A golang http request library for humans
- Light weight
- Simple
- Easy play with JSON and XML
- Easy for debug and logging
- Easy file uploads and downloads
- Easy manage cookie
- Easy set up proxy
- Easy set timeout
- Easy customize http client
go get github.com/imroc/reqreq implements a friendly API over Go's existing net/http library.
Req and Resp are two most important struct, you can think of Req as a client that initiate HTTP requests, Resp as a information container for the request and response. They all provide simple and convenient APIs that allows you to do a lot of things.
func (r *Req) Post(url string, v ...interface{}) (*Resp, error)In most cases, only url is required, others are optional, like headers, params, files or body etc.
There is a default Req object, all of its' public methods are wrapped by the req package, so you can also think of req package as a Req object
// use Req object to initiate requests.
r := req.New()
r.Get(url)
// use req package to initiate request.
req.Get(url)You can use req.New() to create lots of *Req as client with independent configuration
Basic
Set Header
Set Param
Set Body
Debug
Output Format
ToJSON & ToXML
Get *http.Response
Upload
Download
Cookie
Set Timeout
Set Proxy
Customize Client
Set context.Context
header := req.Header{
"Accept": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4=",
}
param := req.Param{
"name": "imroc",
"cmd": "add",
}
// only url is required, others are optional.
r, err := req.Post("http://foo.bar/api", header, param)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
r.ToJSON(&foo) // response => struct/map
log.Printf("%+v", r) // print info (try it, you may surprise) Use req.Header (it is actually a map[string]string)
authHeader := req.Header{
"Accept": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4=",
}
req.Get("https://www.baidu.com", authHeader, req.Header{"User-Agent": "V1.1"})use http.Header
header := make(http.Header)
header.Set("Accept", "application/json")
req.Get("https://www.baidu.com", header)You can also set header from struct, use HeaderFromStruct func to parse your struct
type HeaderStruct struct {
UserAgent string `json:"User-Agent"`
Authorization string `json:"Authorization"`
}
func main(){
h := HeaderStruct{
"V1.0.0",
"roc",
}
authHeader := req.HeaderFromStruct(h)
req.Get("https://www.baidu.com", authHeader, req.Header{"User-Agent": "V1.1"})
}Note: Please add tag 'json' to your argument in struct to let you customize the key name of your header
Use req.Param (it is actually a map[string]interface{})
param := req.Param{
"id": "imroc",
"pwd": "roc",
}
req.Get("http://foo.bar/api", param) // http://foo.bar/api?id=imroc&pwd=roc
req.Post(url, param) // body => id=imroc&pwd=rocuse req.QueryParam force to append params to the url (it is also actually a map[string]interface{})
req.Post("http://foo.bar/api", req.Param{"name": "roc", "age": "22"}, req.QueryParam{"access_token": "fedledGF9Hg9ehTU"})
/*
POST /api?access_token=fedledGF9Hg9ehTU HTTP/1.1
Host: foo.bar
User-Agent: Go-http-client/1.1
Content-Length: 15
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8
Accept-Encoding: gzip
age=22&name=roc
*/Put string, []byte and io.Reader as body directly.
req.Post(url, "id=roc&cmd=query")Put object as xml or json body (add Content-Type header automatically)
req.Post(url, req.BodyJSON(&foo))
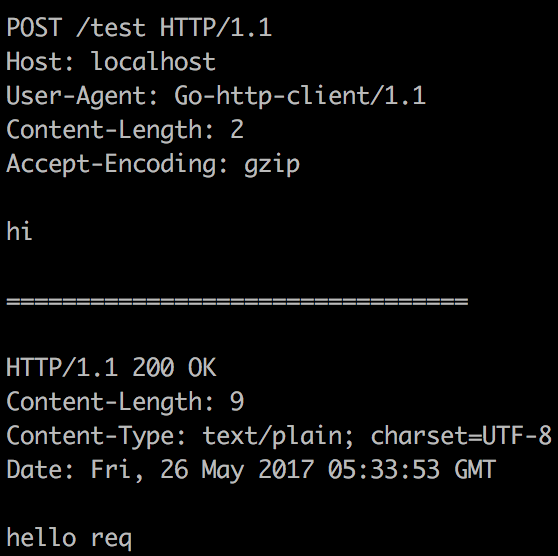
req.Post(url, req.BodyXML(&bar))Set global variable req.Debug to true, it will print detail infomation for every request.
req.Debug = true
req.Post("http://localhost/test" "hi")You can use different kind of output format to log the request and response infomation in your log file in defferent scenarios. For example, use %+v output format in the development phase, it allows you to observe the details. Use %v or %-v output format in production phase, just log the information necessarily.
Output in detail
r, _ := req.Post(url, header, param)
log.Printf("%+v", r) // output the same format as Debug is enabledOutput in simple way (default format)
r, _ := req.Get(url, param)
log.Printf("%v\n", r) // GET http://foo.bar/api?name=roc&cmd=add {"code":"0","msg":"success"}
log.Prinln(r) // same as aboveOutput in simple way and keep all in one line (request body or response body may have multiple lines, this format will replace "\r" or "\n" with " ", it's useful when doing some search in your log file)
You can call SetFlags to control the output content, decide which pieces can be output.
const (
LreqHead = 1 << iota // output request head (request line and request header)
LreqBody // output request body
LrespHead // output response head (response line and response header)
LrespBody // output response body
Lcost // output time costed by the request
LstdFlags = LreqHead | LreqBody | LrespHead | LrespBody
)req.SetFlags(req.LreqHead | req.LreqBody | req.LrespHead)req.SetFlags(req.LstdFlags | req.Lcost) // output format add time costed by request
r,_ := req.Get(url)
log.Println(r) // http://foo.bar/api 3.260802ms {"code":0 "msg":"success"}
if r.Cost() > 3 * time.Second { // check cost
log.Println("WARN: slow request:", r)
}r, _ := req.Get(url)
r.ToJSON(&foo)
r, _ = req.Post(url, req.BodyXML(&bar))
r.ToXML(&baz)// func (r *Req) Response() *http.Response
r, _ := req.Get(url)
resp := r.Response()
fmt.Println(resp.StatusCode)Use req.File to match files
req.Post(url, req.File("imroc.png"), req.File("/Users/roc/Pictures/*.png"))Use req.FileUpload to fully control
file, _ := os.Open("imroc.png")
req.Post(url, req.FileUpload{
File: file,
FieldName: "file", // FieldName is form field name
FileName: "avatar.png", //Filename is the name of the file that you wish to upload. We use this to guess the mimetype as well as pass it onto the server
})Use req.UploadProgress to listen upload progress
progress := func(current, total int64) {
fmt.Println(float32(current)/float32(total)*100, "%")
}
req.Post(url, req.File("/Users/roc/Pictures/*.png"), req.UploadProgress(progress))
fmt.Println("upload complete")r, _ := req.Get(url)
r.ToFile("imroc.png")Use req.DownloadProgress to listen download progress
progress := func(current, total int64) {
fmt.Println(float32(current)/float32(total)*100, "%")
}
r, _ := req.Get(url, req.DownloadProgress(progress))
r.ToFile("hello.mp4")
fmt.Println("download complete")By default, the underlying *http.Client will manage your cookie(send cookie header to server automatically if server has set a cookie for you), you can disable it by calling this function :
req.EnableCookie(false)and you can set cookie in request just using *http.Cookie
cookie := new(http.Cookie)
// ......
req.Get(url, cookie)req.SetTimeout(50 * time.Second)By default, req use proxy from system environment if http_proxy or https_proxy is specified, you can set a custom proxy or disable it by set nil
req.SetProxy(func(r *http.Request) (*url.URL, error) {
if strings.Contains(r.URL.Hostname(), "google") {
return url.Parse("http://my.vpn.com:23456")
}
return nil, nil
})Set a simple proxy (use fixed proxy url for every request)
req.SetProxyUrl("http://my.proxy.com:23456")You can pass context.Context in simple way:
r, _ := req.Get(url, context.Background())Use SetClient to change the default underlying *http.Client
req.SetClient(client)Specify independent http client for some requests
client := &http.Client{Timeout: 30 * time.Second}
req.Get(url, client)Change some properties of default client you want
req.Client().Jar, _ = cookiejar.New(nil)
trans, _ := req.Client().Transport.(*http.Transport)
trans.MaxIdleConns = 20
trans.TLSHandshakeTimeout = 20 * time.Second
trans.DisableKeepAlives = true
trans.TLSClientConfig = &tls.Config{InsecureSkipVerify: true}