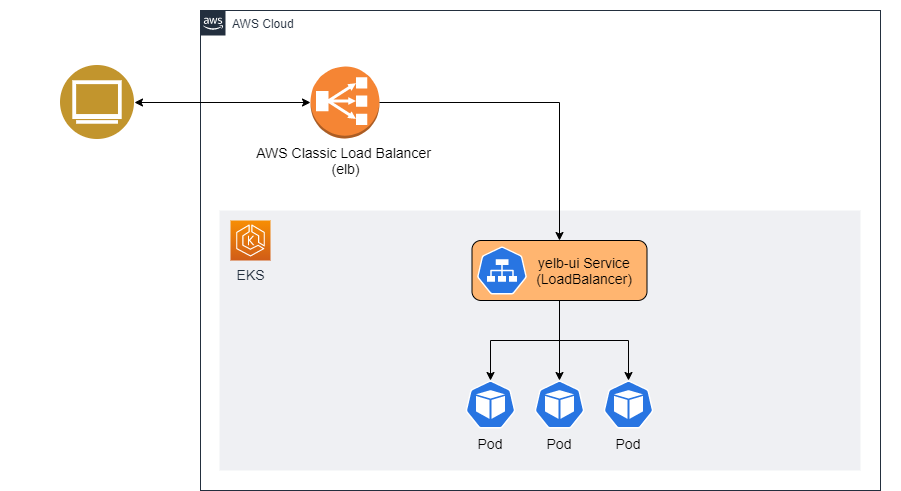
Istio is one of the popular choices for implementing a service mesh to simplify observability, traffic management and security. Customers are adopting Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) to scale their Kubernetes workloads to take advantage of flexibility, elasticity, and reliability of the AWS platform.
I was helping a customer to migrate Kubernetes workload from on-premises data-center into Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS). The Customer had an existing investment in Istio and wanted to continue using it in the EKS environment as their preferred service mesh. However, the customer was struggling to implement end-to-end encryption using Transport Layer Security (TLS) in the AWS environment. After helping the customer, I decided to write a blog on this topic to simplify others' journey.
In this blog post, I will focus on implementing end-to-end encryption using TLS certificate in Amazon Certificate Manager (ACM), Elastic Application Load Balancer (ALB) and Istio in EKS environment. However, before going into details, I have made a few assumptions.
- Existing AWS account with proper permissions.
- Existing and working EKS cluster with Kubernetes v1.21
- Installed and configured latest versions of utilities on the workspace you will use to interact with AWS and EKS cluster
- AWS Load Balancer Controller v2.3 or newer is installed and configured on your EKS cluster.
- Existing and valid certificate in AWS Certificate Manager (ACM). You can request one if not available.
I will demonstrate installing a sample Kubernetes application called yelb and expose it using Kubernetes service of type load balancer. Later, I will configure the ALB ingress controller to pass this traffic to Istio for further processing.
Note: I am using Bash terminal for code, but it is not strictly required. Example code can be easily tweaked for Microsoft Windows Terminal.
git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/eks-alb-istio-with-tls
cd eks-alb-istio-with-tls
kubectl apply -f yelb-k8s-loadbalancer.yamlLet's visualize our current state of application.
Our future state of applications is to configure a TLS certificate from ACM with Application Load Balancer (ALB) to encrypt inbound traffic. We also want to take advantage of Istio for traffic routing and mTLS inside the EKS cluster. The target state of cluster will look like Figure 02
I am installing Istio using istioctl and changing the service type of istio-ingressgateway to NodePort. The service type of NodePort is required when forwarding traffic from ALB to EC2 instances.
istioctl install \
--set profile=demo \
--set values.gateways.istio-ingressgateway.type=NodePortVerify Istio installation using kubectl get po -n istio-system, you should see pods running. Next, attach a label to the default namespace. This will tell Istio to inject a proxy sidecar to pods running in the namespace. You will need to delete existing pods in the default namespace.
# label default namespace
kubectl label default ns istio-injection=enabled --overwrite
# delete existing pods so that Istio can inject sidecar
kubectl delete po --all
# get list of pods
kubectl get poYou will notice that there are two containers running in each pod.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
redis-server-8569c76564-mm26f 2/2 Running 0 47s
yelb-appserver-6455cbcccb-qh9n4 2/2 Running 0 47s
yelb-db-7c776c7d7c-546vn 2/2 Running 0 47s
yelb-ui-f8bf879c9-hb2p4 2/2 Running 0 47s
Generate self-signed certificates. We will use a key/pair to encrypt traffic from ALB to Istio Gateway.
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -sha256 -days 3650 -nodes \
-keyout certs/key.pem -out certs/cert.pem -subj "/CN=yourdomain.com" \
-addext "subjectAltName=DNS:yourdomain"Generate Kubernetes secret containing key.pem and cert.pem. We will use it with Istio Gateway to implement traffic encryption.
kubectl create -n istio-system secret generic tls-secret \
--from-file=key=certs/key.pem \
--from-file=cert=certs/cert.pem
I will configure traffic routing for Istio using gateway and virtual services.
# install and configure Istio gateway
kubectl apply -f istio/gateway.yaml
# install and configure external service
kubectl apply -f istio/external-services.yaml
# install and configure Istio virtual services for yelb
kubectl apply -f istio/yelb-services.yamlI have attached self-signed certificates to Ingress Gateway. Istio will use these certificates to encrypt traffic between ALB and Istio which is a key part to implement end-to-end encryption.
Let's look at Istio Gateway.
cat istio/gateway.yamlapiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: yelb-gateway
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway
servers:
- port:
number: 443
name: https-443
protocol: HTTPS
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
credentialName: "tls-secret"
hosts:
- "*"You will notice that I am using the Kubernetes secret named tls-secret as credentialName which we generated earlier. The secret contains openssl generated key/cert. Gateway yelb-gateway is listening on port 443 for encrypted traffic.
Istio can not use the TLS certificate in ACM directly. However, I will use ACM certificates with AWS Application Load Balancer to terminate HTTPS traffic and then forward to Istio ingress gateway for further processing.
I need arn of ACM public certificate and domain configured in Route53. I’ll create an ingress resource to receive traffic from ALB and forward to Istio gateway. You will need to edit ingress resource to configure annotations for AWS Application Load Balancer with TLS certificates.
To make it simple, I have created a helm chart which accepts ACM certificate arn and host name as parameters; generate and install ingress correctly.
helm install alb-istio-ingress ./helm/ALB-Istio-TLS \
--set host=blog.yourdomain.com \
--set certificate_arn=arn:aws:acm:xxxxxx:999999999999:certificate/xxxxxxxxxNote: Make sure to use your own valid domain and certificate arn.
Once ingress is installed, it will provision AWS Application Load Balancer, bind it with ACM certificate for HTTPS traffic and forward traffic to Istio resources inside EKS cluster. You can get generated manifest of Ingress resource using
kubectl get ingress gw-ingress -n istio-system -o yamlThe generated output will look like the snippet below. Note values corresponding to alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol and host fields.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: alb
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path: /healthz/ready
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-port: status-port
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-protocol: HTTP
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: HTTPS
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTP": 80}, {"HTTPS":443}]'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/actions.ssl-redirect: |
{
"Type": "redirect",
"RedirectConfig": {
"Protocol": "HTTPS",
"Port": "443",
"StatusCode": "HTTP_301"
}
}
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn: |
arn:aws:acm:xxxxxx:999999999999:certificate/xxxxxxxxx
name: gw-ingress
namespace: istio-system
spec:
rules:
- host: blog.yourdomain.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: ssl-redirect
port:
name: use-annotation
path: /
pathType: Prefix
- backend:
service:
name: istio-ingressgateway
port:
number: 443
path: /
pathType: PrefixGet ALB Load balancer DNS and make note of it.
echo $(kubectl get ingress gw-ingress -n istio-system \
-o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[*].hostname}")We should get output similar to this
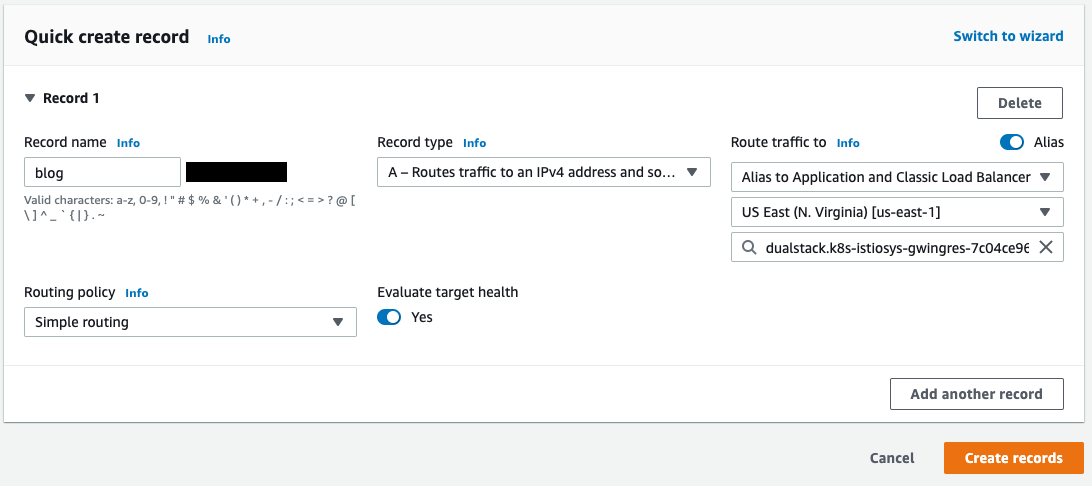
k8s-istiosys-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.comCreate a record in Route53 to bind your domain with ALB. Make sure you are creating a DNS record in the corresponding hosting zone, matching domain name. I have compiled a list of useful resources to learn more about DNS records and hosting zones in AWS.
- Registering domain names using Amazon Route 53
- Working with public hosted zones
- Working with records
- Routing traffic to an ELB load balancer
It can take few minutes to populate DNS servers. Open blog.yourdomain.com in the web browser, you will notice a padlock in the address bar for secure TLS communication. We have a Kubernetes application running in EKS with end-to-end encryption enabled using TLS certificate from ACM, Application Load Balancer (ALB) and Istio.
To undo changes made in Kubernetes cluster, execute following CLI commands in terminal
# remove label from default namespace
kubectl label default ns istio-injection-
# install and configure Istio gateway
kubectl delete -f istio/gateway.yaml
# install and configure external service
kubectl delete -f istio/external-services.yaml
# install and configure Istio virtual services for yelb
kubectl delete -f istio/yelb-services.yaml
# uninstall yelb application
kubectl delete -f yelb-k8s-loadbalancer.yaml
# uninstall istio
istioctl x uninstall -purge
# delete istio namespace
kubectl delete namespace istio-systemSee CONTRIBUTING for more information.
This library is licensed under the MIT-0 License. See the LICENSE file.