A layer on top of hibernate which adheres configurable finite state machine. Prevents dirty commits which violates transitions.
When you have to apply some business logic that can be converted to finite state machine, hiberante-fsm helps you achieve it.
It prevents invalid state transitions before saving it to the database so at the application level you don't have to worry about it.
- Implement state machines over any entity field in your spring boot app with a simple configuration
- Prevent faulty transitions which are not part of state machine (adhering db transaction boundary)
- Add additional validators (on top of normal checks)
- Run side-effects after successful transactions
Finite State Machine wiki
Add following code snippet inside <dependencies> of your pom.xml file.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.skydo.lib</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-fsm</artifactId>
<version>0.1.3-RELEASE</version>
</dependency>Add following line
dependency {
implementation 'com.skydo.lib.hibernate-fsm:0.1.0-RELEASE'
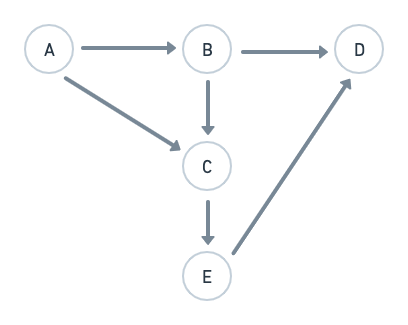
}E.g.: For a User entity, there is a column userState.
- The possible values of
userStateare"A", "B", "C", "D", "E"(finite number of states) - Initial state:
"A" - Valid transitions:
- A → B
- A → C
- B → C
- B → D
- C → E
- E → D
- Invalid transitions:
- A → D
- C → B
- This is how java code will look like for the said FSM.
import com.skydo.lib.fsm.definitions.StateMachine;
import com.skydo.lib.fsm.definitions.Transition;
@Entity(name = "user")
public class User {
private Long id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private int age;
private String userHandle;
/**
* `@StateMachine` conveys hibernate-fsm library, that `userState` is the column
* which should be checked every time there is a database transaction commit.
*/
@StateMachine(
initialState = "A",
/**
* This `config is generated based on the mentioned picture.
*/
config = {
@Transition(fromState = "A", toState = {"B", "C"}),
@Transition(fromState = "B", toState = {"C", "D"}),
@Transition(fromState = "C", toState = {"E"}),
@Transition(fromState = "E", toState = {"D"}),
}
)
private UserState userState;
}While committing to the database transaction,
It runs behind the scenes of save, saveAll function executions, so you don't have to write anything here.
Following checks are done on userState, before committing to the database:
- If a transition from
oldValue→newValueis a valid transition from configuration - If it is a
insert(new row in the table), it checks if the value is correctinitialState.
If checks are passed then transaction is allowed to commit, otherwise the libary raises StateValidationException
Let's say, during the state transition of A → B you want to run some extra validations
on the db and allow transition depending on the status checks.
These validations can be anything like: querying other table payment, if the user had made the payment
then only allow user to move to state from A → B
To achieve this, create a @Component (must), wrap it with annotation
@TransitionValidatorHandler, declare validation function inside this class and annotate this method with @TransitionValidator
import com.skydo.lib.fsm.definitions.validator.TransitionValidator;
import com.skydo.lib.fsm.definitions.validator.TransitionValidatorHandler;
import com.skydo.lib.fsm.exception.StateValidationException;
@Component // <-- this is very important
@TransitionValidatorHandler(
/**
* entity's class reference
*/
entity = User.class,
/**
* As java doesn't support annotation values at run time,
* we must pass field name in form of string, on which we have applied `@StateMachine` annotation.
*/
field = "userState"
)
public class UserStateValidator {
private static final Logger log = Logger.getLogger(UserStateValidator.class.getSimpleName());
/**
* Assumption: transition is already a valid transition and post that this validator is executed.
*
* @param id `id` is user id. can be used to query other tables.
* @param oldState
* @param newState
*/
@TransitionValidator(
/**
* This function is executed only if the `newValue` is going to be `B`.
*/
state = "B"
)
public void validateTransition(Long id, Object oldState, Object newState) {
log.info("validateTransition called. id: " + id + " " + oldState + ", newState: " + newState);
// Add more checks here.
Payment payment = paymentRepository.findByUserId(id);
if (payment.status != "PAID") {
/**
* This exception will roll back the db transaction even though transition
* `A` --> `B` was a valid one.
*/
throw StateValidationException(
"Can't move user of id: " + id + " to state " + newState + " if payment status in unpaid."
);
}
}
}userRepository.save(newUpdateUser);hibernate-fsmchecks if it is a valid transition, in case of invalid it throws exception and transaction is rolled back,- function annotated with
@TransitionValidatorgets executed, if it throws exception, transaction is rolled back. transactionis finally committed.
This validator is executed only after library has already confirmed that the transition is a valid transition.
If you want to execute a side effect based function, which gets executed once a state "B" is reached.
The usage is very similar to the validator.
This is executed outside of database transaction boundary.
import com.skydo.lib.fsm.definitions.postupdate.PostUpdateAction;
import com.skydo.lib.fsm.definitions.postupdate.PostUpdateActionHandler;
@Component // <-- this is very important
@PostUpdateActionHandler(
/**
* entity's class reference
*/
entity = User.class,
/**
* As java doesn't support annotation values at run time,
* we must pass field name in form of string, on which we have applied `@StateMachine` annotation.
*/
field = "userState"
)
public class UserStatePostCommitActions {
private static final Logger log = Logger.getLogger(UserStateValidator.class.getSimpleName());
/**
* Assumption: transition is already a valid transition and post that this validator is executed.
*
* @param id `id` is user id. can be used to query other tables.
* @param oldState
* @param newState
*/
@PostUpdateAction(
/**
* This function is executed only if the `newValue` is going to be `B`.
*/
state = "B"
)
public void postUpdateActionOnStateB(Long id, Object oldState, Object newState) {
log.info("postUpdateActionOnStateB called. id: " + id + " " + oldState + ", newState: " + newState);
// Add any side effect functions here
// e.g. Send Email / Notification
}
@PostUpdateAction(
/**
* This function is executed on all state changes of field userState.
*/
state = "*"
)
public void postUpdateActionGeneric(Long id, Object oldState, Object newState) {
log.info("postUpdateActionGeneric called. id: " + id + " " + oldState + ", newState: " + newState);
// Add any side effect functions here
// e.g. Send Email / Notification
}
}userRepository.save(newUpdateUser);hibernate-fsmchecks if it is a valid transition, in case of invalid it throws exception and transaction is rolled back,- function annotated with
@TransitionValidatorgets executed, if it throws exception, transaction is rolled back. transactionis finally committed.- function annotated with
@PostUpdateActiongets executed, if it throws exception, transaction is NOT rolled back.
This library only support spring boot as of now, PRs are always welcome. Contact contributors to discuss the reasons.
Reach out to @r1jsheth, nineteen94