will renew its remote reference to the Door. To verify that the Door has been properly recovered, open the door again:
command (open|close): open
moved 3 times: door now open
You can see that the Door state (which contains the number of past moves) has been properly failed-over.
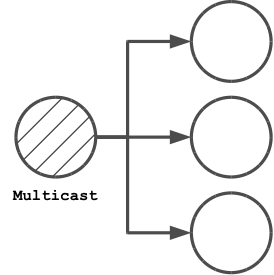
The Multicast processor is a predefined Eventsourced processor that forwards received event messages to multiple targets. Using a Multicast processor with n targets is an optimization of having n Eventsourced processors that receive the same event Messages. Using a multicast processor, a received event message is journaled only once whereas with n Eventsourced processors that message would be journaled n times (once for each processor). Using a Multicast processor for a large number of targets can therefore significantly save disk space and increase throughput.
Applications can create a Multicast processor with the multicast factory method which is defined in package core.
// …
import org.eligosource.eventsourced.core._
val extension: EventsourcingExtension = …
val processorId: Int = …
val target1: ActorRef = …
val target2: ActorRef = …
val multicast = extension.processorOf(Props(multicast(processorId, List(target1, target2))))
This is equivalent to
val multicast = extension.processorOf(Props(new Multicast(List(target1, target2), identity) with Eventsourced { val id = processorId } ))
Applications that want to modify received event Messages, before they are forwarded to targets, can specify a transformer function.
val transformer: Message => Any = msg => msg.event
val multicast = extension.processorOf(Props(multicast(1, List(target1, target2), transformer)))
In the above example, the transformer function extracts the event from a received event Message. If the transformer function is not specified, it defaults to the identity function. Another Multicast factory method is the decorator method for creating a multicast processor with a single target.
TODO
- Eventsourced user forum
- Eventsourced developer forum
- Commercial support by Eligotech B.V.