- Proxmox remote install
- Diagram
- Objectives
- Requirements
- Hypervisor
- Proxmox interface configuration
- Firewall (pfSense)
- VM configuration
- Create a Debian Template
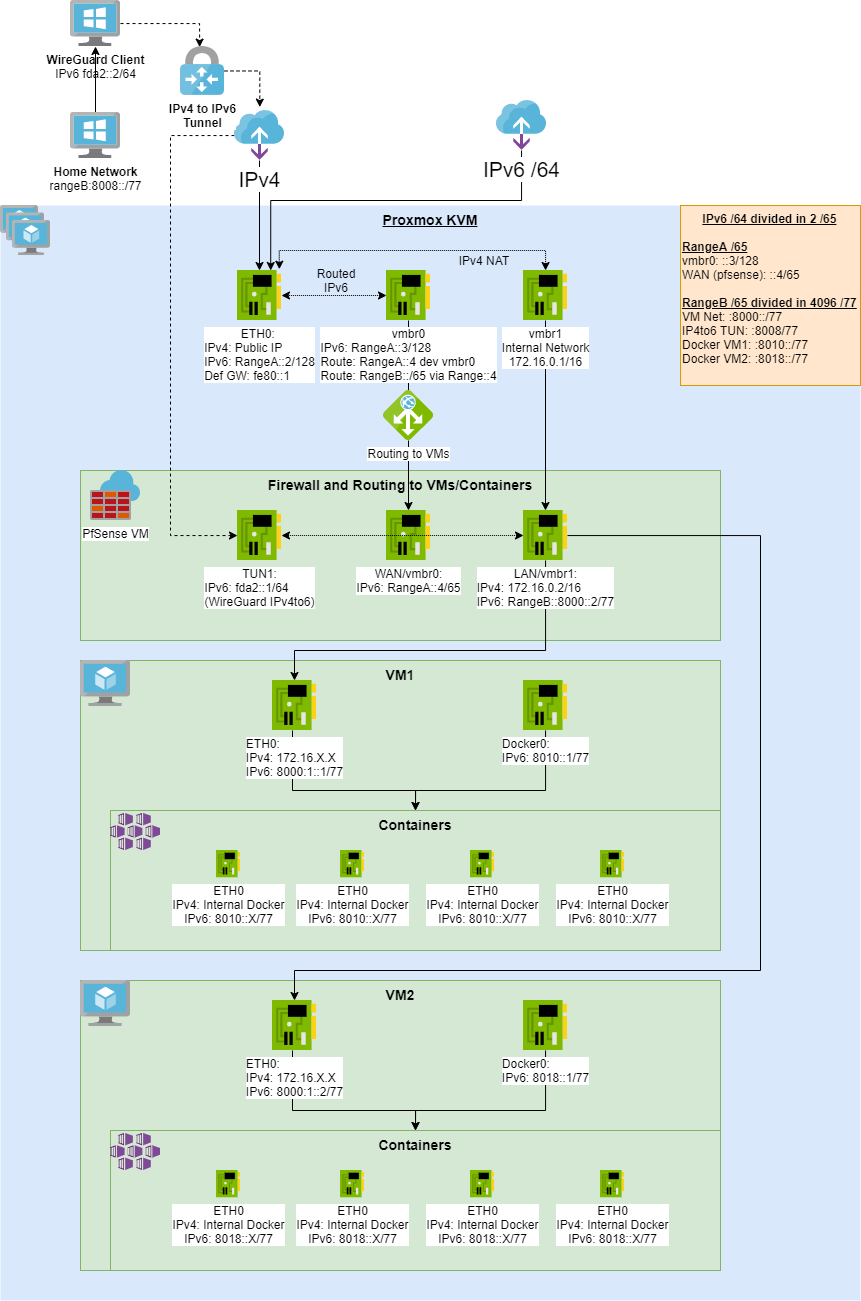
This howto will help you set up a Promox host with a fully routed IPv4 and IPv6 network for VMs with an out of band firewall.
We create 2 routed internal networks between the host and the Firewall
IPv4:
- Host: 169.254.0.1 to Firewall: 169.254.0.2
- 172.16.0.0/16 is routed via 172.16.0.2
IPv6:
- Point to Pint rangeIPv6::3 to Firewall rangeIPv6::4
- rangeIPv6::/64 routed via rangeIPv6::4
For normal install go to: https://www.proxmox.com/en/proxmox-ve/get-started
To install remotely boot into a rescue system with QEMU support.
apt -y install ovmf wget
wget -O pve.iso http://download.proxmox.com/iso/proxmox-ve_7.4-1.iso
Change the password and the disk devices
printf "change vnc password\n%s\n" "password" | qemu-system-x86_64 -enable-kvm -cpu host -smp 4 -m 4096 -boot d -cdrom ./pve.iso -drive file=/dev/sda,format=raw,media=disk,if=virtio -drive file=/dev/sdb,format=raw,media=disk,if=virtio -vnc :0,password -monitor stdio -no-reboot
Connect to your public IP to port 5900 and the password you selected.
Run it under QEMU once more.
printf "change vnc password\n%s\n" "password" | qemu-system-x86_64 -enable-kvm -cpu host -smp 4 -m 4096 -boot d -drive file=/dev/sda,format=raw,media=disk,if=virtio -drive file=/dev/sdb,format=raw,media=disk,if=virtio -vnc :0,password -monitor stdio -no-reboot
Connect via VNC once again and change the following:
nano /etc/default/grub
# Edit this to disable "predictable" network interfaces, so the first interface is always eth0
#GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="net.ifnames=0 biosdevname=0"
# Then run
update-grub
nano /etc/network/interfaces
# Change brodge-ports from ens3 to eth0
# Create a swapfile if you are NOT using ZFS
fallocate -l 8G /swapfile
chmod 600 /swapfile
mkswap /swapfile
echo "/swapfile swap swap defaults 0 0" >> /etc/fstab
# Create ZFS volume for swap
zfs create -V 8G -b $(getconf PAGESIZE) -o compression=zle \
-o logbias=throughput -o sync=always\
-o primarycache=metadata -o secondarycache=none \
-o com.sun:auto-snapshot=false rpool/swap
# Prepare it as swap partition:
mkswap -f /dev/zvol/rpool/swap
swapon /dev/zvol/rpool/swap
# Add it to fstab
echo "/dev/zvol/rpool/swap none swap discard 0 0" >> /etc/fstab
Reboot into Promox and change /etc/network/interfaces as shown in Proxmox interface configuration
systemctl disable --now rpcbind rpcbind.socket
sed -i 's/^\([^#].*\)/# \1/g' /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pve-enterprise.list
echo "deb [arch=amd64] http://download.proxmox.com/debian/pve bullseye pve-no-subscription" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pve-no-subscription-repo.list
sed -i "s|ftp.*.debian.org|ftp.debian.org|g" /etc/apt/sources.list
apt update && apt -y upgrade && apt -y autoremove
pveupgrade
sed -Ezi.bak "s/(Ext.Msg.show\(\{\s+title: gettext\('No valid sub)/void\(\{ \/\/\1/g" /usr/share/javascript/proxmox-widget-toolkit/proxmoxlib.js && systemctl restart pveproxy.service
apt install -y libguestfs-tools unzip iptables-persistent
apt install net-tools
echo "nf_conntrack" >> /etc/modules
echo "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" >> /etc/sysctl.d/99-proxmox.conf
echo "net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=1" >> /etc/sysctl.d/99-proxmox.conf
echo "net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max=1048576" >> /etc/sysctl.d/99-proxmox.conf
echo "net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established=28800" >> /etc/sysctl.d/99-proxmox.conf
# ZFS memory limits
echo "options zfs zfs_arc_min=$[6 * 1024*1024*1024]" >> /etc/modprobe.d/99-zfs.conf
echo "options zfs zfs_arc_max=$[12 * 1024*1024*1024]" >> /etc/modprobe.d/99-zfs.conf
update-initramfs -u
- Fully routed IPv6 and NATed IPv4 to VMs
- Each VM will receive a IPv6 from a /77 subnet
- Each container under this VM will receive an IPv6 automatically.
- Each VM will receive a IPv6 from a /77 subnet
- IPv4 to IPv6 Tunnel using WireGuard
- Out of band Firewall
- PfSense controlling the access to all public traffic
- Having an out of band firewall, meaning outside of the VMs. This will increase the security of the system
For this article, we will use a /64 IPv6 network because its what commonly assiged by ISPs or hosting providers.
Point to Point internal networks will help route IP traffic between the public internet an our internal network avoiding ARP resolution.
Host:
- eth0: Public IP
- Port forward to VMs
- vmbr0: 169.254.0.1/16
- Routes 172.16.0.0/16 via 169.254.0.2 (Firewall WAN)
Firewall VM:
- LAN: 172.16.0.1/16
- WAN: 169.254.0.2/16
- Rotes 0.0.0.0 via 169.254.0.2
Host:
- eth0: rangeIPv6::2/128 (eth0)
- vmbr0: rangeIPv6::3/128 (vmbr0)
- rangeIPv6::4 dev vmbr0 (Firewall)
- rangeIPv6::/64 via rangeIPv6::4
Firewall VM:
- WAN: rangeIPv6::4/128
- LAN: rangeIPv6::/64 (Divided in 65536 /80)
- rangeIPv6:1::/80 (Reserved for Host to Firewall)
- rangeIPv6:2::/80 (WireGuard Tunnel)
- rangeIPv6:3::/80 (VMs main IP)
- rangeIPv6:4-ffff:/80 (Docker networks)
We will need a way to provision VMs, for this article we selected Proxmox More information:
- https://www.proxmox.com/en/proxmox-ve/get-started
- How to install it remotely on any server: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/installing-any-os-headless-server-rodrigo-leven/
We will create 2 bridges and use the phisical network interface.
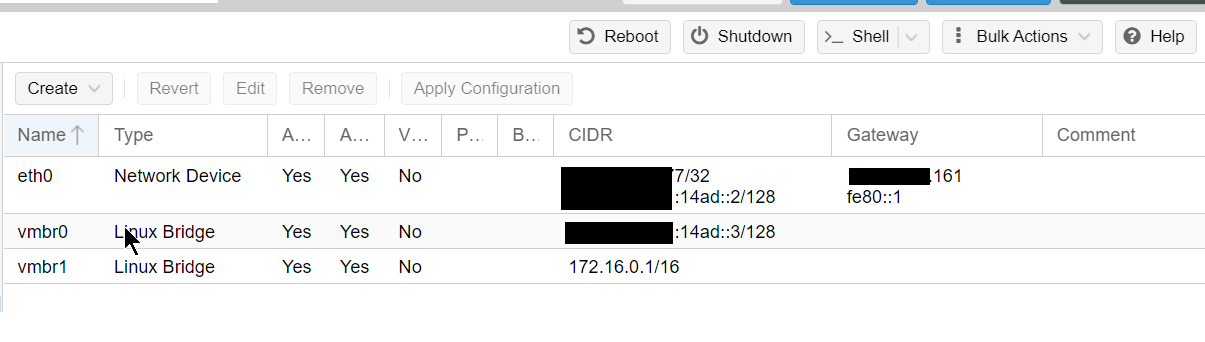
- eth0: Physical interface where we get our public IPv4 and v6 traffic.
- vmbr0: Will be shared to OpenSense as WAN, all the traffic to VMs will go trough here
- vmbr1: Internal IPv4/v6 network, will be shared as LAN with no host IPv4
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# device: eth0
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address xxx.76.28.177
netmask 255.255.255.255
pointopoint xxx.76.28.161
gateway xxx.76.28.161
iface eth0 inet6 static
address rangeIPv6::2
netmask 128
gateway fe80::1
up sysctl -p
# for single IPs
auto vmbr0
iface vmbr0 inet static
address 169.254.0.1
netmask 255.255.0.0
bridge_ports none
bridge_stp off
bridge_fd 0
up ip route add 172.16.0.0/16 via 169.254.0.2 dev vmbr0
# WAN Interface in the Firewall VM
iface vmbr0 inet6 static
address rangeIPv6::3
netmask 128
up ip -6 route add rangeIPv6::4 dev vmbr0
up ip -6 route add rangeIPv6::/64 via rangeIPv6::4 dev vmbr0
# LAN interface in the Firewall VM
auto vmbr1
iface vmbr1 inet static
address 0.0.0.0
We will need an out of band Firewall to be able to whitelist open ports and for this, we are going to use OpnSense.
More information here: https://opnsense.org/
We will add 2 (WAN,LAN) network cards and configure each one to one of the Bridges we created before
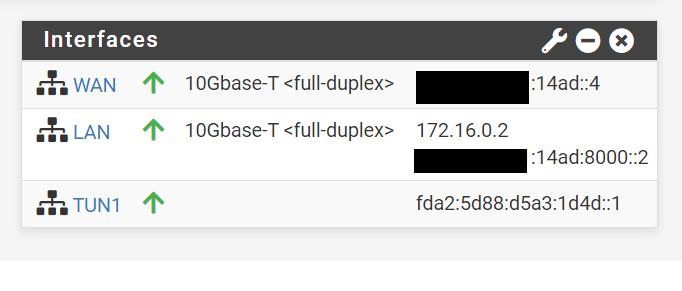
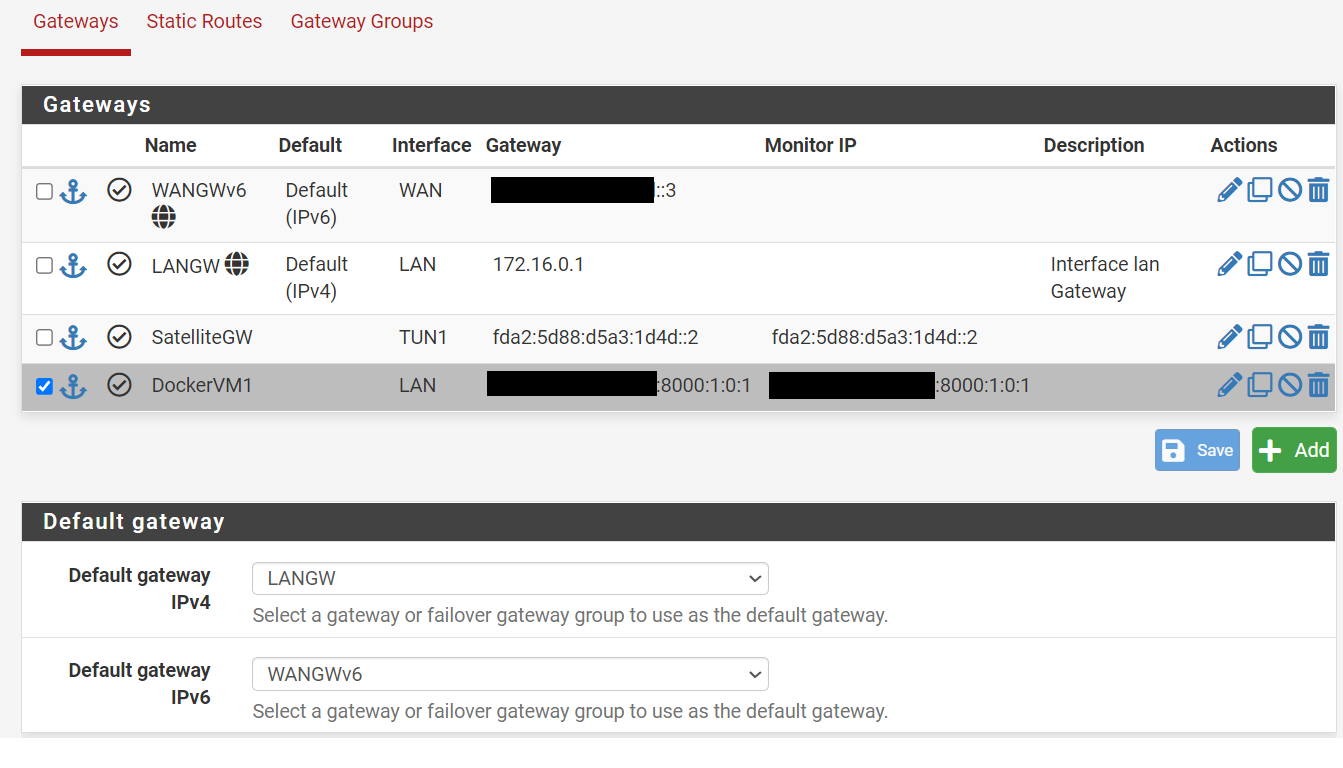
Default gateways for the VM hosts.
- IPv6: rangeIPv6::4 /65
- IPv4: 169.254.0.2 /16
- IPv4: 172.16.0.1/16 (NATed from Host)
- IPv6: rangeIPv6:8000::2 /77
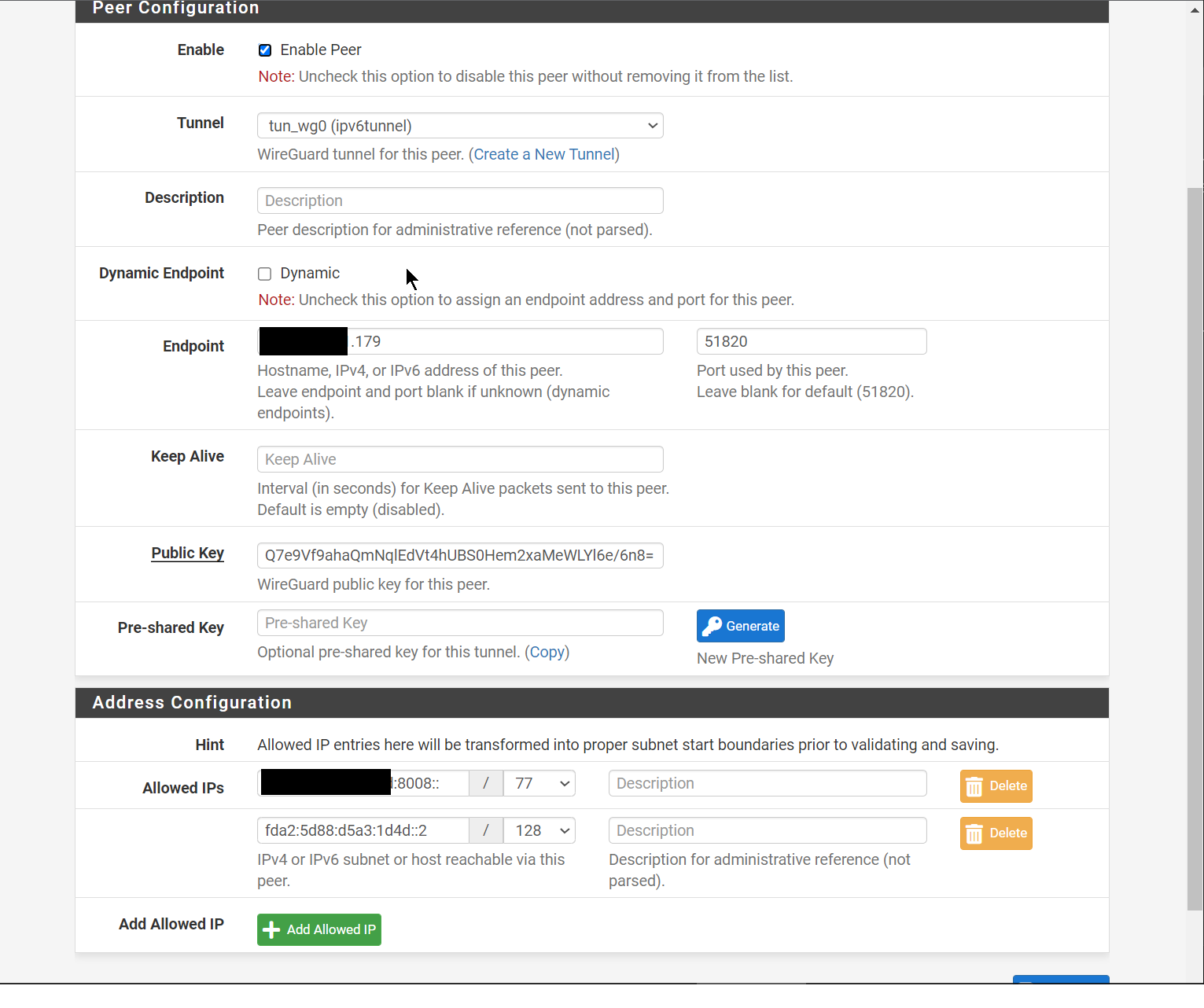
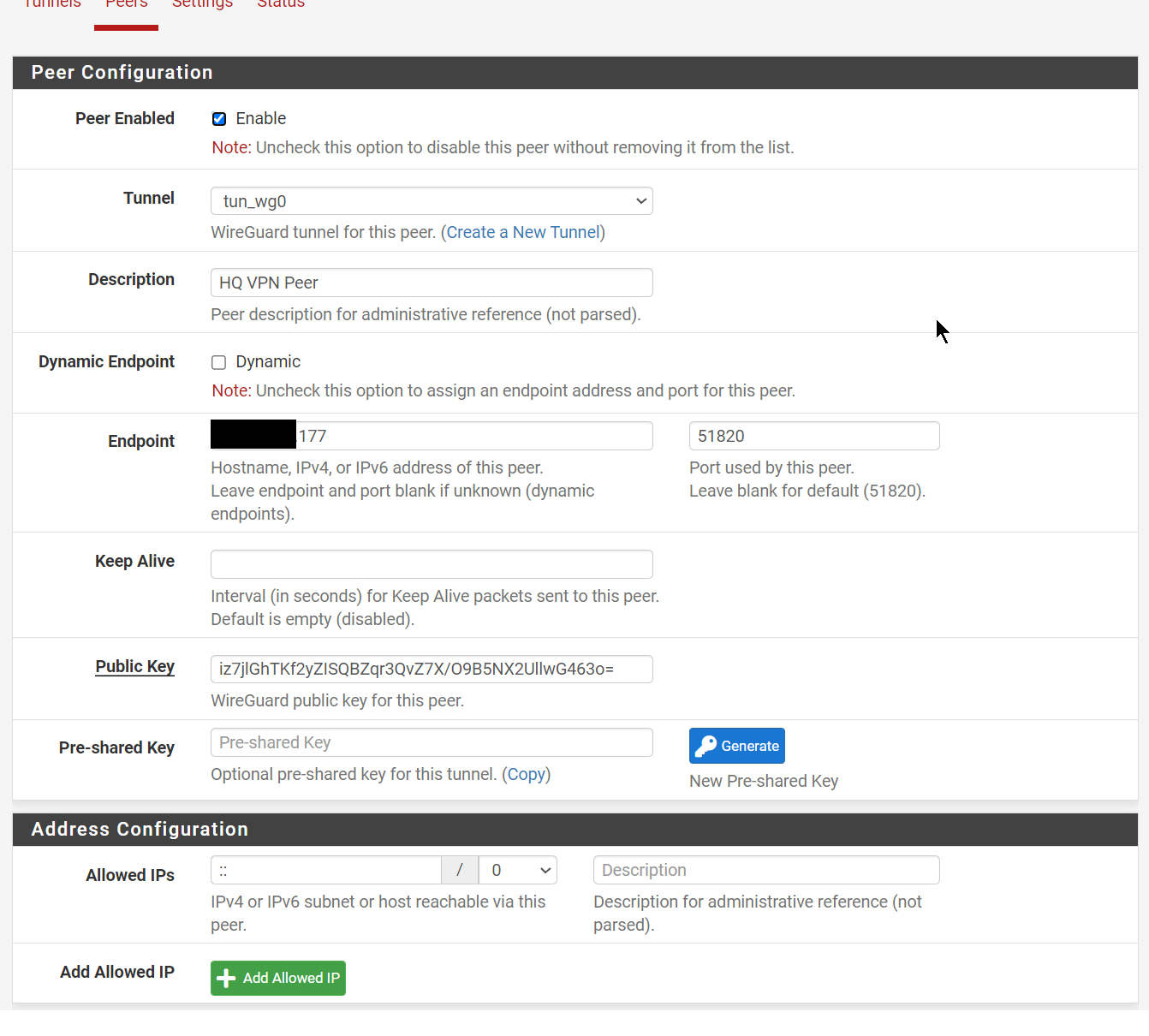
We configure WireGuard in a Site-to-Site setup as described here: https://docs.netgate.com/pfsense/en/latest/recipes/wireguard-s2s.html
With this configuration:
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Design | Site-to-Site, one peer per tunnel |
| Tunnel Subnet | fda2:5d88:d5a3:1d4d::/64 |
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Endpoint IP Address | Home IPv4 |
| TUN IPv6 Address | fda2:5d88:d5a3:1d4d::1/64 |
| Listen Port | 51820 |
| SatelliteGW | fda2:5d88:d5a3:1d4d::2 via TUN interface |
| Static Route | rangeIPv6:8008::/77 via SatelliteGW |
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Endpoint IP Address | Proxmox IPv4 |
| TUN IPv6 Address | fda2:5d88:d5a3:1d4d::2/64 |
| Listen Port | 51820 |
| LAN IPv6 | rangeIPv6:8008::1/77 |
| GW IPv6 | fda2:5d88:d5a3:1d4d::1/64 via TUN |
| DHCPv6 on LAN | rangeIPv6:8008:1:: to rangeIPv6:800f:ffff:ffff:ffff |
| RA on LAN | Assisted |
The default GW for IPv6 is rangeIPv6::3 trough the WAN interface, this is because this interface is connected to the KVM bridge that has access to the connection to the internet.
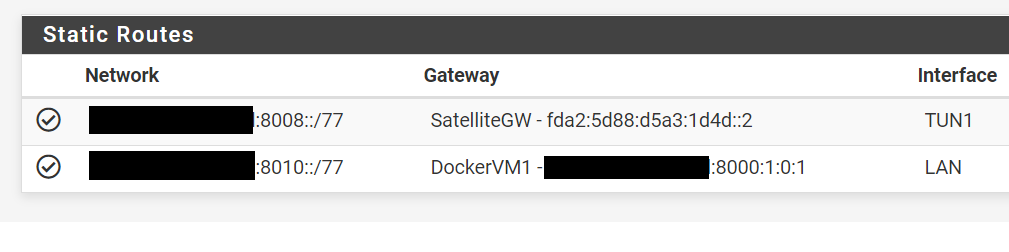
Each Docker network in the VM host gets a static route so they can communicate between each other.
For this we need to define a Gateway as rangeIPv6:8000:1:0:1 (VM1) trough the LAN interface called "DockerVM1" in the picture.
SatelliteGW is the gateway on the other side of the WireGuard Tunnel.
Finally we add a 2 static routes:
- Containers in VM1: Our container subnet rangeIPv6:8010::/77 can be reached trough the "DockerVM1" gateway that means trough the LAN interface via the host at rangeIPv6:8000:1:0:1
- IPv4 to Ipv6 Tunnel: rangeIPv6:8008::/77 will be served to clients connected to the WireGuard tunnel via the other side of the TUN1 interface at fda2:5d88:d5a3:1d4d::2
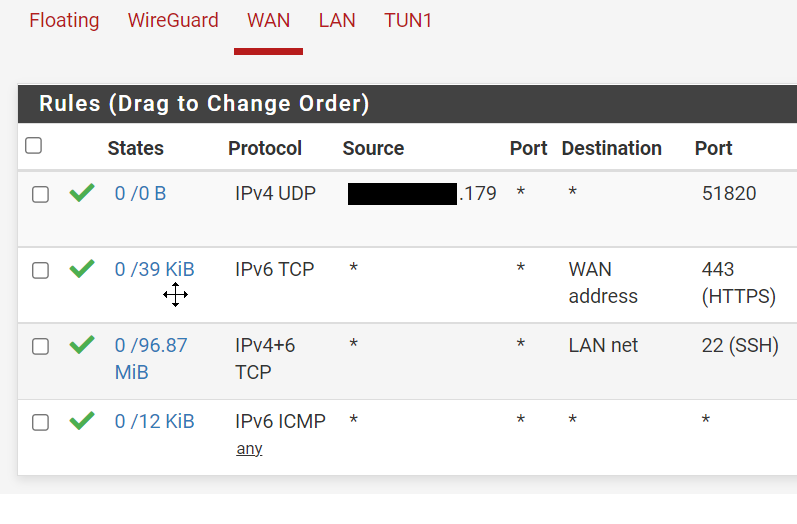
The rules to allow a Port in our IPv6 networks is done in the WAN interface.
Allow all IPv4 and IPv6 in the LAN interface
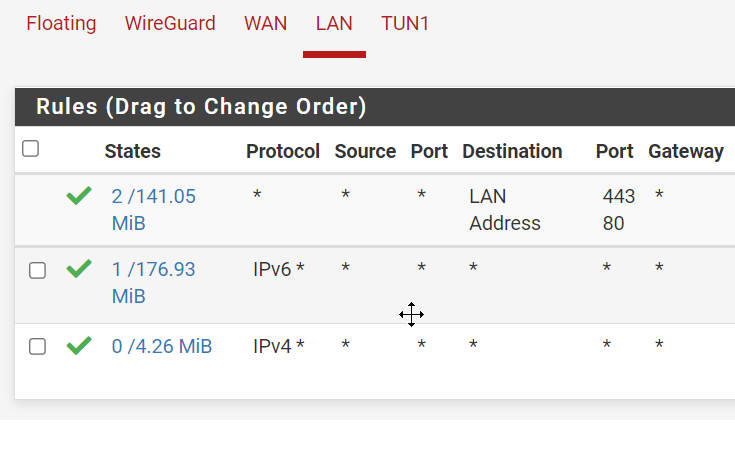
This is the VM ipv6 range that will be managed by the DHCP
- Enable DHCPv6 server with range: rangeIPv6:8000:2:: to rangeIPv6:ffff:ffff:ffff
- Enable Assisted RA
- NO dhcpv6 on LAN6(wan)
- ifconfig
docker0: flags=4099<UP,BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 172.17.0.1 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 172.17.255.255
inet6 rangeIPv6:8010::1 prefixlen 77 scopeid 0x0<global>
ens19: flags=4675<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,ALLMULTI,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 172.16.99.10 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 172.16.255.255
inet6 rangeIPv6:8000:1:0:1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x0<global>
- route
::1 dev lo proto kernel metric 256 pref medium
rangeIPv6:8000:1:0:1 dev ens19 proto kernel metric 100 pref medium
rangeIPv6:8000::/77 dev ens19 proto ra metric 100 pref medium
rangeIPv6:8008::/77 dev docker0 metric 1024 linkdown pref medium
rangeIPv6:8010::/77 dev docker0 proto kernel metric 256 linkdown pref medium
rangeIPv6:8010::/77 dev docker0 metric 1024 linkdown pref medium
fe80::/64 dev ens19 proto kernel metric 100 pref medium
fe80::/64 dev docker0 proto kernel metric 256 linkdown pref medium
default via fe80::3039:93ff:fe18:ccdd dev ens19 proto ra metric 20100 pref high
More information: https://docs.docker.com/v17.09/engine/userguide/networking/default_network/ipv6/#routed-network-environment
We configure docker to use a /77 subnets under rangeIPv6
- /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"ipv6": true,
"fixed-cidr-v6": "rangeIPv6:8010::/77"
}
Test it by using an alpine container:
# docker run -it alpine ash
/ # ip -6 addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 state UNKNOWN qlen 1000
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
11: eth0@if12: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP,M-DOWN> mtu 1500 state UP
inet6 rangeIPv6:8010:242:ac11:2/77 scope global flags 02
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::42:acff:fe11:2/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
/ # ip -6 route
rangeIPv6:8010::/77 dev eth0 metric 256
fe80::/64 dev eth0 metric 256
default via rangeIPv6:8010::1 dev eth0 metric 1024
multicast ff00::/8 dev eth0 metric 256
/ # ping -6 www.google.com
PING www.google.com (2a00:1450:4001:810::2004): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 2a00:1450:4001:810::2004: seq=0 ttl=115 time=5.769 ms
64 bytes from 2a00:1450:4001:810::2004: seq=1 ttl=115 time=5.885 ms
^C
--- www.google.com ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 5.769/5.827/5.885 ms
From here we can see we got rangeIPv6:ac11:2/77 and ping to Google over IPv6 works.
From https://cloud.debian.org/images/cloud/ Download the latest qcow2 file.
wget https://cloud.debian.org/images/cloud/bullseye/20230515-1381/debian-11-genericcloud-amd64-20230515-1381.qcow2
qm create 9500 --name Debian11CloudInit --net0 virtio,bridge=vmbr0
qm importdisk 9500 debian-11-genericcloud-amd64-20220613-1045.qcow2 local-lvm
qm set 9500 --scsihw virtio-scsi-pci --scsi0 local-lvm:vm-9500-disk-0
qm set 9500 --ide2 local-lvm:cloudinit
qm set 9500 --boot c --bootdisk scsi0
qm set 9500 --serial0 socket --vga serial0
qm set 9500 --agent enabled=1 #optional but recommended
qm template 9500