MNIST Handwritten Digit Classification
This code demonstrates how to build, train, and evaluate a convolutional neural network (CNN) for classifying handwritten digits from the MNIST dataset using TensorFlow and Keras.
1. Dependencies
The code requires the following Python libraries:
- TensorFlow
- Keras
- Matplotlib
- NumPy
2. Data Loading and Preprocessing
The code begins by loading the MNIST dataset using the tf.keras.datasets.mnist function. This function returns two tuples:
- The first tuple contains the training data (
x_trainandy_train). - The second tuple contains the test data (
x_testandy_test).
The MNIST dataset consists of grayscale images of handwritten digits (0-9). Each image is 28x28 pixels. The labels (y_train and y_test) are integers representing the digit class (0-9).
The code then normalizes the pixel values of both the training and test images by dividing them by 255.0. This normalization step helps improve the training process.
3. Training and Validation Split
The code splits the training data into two sets: training and validation sets. The validation set is used to monitor the model's performance during training and prevent overfitting.
The validation_split variable controls the proportion of the training data to be used for validation. In this case, 20% of the training data is used for validation.
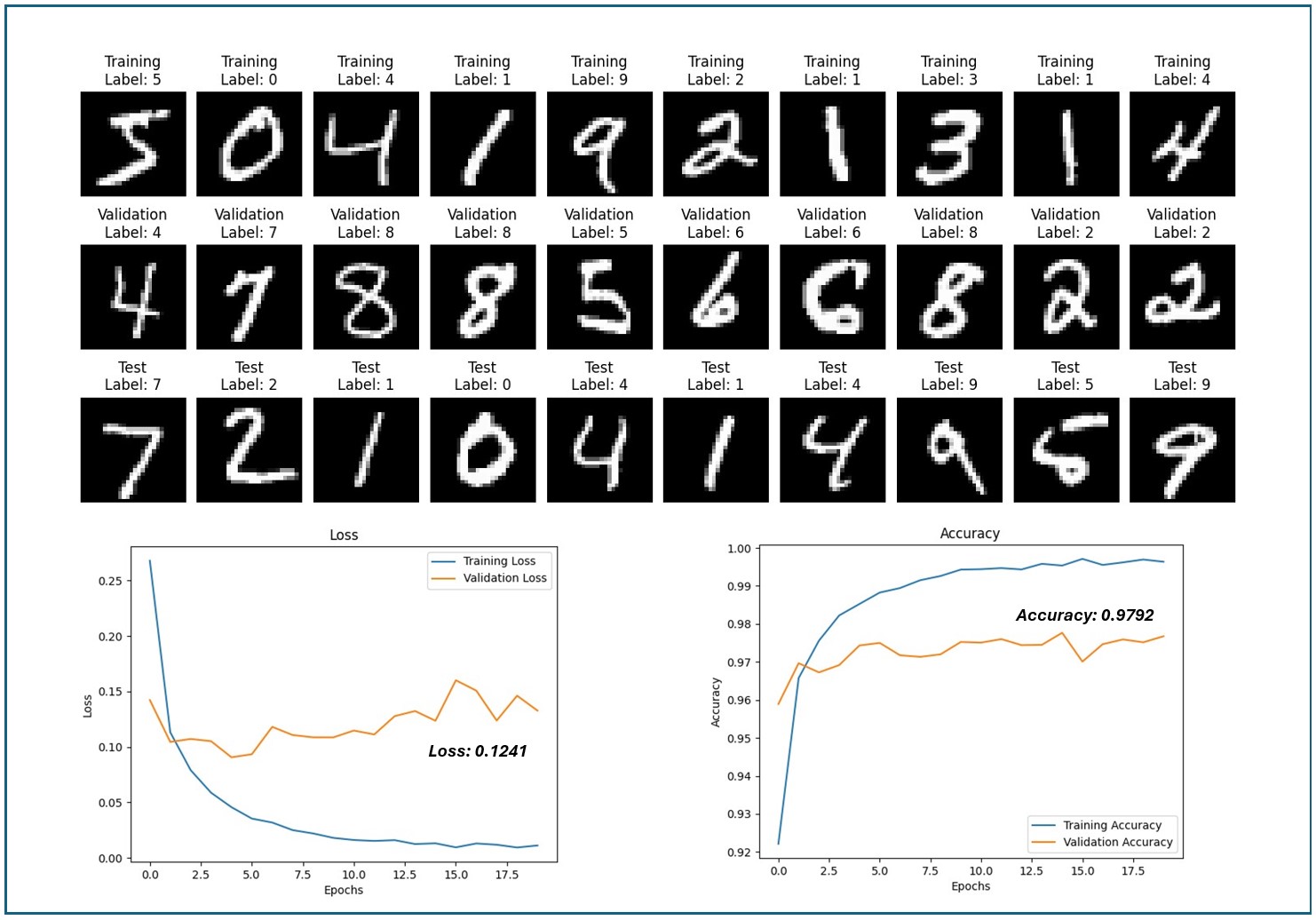
4. Visualization of Sample Images
The code utilizes the plot_all_samples function to visualize sample images from the training, validation, and test datasets. This function displays 10 images from each dataset in a grid format, along with their corresponding labels.
5. Building the CNN Model
The code defines a sequential model using the Sequential class from Keras. The model consists of the following layers:
- Flatten: This layer flattens the 28x28 pixel images into a one-dimensional vector of 784 elements.
- Dense (128 units, ReLU activation): This layer is a fully connected layer with 128 neurons and uses the ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) activation function.
- Dense (64 units, ReLU activation): Another fully connected layer with 64 neurons and ReLU activation.
- Dense (10 units, softmax activation): The output layer has 10 units, corresponding to the ten digit classes (0-9). The softmax activation function ensures the output probabilities sum to 1.
6. Model Compilation
The code compiles the model using the compile method. The compilation process specifies the optimizer, loss function, and metrics to be used during training.
- Optimizer: Adam is used as the optimizer.
- Loss function: Sparse categorical cross-entropy is used as the loss function for multi-class classification problems.
- Metrics: Accuracy is used as the metric to track the model's performance.
7. Model Training
The code trains the model using the fit method. The training process involves feeding the training data (x_train and y_train) to the model in batches. The model updates its internal parameters (weights and biases) based on the calculated loss and gradients.
The validation_data argument is used to evaluate the model's performance on the validation set during each epoch. This helps prevent overfitting by monitoring the model's ability to generalize to unseen data.
8. Model Evaluation
After training, the code evaluates the model's performance on the test dataset using the evaluate method. This method returns the loss and accuracy values on the test data.
9. Prediction and Classification Report
The code makes predictions on the test data using the predict method. The predicted labels are obtained by taking the argmax (index of the maximum value) of the predicted probabilities for each sample.
A classification report is generated using the classification_report function from scikit-learn. This report provides detailed information about the model's performance, including precision, recall, F1-score, and support for each digit class.
10. Visualization of Training Metrics
The code utilizes the plot_metrics function to visualize the training and validation accuracy and loss curves over the training epochs. This visualization helps to diagnose potential issues such as underfitting or overfitting.
Result
Note
- The code demonstrates the essential steps involved in building, training, and evaluating a CNN model for handwritten digit classification using TensorFlow and Keras.
- This code provides a basic example of CNN for MNIST classification.