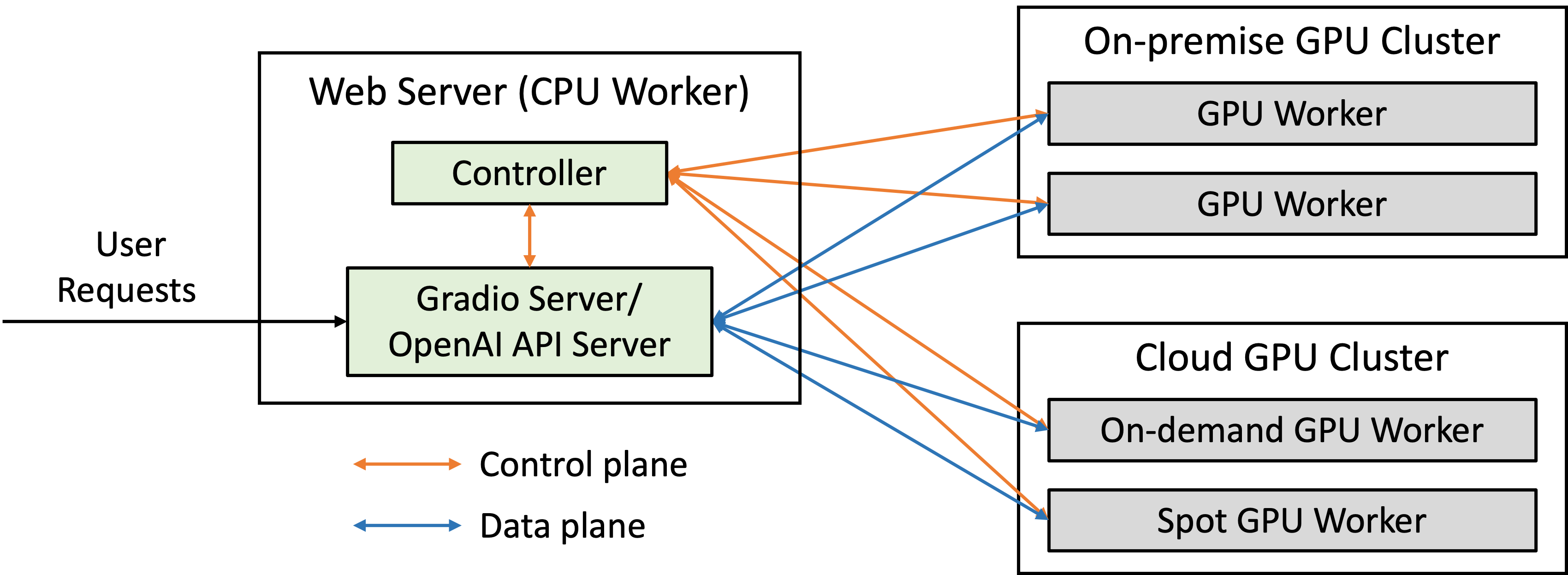
FastChat is an open-source platform designed for training, serving, and evaluating large language models (LLMs) for chatbot applications. It offers a comprehensive set of features that cater to various needs, making it a popular choice for LLM developers and enthusiasts.
Here's a breakdown of its key aspects:
Core Features:
- Pre-trained Models: FastChat comes with pre-trained weights and training/evaluation code for state-of-the-art models like Vicuna and FastChat-T5. These models are known for their impressive performance in chatbot tasks.
- Multi-Model Serving System: FastChat boasts a distributed multi-model serving system with a user-friendly web interface and OpenAI-compatible RESTful APIs. This allows you to easily deploy and manage multiple LLM models simultaneously.
- OpenAI Compatibility: The OpenAI-compatible APIs make FastChat a seamless drop-in replacement for OpenAI in existing applications. This simplifies integration and leverages familiar tools and workflows.
- Chatbot Arena: FastChat powers Chatbot Arena, a platform for hosting LLM battles and comparing their performance through user votes. This fosters a competitive environment for LLM development and provides valuable insights for researchers and developers.
Benefits of using FastChat:
- Flexibility: Train, serve, and evaluate diverse LLM models with a single platform.
- Ease of Use: The web UI and OpenAI compatibility make interaction intuitive and effortless.
- Scalability: The distributed architecture allows for handling large volumes of chat requests efficiently.
- Openness: The open-source nature fosters community contributions and continuous improvement.
pip3 install "fschat[model_worker,webui]"- Clone this repository and navigate to the FastChat folder
git clone https://github.com/lm-sys/FastChat.git
cd FastChatIf you are running on Mac:
brew install rust cmake- Install Package
pip3 install --upgrade pip # enable PEP 660 support
pip3 install -e ".[model_worker,webui]"The command below requires around 14GB of GPU memory for Vicuna-7B and 28GB of GPU memory for Vicuna-13B.
--model-path can be a local folder or a Hugging Face repo name.
python3 -m fastchat.serve.cli --model-path lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5
You can use model parallelism to aggregate GPU memory from multiple GPUs on the same machine.
python3 -m fastchat.serve.cli --model-path lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5 --num-gpus 2
Tips:
Sometimes the "auto" device mapping strategy in huggingface/transformers does not perfectly balance the memory allocation across multiple GPUs.
You can use --max-gpu-memory to specify the maximum memory per GPU for storing model weights.
This allows it to allocate more memory for activations, so you can use longer context lengths or larger batch sizes. For example,
python3 -m fastchat.serve.cli --model-path lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5 --num-gpus 2 --max-gpu-memory 8GiB
If you do not have enough memory, you can enable 8-bit compression by adding --load-8bit to commands above.
This can reduce memory usage by around half with slightly degraded model quality.
It is compatible with the CPU, GPU, and Metal backend.
Vicuna-13B with 8-bit compression can run on a single GPU with 16 GB of VRAM, like an Nvidia RTX 3090, RTX 4080, T4, V100 (16GB), or an AMD RX 6800 XT.
python3 -m fastchat.serve.cli --model-path lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5 --load-8bit
Here are the commands to follow in your terminal:
python3 -m fastchat.serve.controllerThis controller manages the distributed workers.
python3 -m fastchat.serve.model_worker --model-path lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5Wait until the process finishes loading the model and you see "Uvicorn running on ...". The model worker will register itself to the controller .
To ensure that your model worker is connected to your controller properly, send a test message using the following command:
python3 -m fastchat.serve.test_message --model-name vicuna-7b-v1.5You will see a short output.
python3 -m fastchat.serve.gradio_web_serverThe following will be the output GUI
The above command will only only open
Single TabGUI
python3 -m fastchat.serve.gradio_web_server_multivLLM can be used as an optimized worker implementation in FastChat. It offers advanced continuous batching and a much higher (~10x) throughput.
-
Install vLLM.
pip install vllm -
When you launch a model worker, replace the normal worker (
fastchat.serve.model_worker) with the vLLM worker (fastchat.serve.vllm_worker). All other commands such as controller, gradio web server, and OpenAI API server are kept the same.python3 -m fastchat.serve.vllm_worker --model-path lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5If you see tokenizer errors, try
python3 -m fastchat.serve.vllm_worker --model-path lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5 --tokenizer hf-internal-testing/llama-tokenizerIf you use an AWQ quantized model, try ''' python3 -m fastchat.serve.vllm_worker --model-path TheBloke/vicuna-7B-v1.5-AWQ --quantization awq '''
First, launch the controller
python3 -m fastchat.serve.controllerThen, launch the model worker(s)
python3 -m fastchat.serve.model_worker --model-path lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5Finally, launch the RESTful API server
python3 -m fastchat.serve.openai_api_server --host localhost --port 8000First, install OpenAI python package >= 1.0:
pip install --upgrade openaiThen, interact with the Vicuna model:
import openai
openai.api_key = "EMPTY"
openai.base_url = "http://localhost:8000/v1/"
model = "vicuna-7b-v1.5"
prompt = "Once upon a time"
# create a completion
completion = openai.completions.create(model=model, prompt=prompt, max_tokens=64)
# print the completion
print(prompt + completion.choices[0].text)
# create a chat completion
completion = openai.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Hello! What is your name?"}]
)
# print the completion
print(completion.choices[0].message.content)Start the controller
python3 -m fastchat.serve.controller --host 0.0.0.0 --port 10002Start the vLLM model workers
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 -m fastchat.serve.vllm_worker \
--model-path lmsys/vicuna-13b-v1.5 \
--model-name vicuna-13b \
--controller http://node-01:10002 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 31000 \
--worker-address http://$(hostname):31000CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1 python3 -m fastchat.serve.vllm_worker \
--model-path lmsys/vicuna-13b-v1.5 \
--model-name vicuna-13b \
--controller http://node-01:10002 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 31001 \
--worker-address http://$(hostname):31001Start Ray Head
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2,3 ray start --headpython3 -m fastchat.serve.vllm_worker \
--model-path lmsys/vicuna-33b-v1.3 \
--model-name vicuna-33b \
--controller http://node-01:10002 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 31002 \
--worker-address http://$(hostname):31002 \
--num-gpus 2CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 -m fastchat.serve.vllm_worker \
--model-path meta-llama/Llama-2-13b-chat-hf \
--model-name llama-2-13b-chat \
--controller http://node-01:10002 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 31000 \
--worker-address http://$(hostname):31000 \
--tokenizer meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hfCUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1 python3 -m fastchat.serve.vllm_worker \
--model-path meta-llama/Llama-2-13b-chat-hf \
--model-name llama-2-13b-chat \
--controller http://node-01:10002 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 31001 \
--worker-address http://$(hostname):31001 \
--tokenizer meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hfCUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2 python3 -m fastchat.serve.vllm_worker \
--model-path meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf \
--model-name llama-2-7b-chat \
--controller http://node-01:10002 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 31002 \
--worker-address http://$(hostname):31002 \
--tokenizer meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hfCUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=3 python3 -m fastchat.serve.vllm_worker \
--model-path WizardLM/WizardLM-13B-V1.1 \
--model-name wizardlm-13b \
--controller http://node-01:10002 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 31003 \
--worker-address http://$(hostname):31003python3 -m fastchat.serve.vllm_worker \
--model-path mosaicml/mpt-30b-chat \
--controller http://node-01:10002 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 31000 \
--worker-address http://$(hostname):31000 \
--num-gpus 2python3 -m fastchat.serve.vllm_worker \
--model-path timdettmers/guanaco-33b-merged \
--model-name guanaco-33b \
--controller http://node-01:10002 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 31002 \
--worker-address http://$(hostname):31002 \
--num-gpus 2 \
--tokenizer hf-internal-testing/llama-tokenizerCUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 -m fastchat.serve.multi_model_worker \
--model-path ~/model_weights/RWKV-4-Raven-14B-v12-Eng98%25-Other2%25-20230523-ctx8192.pth \
--model-name RWKV-4-Raven-14B \
--model-path lmsys/fastchat-t5-3b-v1.0 \
--model-name fastchat-t5-3b \
--controller http://node-01:10002 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 31000 \
--worker http://$(hostname):31000 \
--limit 4CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1 python3 -m fastchat.serve.multi_model_worker \
--model-path OpenAssistant/oasst-sft-4-pythia-12b-epoch-3.5 \
--model-name oasst-pythia-12b \
--model-path mosaicml/mpt-7b-chat \
--model-name mpt-7b-chat \
--controller http://node-01:10002 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 31001 \
--worker http://$(hostname):31001 \
--limit 4CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2 python3 -m fastchat.serve.multi_model_worker \
--model-path lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5 \
--model-name vicuna-7b \
--model-path THUDM/chatglm-6b \
--model-name chatglm-6b \
--controller http://node-01:10002 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 31002 \
--worker http://$(hostname):31002 \
--limit 4CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=3 python3 -m fastchat.serve.vllm_worker \
--model-path ~/model_weights/alpaca-13b \
--controller http://node-01:10002 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 31003 \
--worker-address http://$(hostname):31003python3 -m fastchat.serve.test_message \
--model vicuna-13b \
--controller http://localhost:10002- Gather battles
python3 clean_battle_data.py --max-num 10 --mode conv_release
- Tag OpenAI moderation
python3 tag_openai_moderation.py --in clean_battle_conv_20230814.json
- Clean PII
- Filter additional blocked words
python3 filter_bad_conv.py --in clean_battle_conv_20230630_tagged_v1_pii.json
- Add additional toxicity tag
- Gather chats
python3 clean_chat_data.py
- Sample
python3 conv_release_scripts/sample.py
git clone https://github.com/lm-sys/FastChat.git
cd FastChat
pip install -e ".[model_worker,llm_judge]"We provide pre-generated model answers and judgments for some models. You can view them at this demo.
To download the pre-generated data, use
python3 download_mt_bench_pregenerated.py
After downloading the data, you can view them locally by
python3 qa_browser.py --share
You can use this QA browser to view the answers generated by you later.
python gen_model_answer.py --model-path [MODEL-PATH] --model-id [MODEL-ID]Arguments:
[MODEL-PATH]is the path to the weights, which can be a local folder or a Hugging Face repo ID.[MODEL-ID]is a name you give to the model.
e.g.,
python gen_model_answer.py --model-path lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5 --model-id vicuna-7b-v1.5The answers will be saved to data/mt_bench/model_answer/[MODEL-ID].jsonl.
You can also specify --num-gpus-per-model for model parallelism (needed for large 65B models) and --num-gpus-total to parallelize answer generation with multiple GPUs.
There are several options to use GPT-4 as a judge, such as pairwise winrate and single-answer grading. In MT-bench, we recommend single-answer grading as the default mode. This mode asks GPT-4 to grade and give a score to model's answer directly without pairwise comparison. For each turn, GPT-4 will give a score on a scale of 10. We then compute the average score on all turns.
export OPENAI_API_KEY=XXXXXX # set the OpenAI API key
python gen_judgment.py --model-list [LIST-OF-MODEL-ID] --parallel [num-concurrent-api-call]e.g.,
python gen_judgment.py --model-list vicuna-13b-v1.3 alpaca-13b llama-13b claude-v1 gpt-3.5-turbo gpt-4 --parallel 2The judgments will be saved to data/mt_bench/model_judgment/gpt-4_single.jsonl
- Show the scores for selected models
python show_result.py --model-list vicuna-13b-v1.3 alpaca-13b llama-13b claude-v1 gpt-3.5-turbo gpt-4
- Show all scores
python show_result.py
Besides score-based single-answer grading, we also support two additional grading options based on win rates:
pariwise-baseline: run pairwise comparison against a baseline model.pairwise-all: run pairwise comparison between all model pairs on all questions.
- Generate GPT-4 judgments
python gen_judgment.py --mode pairwise-baseline --model-list vicuna-13b-v1.3 alpaca-13b llama-13b --parallel 2The judgments will be saved to data/mt_bench/model_judgment/gpt-4_pair.jsonl
- Show results
python show_result.py --mode pairwise-baselineAnother option is to run pairwise comparisons on all possible pairs. This could be more expensive when #models increases, but it gives you a more comprehensive information.
python gen_judgment.py --mode pairwise-all --model-list [LIST-OF-MODEL-ID] --parallel [num-concurrent-api-call]python show_result.py --mode pairwise-alldata/allam_bench/question.jsonlpython gen_model_answer.py \
--model-path /models/allam-13b \
--model-id allam-13b \
--bench-name allam_benchThe answers will be saved to data/allam_bench/model_answer/[MODEL-ID].jsonl.