Keyboard latency testing script based on LagBox
If you test your own keyboards with this, please create a PR and contribute your results!
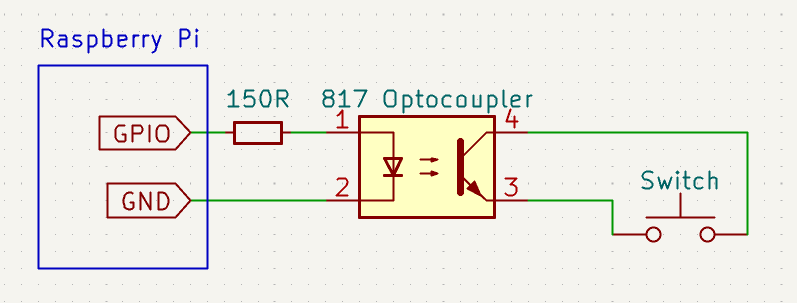
This repo contains a Python program which runs on a Rasbperry Pi. It uses a GPIO to control an optocoupler which is connected across the pins of a keyboard switch. Setting the GPIO on connects the switch pins together, simulating a key press. Setting the GPIO off disconnects the pins, simulating a key release. It uses this to measure the latency between when a switch actuates and when the OS registers a key press event. The recorded latency is then the latency of the keyboard plus the latency of the OS. Ideally, we would not want to include the OS latency, but this is difficult without more specialized hardware.
It first triggers one key press and watches for a key press event on the selected input device and learns which key code is triggered.
It then runs the following process the number of iterations specified with -n (default 100):
- Wait a random amount of time.
- Record the current time and simulate a key press by setting the trigger GPIO on.
- Wait for a key press event for the correct key.
- Record the difference in time between the trigger GPIO being set and the key event.
- Release the key by setting the trigger GPIO off.
The script creates a list of delays evenly distributed between --tmin (default 50 ms) and --tmax (default 1 s), then randomly assigns a delay to each iteration. This attempts to ensure that the latency tester does not run in lock step with any process on the keyboard such as key scanning, which might artificially increase or decrease the tested latency compared to real-world usage.
For step 2, it records the time before and after the call to change the GPIO and uses the average. The potential error +/- that average value is recorded in a second column for each sample.
For step 4, it uses the event timestamp reported by the OS, so it isn't affected by how long the script takes to handle each event.
This project uses identical hardware to LagBox.
- Rasbperry Pi (with wireless if you want to test Bluetooth latency)
- A817 optocoupler (or equivalent)
- 150 ohm resistor
Connect pin 1 of the optocoupler through a 150 Ohm resistor to a GPIO pin on the Raspberry Pi, then connect pin 2 to a ground pin. By default, this script uses GPIO 21, but this can be changed with the --gpio option.
Connect pins 3 and 4 of the optocoupler to either side of a switch on the keyboard to test.
If the keyboard has hotswap sockets, you can take an extra, sacrificial switch, open it, remove the spring and slider, and solder wires onto the two contacts inside. Use heat shrink tubing or something else nonconductive to keep the contacts from touching.
If not, you will typically need to disassemble the keyboard to access the back of its PCB and tape a pair of wires to a switch's solder joints (you can also do this with a hotswap keyboard if you don't want to destroy a switch).
Clone this repo, then open a terminal to the repo directory and install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txtTo print a list of the attached keyboards, run:
./test --listSome keyboards will appear as multiple input devices. If you aren't sure which one is correct, you can scan to see which one responds to a triggered key press:
./test --scanTo test the keyboard at index 2, run:
./test -i 2If there is only one keyboard or it's the first in the list, you can omit the -i argument.
To write the results to a CSV file, add -o followed by the file name:
./test -o result.csvFor a full list of options, run:
./test --helpThe results folder contains test results for various keyboards.
For aggregate results and latency rankings, see results/chart.ipynb.
The results for individual keyboards are organized as follows:
results/<firmware>/<keyboard>/<interface>-<interface_speed>[-<debounce_type>].csv
For example, results/ZMK/nRF5340-DK-ZMK-Uno/usb-1000hz-debounce-5ms would be:
- ZMK Firmware
- nRF5340 DK with ZMK Uno shield
- Keyboard connected via USB with 1000 Hz polling
- Keyboard debounce set to 5 milliseconds
Each keyboard was tested using the script's default settings. Additional information about each test setup can be found in README.md files in each keyboard folder.
- Bluetooth:
ble-<connection_interval>, e.g.ble-15ms - USB:
usb-<polling_rate>, e.g.usb-1000hz - Logitech Lightspeed USB receiver:
lightspeed-<usb_polling_rate>, e.g.lightspeed-1000hz
USB poll rate defaults to 1000 Hz but can be changed with:
#define USB_POLLING_INTERVAL_MS 8 // poll rate = 1000 Hz/valueUSB poll rate defaults to 1000 Hz but can be changed with:
CONFIG_USB_HID_POLL_INTERVAL_MS=8 # poll rate = 1000 Hz/valueBLE connection interval defaults to 7.5-15 ms, where the host OS gets to pick any value within the range. It can be forced to a specific interval by changing the min and max values:
CONFIG_BT_PERIPHERAL_PREF_MIN_INT=6 # interval = value * 1.25 ms
CONFIG_BT_PERIPHERAL_PREF_MAX_INT=6 # interval = value * 1.25 msTo check the BLE connection interval being used, open a terminal and run
sudo btmonthen cycle power on the keyboard and watch the events as it connects. You should see an event that looks like this:
> HCI Event: LE Meta Event (0x3e) plen 10
LE Connection Update Complete (0x03)
Status: Success (0x00)
Handle: 64
Connection interval: 15.00 msec (0x000c)
Connection latency: 30 (0x001e)
Supervision timeout: 4000 msec (0x0190)
In this case, the connection interval was 15 ms.
Debounce algorithms differ slightly between firmwares. The debounce types refer to the following settings.
debounce-7ms
MinDebounceTime = 7;debounce-5ms
# No options set. Equivalent to
DEBOUNCE_TYPE = sym_defer_g
DEBOUNCE = 5debounce-eager-5ms
DEBOUNCE_TYPE = asym_eager_defer_pk
DEBOUNCE = 5debounce-5ms
# No options set. Equivalent tos
CONFIG_ZMK_KSCAN_DEBOUNCE_PRESS_MS=5
CONFIG_ZMK_KSCAN_DEBOUNCE_RELEASE_MS=5debounce-eager-5ms
CONFIG_ZMK_KSCAN_DEBOUNCE_PRESS_MS=0
CONFIG_ZMK_KSCAN_DEBOUNCE_RELEASE_MS=5debounce-eager-1ms-5ms
CONFIG_ZMK_KSCAN_DEBOUNCE_PRESS_MS=1
CONFIG_ZMK_KSCAN_DEBOUNCE_RELEASE_MS=5The results folder contains a Jupyter notebook for visualizing the results.
To update the notebook with new results, first install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.chart.txt
Then open results/chart.ipynb in Visual Studio Code or Jupyter and run all cells.
Testing hardware is taken from LagBox and the test methodology was derived from the LagBox software documentation.
Keyboard event handling is based on the Python keyboard library.