spring boot + aop
我们都知道,aop的原理就是动态代理,所以首先来介绍下java的动态代理
主要有两种:
- jdk自带动态代理
- cglib
JDK自带的动态代理方式必须要被代理对象实现某些接口;
JDK动态代理所用到的代理类在程序调用到代理类对象时才由JVM真正创建,JVM根据传进来的 业务实现类对象 以及 方法名 ,动态地创建了一个代理类的class文件并被字节码引擎执行,然后通过该代理类对象进行方法调用。我们需要做的,只需指定代理类的预处理、调用后操作即可。
- 实现InvocationHandler接口
- 调用java.lang.reflect.Proxy类的newProxyInstance或者getProxyClass方法
将被代理类传给即将生成的代理类 Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(),target.getClass().getInterfaces(),this);
-
重载invoke方法,将要处理的统一事件填入
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {.....}
newProxyInstance ---> getProxyClass0 --->proxyClassCache.get(loader, interfaces)--->Object subKey = Objects.requireNonNull(subKeyFactory.apply(key, parameter));---->ProxyClassFactory.apply
//生成代理类class文件
long num = nextUniqueNumber.getAndIncrement();
String proxyName = proxyPkg + proxyClassNamePrefix + num;
byte[] proxyClassFile = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass(proxyName, interfaces, accessFlags);
cglib是针对类来实现代理的,原理是对指定的业务类生成一个子类,并覆盖其中业务方法实现代理。因为采用的是继承,所以不能对final修饰的类进行代理。
demo中使用的是apache实现的cglib动态代理类:
github地址:
https://github.com/cglib/cglib
在这个项目中,我用apache的cglib实现去模拟spring aop的工作原理
Javassist是一个编辑字节码的框架,可以让你很简单地操作字节码。它可以在运行期定义或修改Class。使用Javassist实现AOP的原理是在字节码加载前直接修改需要切入的方法。这比使用Cglib实现AOP更加高效,并且没太多限制
Aspect-Oriented Programming 就是面向切面编程。
先引入官方文档的介绍:
我看的是4.3.12的文档,地址在这里
AOP and Instrumentation The spring-aop module provides an AOP Alliance-compliant aspect-oriented programming implementation allowing you to define, for example, method interceptors and pointcuts to cleanly decouple code that implements functionality that should be separated. Using source-level metadata functionality, you can also incorporate behavioral information into your code, in a manner similar to that of .NET attributes.
The separate spring-aspects module provides integration with AspectJ.
The spring-instrument module provides class instrumentation support and classloader implementations to be used in certain application servers. The spring-instrument-tomcat module contains Spring’s instrumentation agent for Tomcat.
也就是说,aop的核心是用AspectJ集成了spring-aspects,和spring-instrument工具模块组成。
那AspectJ是个什么玩意?
看文档中介绍:
The separate spring-aspects module provides integration with AspectJ.
是不是aop的实现就是用的AspectJ的源码来实现的呢? 答案当然不是,而是用的AspectJ的织入风格。
看spring官网的说法:
Aspect: a modularization of a concern that cuts across multiple classes. Transaction management is a good example of a crosscutting concern in enterprise Java applications. In Spring AOP, aspects are implemented using regular classes (the schema-based approach) or regular classes annotated with the @Aspect annotation (the @AspectJ style).
看关键字,the @AspectJ style,用的是AspectJ的风格。
而他的实现是eclipse社区实现的:
@AspectJ refers to a style of declaring aspects as regular Java classes annotated with annotations. The @AspectJ style was introduced by the AspectJ project as part of the AspectJ 5 release. Spring interprets the same annotations as AspectJ 5, using a library supplied by AspectJ for pointcut parsing and matching. The AOP runtime is still pure Spring AOP though, and there is no dependency on the AspectJ compiler or weaver. https://www.eclipse.org/aspectj/
用的是eclipse的aspectJ的5.0 Reliase版本。
aspectJ的官网上说:
AspectJ provides an implementation of AOP and has three core concepts:
Join Point Pointcut Advice
也就是凡是包含这三种概念的,都是AspectJ的风格。
至于aspectJ的原理,其实也是基于JDK动态代理和cglib去实现的。
spring采用了两种动态代理去实现。根据可用性,首选jdk动态代理(接口的情况下),jdk不满足时,会采用cglib实现。
spring默认是用的这种方式。
如果想直接使用cglib去实现动态代理的话,则需要在配置文件中配置这项(默认为false):
spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true
Join Point字面意思就是连接点,那什么是连接点呢?
先来看看spring AOP中关于AspectJ的aop概念介绍:
Join point: a point during the execution of a program, such as the execution of a method or the handling of an exception. In Spring AOP, a join point always represents a method execution.
简单说就是在程序执行的时候所表现的一个点。 在spring中,join point总是表现在一个方法执行上。
而Pointcut是用来匹配连接点的一个切面。
Pointcut: a predicate that matches join points. Advice is associated with a pointcut expression and runs at any join point matched by the pointcut (for example, the execution of a method with a certain name). The concept of join points as matched by pointcut expressions is central to AOP, and Spring uses the AspectJ pointcut expression language by default.
ps: Pointcut切入方法在被执行前会被代理方法(target source)所覆盖
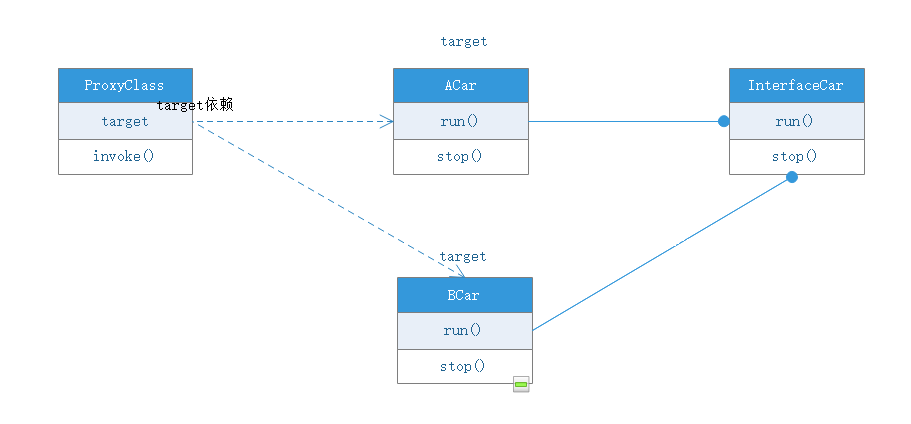
- target
被代理目标对象
- Join point
连接点,连接被代理对象与代理对象的切入点,简单说就是对象的某个方法method
- Pointcut
切入点,简单来说就是写的拦截方法类,是在invoke方法里去加判断规则的。
-
Advice 通知方式,在这里是下面例子的
RetryAdvice -
target source
就是最后生成的代理类源对象
先来看看jdk动态代理的方式,需要给汽车加上记录开车时间的记录,则设计如下:
spring的动态代理方式:
代码参考另一个专门介绍动态代理的项目:
设计一个controller日志记录器,可以记录方法调用时和调用后的时间,参数,返回值等的日志记录。
设计类名为:OperationLogAspect
@Aspect
@Component
public class OperationLogAspect {
//所有类的方法
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.example.demo.controller.*.*(..))")
private void allLogRecord(){
//这个方法体将会被aspectj切面监控的方法覆盖,实际不会被执行
System.out.println("allLogRecord.......");
}
//前置通知,即被切入方法执行前衩执行
@Before("allLogRecord()")
private void doBefore(){
System.out.println("doBefore........");
}
@After("allLogRecord()")
private void doAfter(){
System.out.println("doAfter......");
}
//返回值
@AfterReturning(returning = "result",pointcut = "execution(public * com.example.demo.controller.*.*(..))")
private void doAfterReturn(Object result){
System.out.println("获取目标方法返回值:" + result);
//这种方式无法改变返回的值
System.out.println("模拟记录日志功能...");
}
}
- 通知类型
@before
//前置通知,即被切入方法执行前衩执行
@Before("allLogRecord()")
private void doBefore(){
System.out.println("doBefore........");
}
- join point(连接点)
切入点的显示表现就是allLogRecord()。
-
pointCut(切面)
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.example.demo.controller..(..))")
这就是切面,被这个Aspect切入的方法平面。
上面使用@AspectJ的方式定义描述了Spring对AOP的支持。
现在用spring 提供的aop API来实现对aop的支持与扩展
spring AOP API有以下几类:
-
Pointcut API
public interface Pointcut {
ClassFilter getClassFilter(); MethodMatcher getMethodMatcher();}
以两部分组成,
- ClassFilter getClassFilter();
ClassFilter 接口用来约束切入点目标切入对象类型。
- MethodMatcher getMethodMatcher();
如果ClassFilter 的matches方式返回为true,则对象目标匹配类型将会被匹配。
Using the JdkRegexpMethodPointcut class, you can provide a list of pattern Strings. If any of these is a match, the pointcut will evaluate to true. (So the result is effectively the union of these pointcuts.)
Spring官方为我们提供了一个基于正则表达式来匹配方法名的Pointcut,JdkRegexpMethodPointcut。该Pointcut是继承自StaticMethodMatcherPointcut的。我们在定义JdkRegexpMethodPointcut时可以通过patterns和excludedPatterns来注入需要满足和排除的正则表达式,它们对应的都是一个String[]。比如我们想匹配所有的方法名以find开头的方法,我们可以如下定义:
<bean id="regexPointcut" class="org.springframework.aop.support.JdkRegexpMethodPointcut">
<property name="patterns">
<list>
<value>find.*</value><!-- 所有方法名以find开始的方法 -->
</list>
</property>
</bean>
但是光这样配置是不起作用的,需要一个桥接类:DefaultPointcutAdvisor.java
todo
- Advice API
Advice types in Spring
-
Interception around advice(拦截环绕通知)
public interface MethodInterceptor extends Interceptor {
Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable;}
eg:
public class DebugInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Before: invocation=[" + invocation + "]");
Object rval = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("Invocation returned");
return rval;
}
}
-
Before advice(前置通知)
-
Around advice
注意,这个不是拦截器。。。。。
官方例子写的非常含蓄,现将例子重新整理一遍
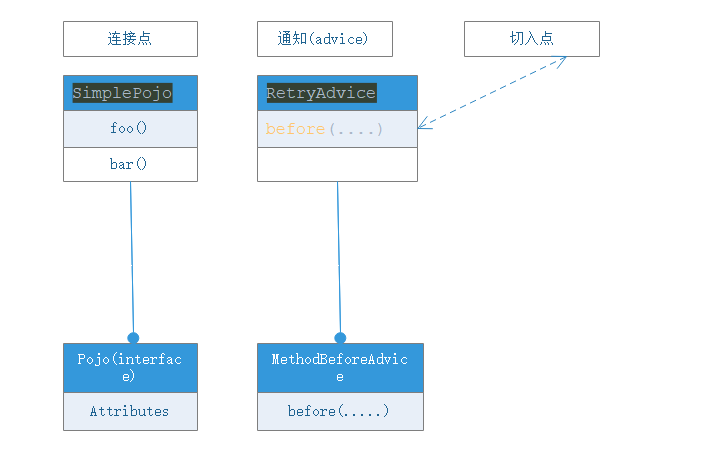
SimplePojo.java:
public class SimplePojo implements Pojo {
public void foo() {
// this next method invocation is a direct call on the 'this' reference
this.bar();
}
public void bar() {
// some logic...
}
}
Pojo.java:
public interface Pojo {
public void foo();
public void bar();
}
RetryAdvice.java:
public class RetryAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] objects, Object o) throws Throwable {
if (method.getName().equals("foo")){
System.out.println("check password");
}
}
}
SpringAopTest.java:
public class SpringAopTest {
@Test
public void testSpringAop(){
//1. 设置被代理对象(target),而SimplePojo的foo方法就是切入点:Join Point
ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory(new SimplePojo());
//2.将被代理对象的接口类添加进去(其实也可以不加,暂时还不清楚它有什么作用)
// factory.addInterface(Pojo.class);
//3, 添加advice拦截,拦截中的before方法就是Pointcut
factory.addAdvice(new RetryAdvice());
//是否暴露被代理目标类
factory.setExposeProxy(true);//指定对外发布代理对象,即在目标对象方法中可以通过AopContext.currentProxy()访问当前代理对象。
// Pojo pojo = (Pojo) factory.getProxy();
SimplePojo pojo = (SimplePojo) factory.getProxy();
// 这个连接点被调用时,就会调用代理类Proxy,pojo.foo()方法被调用前会被proxy的target source所覆盖(这里新的代理类名称(target source)是:SingletonTargetSource)
pojo.foo();
}
}
例子,需要设计一个注解标签,用来检查当前方法是否有权限被用户访问
-
必须是接口
-
需要加上以下注解
@Target({ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented
如果需要在方法上添加注解,则target的值是METHOD,加类上则值是TYPE
https://www.mkyong.com/java/java-custom-annotations-example/
http://blog.csdn.net/tianyaleixiaowu/article/details/73844568
使用@AfterReturning注解可指定如下两个常用属性。
-
pointcut/value:这两个属性的作用是一样的,它们都属于指定切入点对应的切入表达式。一样既可以是已有的切入点,也可直接定义切入点表达式。当指定了pointcut属性值后,value属性值将会被覆盖。 -
returning:该属性指定一个形参名,用于表示Advice方法中可定义与此同名的形参,该形参可用于访问目标方法的返回值。除此之外,在Advice方法中定义该形参(代表目标方法的返回值)时指定的类型,会限制目标方法必须返回指定类型的值或没有返回值。