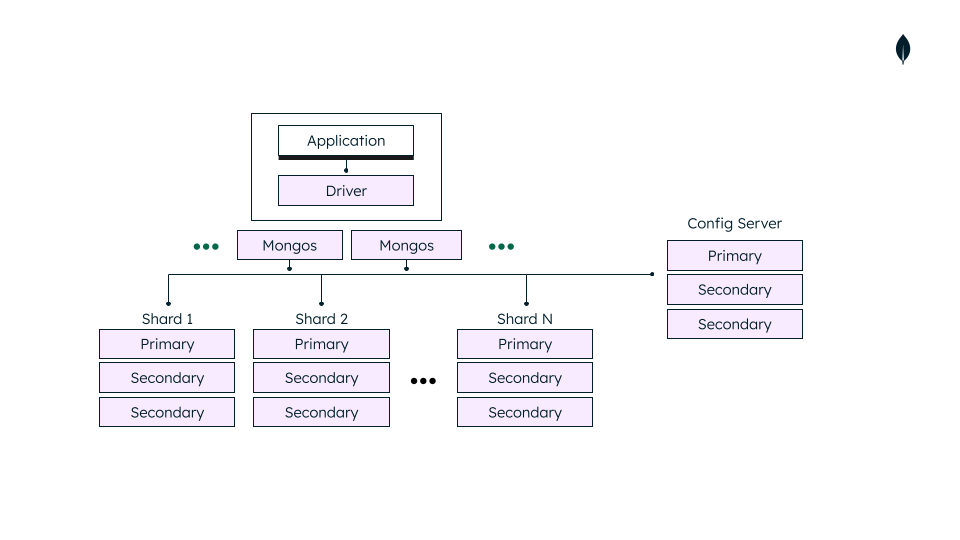
MongoDB's sharded cluster is a strategy to manage vast data sets by partitioning data across multiple servers. This guide assists you in configuring a MongoDB sharded cluster with Docker Compose and Kubernetes.
MongoDB sharded cluster components include:
- Shard: Each shard contains a portion of your data.
- Config Server: Maintains metadata and configuration settings.
- Mongos: Acts as a query router, guiding client applications to the appropriate shard.
Refer to the detailed architecture diagram for a visual representation:
❯ tree
.
├── docker-compose.yml # Docker Compose configuration
├── Dockerfile # Docker build instructions for the MongoDB instance
├── k8 # Kubernetes configurations
│ ├── 1-mongodb-configservers.yaml # Config server setup
│ ├── 2-mongodb-shard1.yaml # Shard 1 setup
│ ├── 3-mongodb-shard2.yaml # Shard 2 setup
│ ├── 4-mongodb-routers.yaml # Router setup
│ ├── 5-setup-rs-job.yaml # Job to initialize the replica sets
│ └── mongo-cluster-spin.sh # Shell script that creates the entire cluster manifests
├── README.md # This documentation file
└── setup # Scripts and Dockerfiles for cluster initialization
├── addShards.js # Script to add shards to the cluster
├── Dockerfile # Docker build instructions for the setup
├── initConfig.js # Initialization for the config replica set
├── initShard1.js # Initialization for Shard 1
├── initShard2.js # Initialization for Shard 2
└── setup.sh # Main setup script
To boot up the MongoDB cluster via Docker Compose, use:
╰─❯ docker-compose up --build --force-recreate -dThis action will construct the Docker images, generate the containers, and ensure they're running without hitches.
For MongoDB interaction, MongoDB Compass is a potent GUI tool. Connect using:
mongodb://localhost:27019/mdeforge
Upon connection, the testdb should display the preloaded dummy data.
To dismantle the cluster or start afresh, employ:
╰─❯ docker-compose down -v --remove-orphans && docker system prune -a --volumesThis command halts and eradicates containers, their volumes, and cleans up idle Docker assets.
Deploying a MongoDB sharded cluster on Kubernetes provides scalability, high availability, and flexibility. This guide utilizes kind for local Kubernetes cluster creation and deployment.
- Ensure you have
kindandkubectlinstalled. - MongoDB Compass installed for GUI interactions.
Before running any commands, ensure you are in the k8 directory where the Kubernetes manifests are located.
cd k8This script will generate the necessary Kubernetes manifests for the MongoDB cluster.
./mongo-cluster-spin.shIf you already have a cluster named mongo-cluster, it's best to delete it and recreate:
kind delete cluster --name mongo-cluster
kind create cluster --name mongo-clusterApply the generated Kubernetes manifests to your kind cluster:
kubectl apply -f .To observe the status of the pods as they are being created:
watch -n 3 kubectl get poRemember, the MongoDB cluster components might take some time to initialize and become ready.
Once all the pods are up and running, establish a connection to the mongos router:
kubectl port-forward svc/mongos1 27017Now, you can use MongoDB Compass to interface with your sharded cluster:
mongodb://localhost:27017/mdeforge
For a deeper inspection of pods, services, or deployments, you can use the describe or logs commands:
# For Pod details
kubectl describe po [POD_NAME]
# For Service details
kubectl describe svc [SERVICE_NAME]
# For Deployment details
kubectl describe deploy [DEPLOYMENT_NAME]
# To view logs of a specific pod
kubectl logs [POD_NAME]When done with the cluster, don't forget to delete the kind cluster to free up resources:
kubectl delete all,secrets,configmaps,pv,pvc --all --all-namespaces
kind delete cluster --name mongo-clusterCongratulations! 🎉 You've successfully deployed a MongoDB sharded cluster on Kubernetes using kind. Keep exploring and optimizing your deployments.