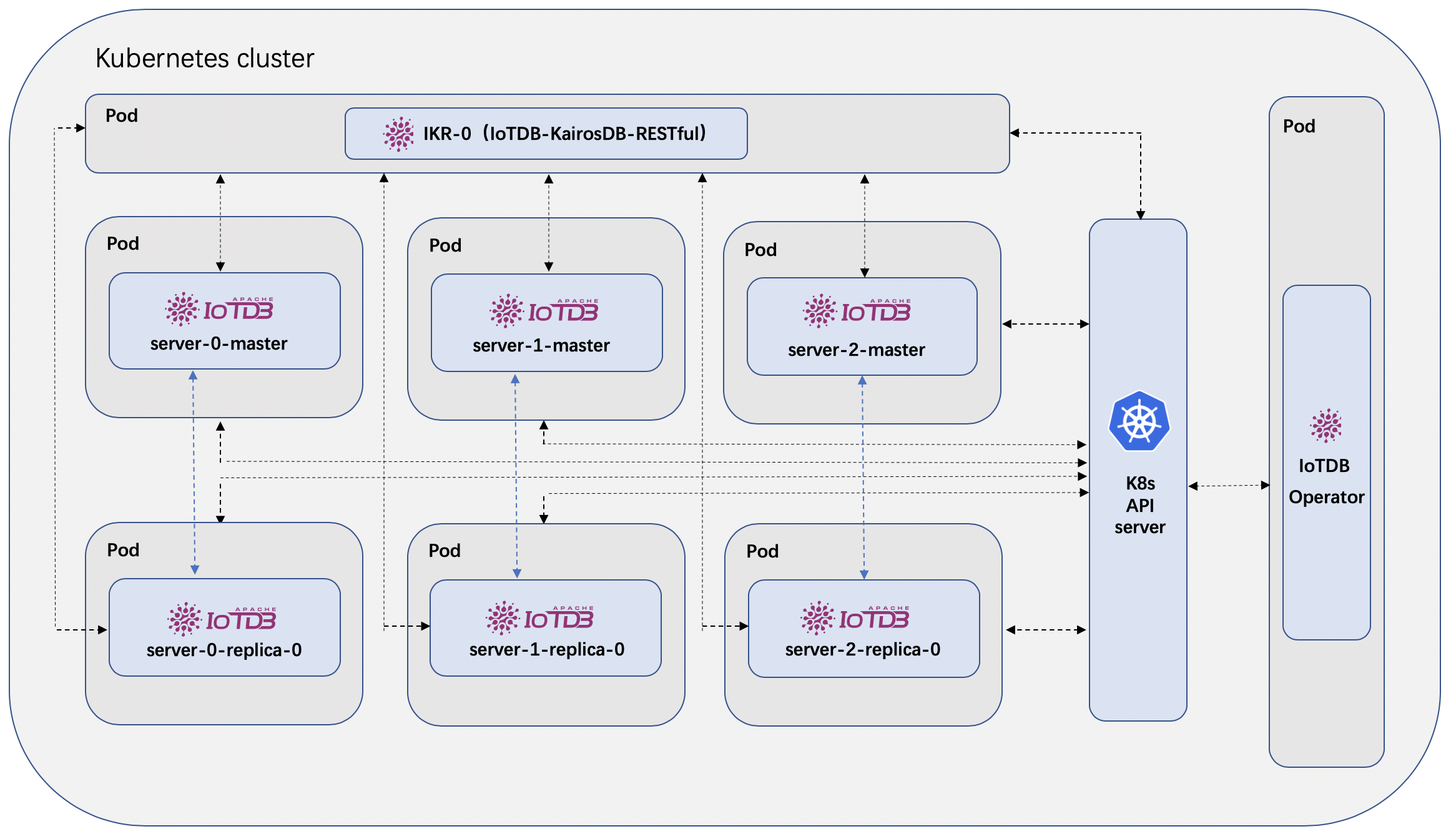
IoTDB Operator is to manage IoTDB service instances deployed on the Kubernetes cluster. It is built using the Operator SDK, which is part of the Operator Framework.
- Clone the project on your Kubernetes cluster master node:
$ git clone https://github.com/liuruiyiyang/iotdb-operator
$ cd iotdb-operator
- To deploy the IoTDB Operator on your Kubernetes cluster, please run the following script:
$ ./install-operator.sh
- Use command
kubectl get podsto check the IoTDB Operator deploy status like:
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
iotdb-operator-564b5d75d-jllzk 1/1 Running 0 108s
Now you can use the CRDs provide by IoTDB Operator to deploy your IoTDB cluster.
Before IoTDB deployment, you may need to do some preparation steps for IoTDB data persistence.
Currently we provide several options for your IoTDB data persistence: EmptyDir, HostPath and NFS, which can be configured in CR files, for example in iotdb_v1alpha1_iotdb_cr.yaml:
...
# storageMode can be EmptyDir, HostPath, NFS
storageMode: HostPath
...
If you choose EmptyDir, you don't need to do extra preparation steps for data persistence. But the data storage life is the same with the pod's life, if the pod is deleted you may lost the data.
If you choose other storage modes, please refer to the following instructions to prepare the data persistence.
This storage mode means the IoTDB data (including all the logs and store files) is stored in each host where the pod lies on. In that case you need to create an dir where you want the IoTDB data to be stored on.
We provide a script in deploy/storage/hostpath/prepare-host-path.sh, which you can use to create the HostPath dir on every worker node of your Kubernetes cluster.
$ cd deploy/storage/hostpath
$ sudo su
$ ./prepare-hostpath.sh
Changed hostPath /data/iotdb/iotdb uid to 2000, gid to 2000
You may refer to the instructions in the script for more information.
If you choose NFS as the storage mode, the first step is to prepare a storage class based on NFS provider to create PV and PVC where the IoTDB data will be stored.
-
Deploy NFS server and clients on your Kubernetes cluster. You can refer to NFS deployment document for more details. Please make sure they are functional before you go to the next step. Here is a instruction on how to verify NFS service.
- On your NFS client node, check if NFS shared dir exists.
$ showmount -e 192.168.130.32 Export list for 192.168.130.32: /data/k8s *- On your NFS client node, create a test dir and mount it to the NFS shared dir (you may need sudo permission).
$ mkdir -p ~/test-nfc $ mount -t nfs 192.168.130.32:/data/k8s ~/test-nfc- On your NFS client node, create a test file on the mounted test dir.
$ touch ~/test-nfc/test.txt- On your NFS server node, check the shared dir. If there exists the test file we created on the client node, it proves the NFS service is functional.
$ ls -ls /data/k8s/ total 4 4 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 4 Jul 10 21:50 test.txt -
Modify the following configurations of the
deploy/storage/nfs-client.yamlfile:
...
- name: NFS_SERVER
value: 192.168.130.32
- name: NFS_PATH
value: /data/k8s
volumes:
- name: nfs-client-root
nfs:
server: 192.168.130.32
path: /data/k8s
...
Replace 192.168.130.32 and /data/k8s with your true NFS server IP address and NFS server data volume path.
- Create a NFS storage class for IoTDB, run
$ cd deploy/storage
$ ./deploy-storage-class.sh
- If the storage class is successfully deployed, you can get the pod status like:
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nfs-client-provisioner-7cf858f754-7vxmm 1/1 Running 0 136m
iotdb-operator-564b5d75d-jllzk 1/1 Running 0 108s
IoTDB Operator provides several CRDs to allow users define their IoTDB service component cluster, which currently includes the IoTDB Server cluster and the IKR cluster.
Check the file iotdb_v1alpha1_iotdb_cr.yaml in the example directory, for example:
apiVersion: iotdb.apache.org/v1alpha1
kind: IoTDB
metadata:
name: iotdb
spec:
# sharding define how the instances are distributed by time and schema
sharding:
- scaleTime: "2018-9-20T00:00:00+08:00"
schemaSegmentNum: 2
- scaleTime: "2019-5-14T00:53:28+08:00"
schemaSegmentNum: 3
# iotdbImage is the customized docker image repo of IoTDB
iotdbImage: 2019liurui/iotdb-iotdb:0.9.0-alpine
# replicaNum is the size of replica
replicaNum: 0
# imagePullPolicy is the image pull policy
imagePullPolicy: Always
# storageMode can be EmptyDir, HostPath, NFS
storageMode: EmptyDir
# hostPath is the local path to store data
hostPath: /data/iotdb/server
# volumeClaimTemplates defines the storageClass
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: iotdb-storage
annotations:
volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-class: iotdb-storage
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
resources:
requests:
storage: 8Gi
# ikrImage is the customized docker image repo of IKR
ikrImage: 2019liurui/iotdb-ikr:0.9.0-alpine
# ikrSize is the number of IKR instance
ikrSize: 2
which defines the IoTDB server cluster scale, the IKR cluster scale and so on.
- Deploy the IoTDB cluster by running:
$ kubectl apply -f example/iotdb_v1alpha1_iotdb_cr.yaml
- After a while when all the IoTDB server pod status is running, the IKR pod will be launched. Then check the status:
$ kubectl get pods -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
iotdb-0-0-master-0 1/1 Running 0 114s 10.1.0.179 docker-desktop <none> <none>
iotdb-0-1-master-0 1/1 Running 0 114s 10.1.0.180 docker-desktop <none> <none>
iotdb-1-0-master-0 1/1 Running 0 114s 10.1.0.181 docker-desktop <none> <none>
iotdb-1-1-master-0 1/1 Running 0 114s 10.1.0.183 docker-desktop <none> <none>
iotdb-1-2-master-0 1/1 Running 0 114s 10.1.0.182 docker-desktop <none> <none>
iotdb-ikr-0 1/1 Running 0 30s 10.1.0.184 docker-desktop <none> <none>
iotdb-ikr-1 1/1 Running 0 22s 10.1.0.185 docker-desktop <none> <none>
iotdb-operator-5c57b6667c-mfxkh 1/1 Running 0 2m14s 10.1.0.178 docker-desktop <none> <none>
We can see that there are 5 IoTDB server pods and 2 IKR pods as we expected and defined in the example CRD file iotdb_v1alpha1_iotdb_cr.yaml.
We can use the port provided by k8s service to access IoTDB and IKR outside the cluster network:
$ kubectl apply -f example/service_ikr.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f example/service_iotdb.yaml
- Check the PV and PVC status :
$ kubectl get pvc
$ kubectl get pv
Notice: if you don't choose the NFS storage mode, then the above PV and PVC won't be created.
Congratulations! You have successfully deployed your IoTDB cluster by IoTDB Operator.
Access on any node which contains the IoTDB service pod, check the hostPath you configured, for example:
$ ls /data/iotdb/iotdb
logs store
...
Access the NFS server node of your cluster and verify whether the IoTDB data have been stored in your NFS data volume path:
$ cd /data/k8s/
$ ls
...
If you want to tear down the IoTDB cluster, to remove the all the service instances run
$ kubectl delete -f example/iotdb_v1alpha1_iotdb_cr.yaml
to remove the IoTDB Operator:
$ ./purge-operator.sh
to remove the storage class for IoTDB:
$ cd deploy/storage
$ ./remove-storage-class.sh
Note: the NFS and HostPath persistence data will not be deleted by default.
- git
- go version v1.12+.
- mercurial version 3.9+
- docker version 17.03+.
- Access to a Kubernetes v1.11.3+ cluster.
- dep version v0.5.0+.
- operator-sdk version v0.11.0+
For developers who want to build and push the operator-related images to the docker hub, please follow the instructions below.
IoTDB-Operator uses operator-sdk to generate the scaffolding and build the operator image. You can refer to the operator-sdk user guide for more details.
If you want to push the newly build operator image to your own docker hub, please modify the DOCKERHUB_REPO variable in the create-operator.sh script using your own repository. Then run the build script:
$ ./create-operator.sh
IoTDB-Operator is based on customized images of IoTDB server and IKR, which are build by build-iotdb-image.sh and similar scripts in the IKR project, which contains customized scripts. Therefore, the images used in the IoTDB CR yaml files should be build by these scripts.
You can also modify the DOCKERHUB_REPO variable in the scripts to push the newly build images to your own repository:
$ cd images/iotdb
$ ./build-iotdb-image.sh
Note: for users who just want to use the operator, there is no need to build the operator and customized IKR and IoTDB server images themselves. Users can simply use the default official images which are maintained by the IoTDB community.