This repository demonstrates a flexible navigation pattern for a Jetpack Compose application using the Coordinator pattern. The Coordinator pattern helps manage complex navigation flows and screen transitions within an Android app, providing a clear structure for controlling navigation between screens.
This example introduces the Coordinator interface and its implementations, which enable clean and manageable navigation flows. The architecture is built with reusability and scalability in mind, making it easy to add new flows or coordinators without disrupting existing ones.
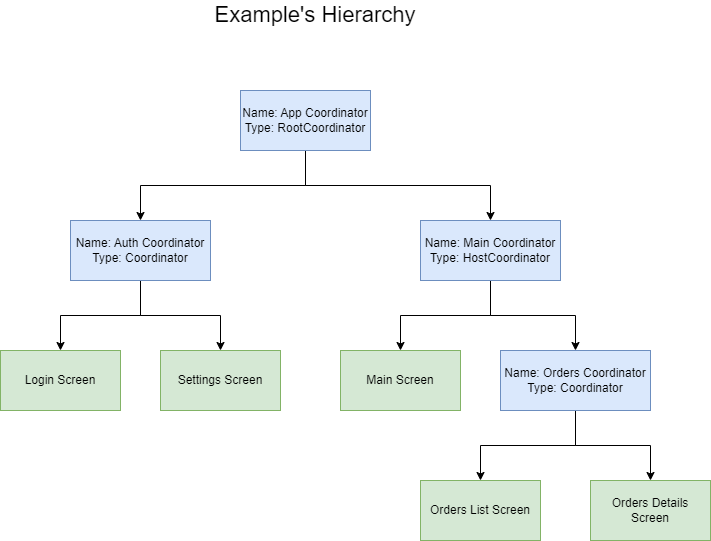
The following flow chart represents the hierarchy of coordinators in this example:
-
CoordinatorAction: A sealed interface representing actions that can be handled by a
Coordinator.interface CoordinatorAction
-
GeneralAction: A sealed class that defines common actions, such as
DoneandCancel.sealed class GeneralAction : CoordinatorAction { data class Done(val data: Any) : GeneralAction() data class Cancel(val reason: Any) : GeneralAction() }
-
Coordinator: The core interface that all coordinators implement. Each coordinator can navigate, set up navigation, and handle actions. It also holds a reference to its parent coordinator.
interface Coordinator { val parent: Coordinator? fun navigate(route: Navigable) { parent?.navigate(route) } fun setupNavigation(builder: NavHostBuilder) { // Default implementation can be overridden } @Composable fun handle(action: CoordinatorAction) }
-
Host: An interface that tracks the active coordinator.
interface Host { val activeCoordinator: Coordinator? }
-
HostCoordinator: Combines the
CoordinatorandHostinterfaces, enabling a coordinator to host other coordinators.interface HostCoordinator: Coordinator, Host
-
RootCoordinator: The main coordinator that initializes the navigation graph and handles global navigation actions. It extends
HostCoordinatorand includes a navigator for managing the navigation stack.interface RootCoordinator : HostCoordinator { val navigator: Navigator @Composable fun start(action: AppCoordinatorAction) }
-
RootCoordinator: Manages the app's overall navigation flow and initializes either the authentication flow or the main flow based on the current state.
-
AuthCoordinator: Manages the authentication flow, including login and settings screens.
-
MainCoordinator: Manages the main flow, including the main screen and order-related screens.
Each Coordinator can define its navigation routes using the setupNavigation method. The navigate method is called to switch between different routes or screens within a flow. Coordinators can also delegate navigation to their parent coordinators, creating a nested and hierarchical navigation structure.
-
RootCoordinator Implementation:
class AppCoordinator : RootCoordinator { override val activeCoordinator: Coordinator? = null override val navigator: Navigator = Navigator("root") private val authCoordinator: AuthCoordinator by lazy { AuthCoordinator(this) } private val mainCoordinator: MainCoordinator by lazy { MainCoordinator(this) } @Composable override fun start(action: AppCoordinatorAction) { handle(action) } @Composable override fun handle(action: CoordinatorAction) { when (action) { is AppCoordinatorAction.StartMainFlow -> { activeCoordinator = mainCoordinator navigator.navigateTo(MainNavigationRoute.MAIN.route) } is AppCoordinatorAction.StartLoginFlow -> { activeCoordinator = authCoordinator navigator.navigateTo(AuthNavigationRoute.LOGIN.route) } else -> throw IllegalArgumentException("Unsupported action") } } }
-
AuthCoordinator Implementation:
class AuthCoordinator( override val parent: Coordinator ) : Coordinator { override fun setupNavigation(builder: NavHostBuilder) { builder.composable(AuthNavigationRoute.LOGIN) { LoginScreen(coordinator = this@AuthCoordinator) } } @Composable override fun handle(action: CoordinatorAction) { // Handle auth-related actions here } }
-
MainCoordinator Implementation:
class MainCoordinator( override val parent: Coordinator ) : Coordinator { override fun setupNavigation(builder: NavHostBuilder) { builder.composable(MainNavigationRoute.MAIN) { MainScreen(coordinator = this@MainCoordinator) } } @Composable override fun handle(action: CoordinatorAction) { // Handle main-related actions here } }
In your MainActivity, initialize the AppCoordinator and start the appropriate flow:
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
val appCoordinator = remember { AppCoordinator() }
appCoordinator.start(AppCoordinatorAction.StartLoginFlow)
}
}
}Coordinators can navigate to different screens or delegate navigation to their parent coordinators:
override fun navigate(route: Navigable) {
parent?.navigate(route)
}This pattern provides a scalable and flexible navigation architecture for Jetpack Compose applications. It decouples navigation logic from UI components, making it easier to manage complex navigation flows. The Coordinator pattern is especially useful for large applications with multiple flows and nested navigation requirements.