Install Docker Engine by following instructions here.
Run the command to check that Docker Engine is working correctly.
sudo docker run hello-worldFollow the instructions here to run Docker without sudo.
Running a container from image, detached to background. The container will be running automatically.
To run the programs interactive, use the -it flag.
To delete container after finishing run, use the --rm flag.
docker run --detach --name webcontainer nginx:latestHowever, to create a container from an image but in stopped state, use the create command.
docker create --name webcontainer nginx:latest
docker start webcontainerTo check actively running containers, run the ps command.
docker psContainers can be restart and verified to be restarted correctly.
docker stop webcontainer # Stops the container
docker restart webcontainer
docker logs webcontainerTo run additional programs in a docker container, use the exec command.
docker exec webcontainer ls # Runs the ls command inside webcontainerTo pull an image only rather than spin containers up, use the pull command.
docker pull nginx:latest
docker pull quay.io/dockerinaction/ch3_hello_registry:latest # from alternate sources not from docker hubTo save the image as a tar file, use the save command. Then, load it using the load command.
docker save -o nginx.tar nginx:latest
docker load –i nginx.tarA docker image can also be built using a dockerfile.
docker build -t test:latest ch3_dockerfile # ch3_dockerfile is a directory containing the DockerfileImages can be deleted using the rmi command.
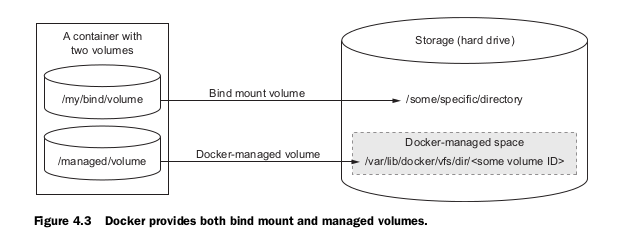
docker rmi test:latestThere are 2 types of volumes in Docker: Bind mounts and Docker-managed volumes.
Bind Mount volumes are useful to share data across processes.
The -v flag is used to create a mapping: key is the path on the host and value is absolute path to container location.
docker run -d --name bmweb -v ~/example-docs:/usr/local/apache2/htdocs -p 80:80 httpd:latest