BDH is an open source project developed using Shell Script and AWK languages that allowing Linux and Unix users a symple way to monitor their File Systems(FS) through visual messages with colors and effects to classify among NORMAL, MAJOR, CRITICAL or URGENT usage thresholds. But the main functionality of BDH is the possibility to configure the program to automatically send alarms messages of the usage of each FS through Slack and Webhook with no additional programs or libraries required.
- Intro
- Getting Started
- Prerequisites
- Installing
- How to use bdh in manually mode
- How to use bdh in automatic mode
- Log file
- Author
These instructions will get you a copy of the project up and running on your local machine for development and testing purposes. See deployment for notes on how to deploy the project on a live system.
BDH needs Linux or Unix OS with BASH 4.1 (or higher), internet connection (to send alert messages), and a SLACK account with WebHook app installed. For further information to install Webhook app at Slack and how to generate HTTPS URL click here
Download bdh file in zip format or tar format, unzip, and move it to any directory which is in the system PATH.
To see which directories were set up in the system PATH, type the command below using the system terminal:
$ echo $PATH
The output will show the variable PATH content similar as follows:
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/snap/bin:/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-oracle/bin:/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-oracle/db/bin:/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-oracle/jre/bin
Choose one of these directories to copy bdh file (usually is /usr/local/bin) type the following command line:
$ cp bdh <path directory>
Give eXecution permission to the file typing in the command line:
$ chmod +x <path directory>/bdh
And DONE! bdh was successfully installed!
To confirm if everything is working well, use bdh help command to see usage message.
$ bdh -h
In the manually mode bdh shows all FS usage on the screen, printing NORMAL, MAJOR, CRITICAL, and URGENT alert messages through the colors and visual effects.
The commands and their options to run bdh program in manually mode are:
$ bdh -g or $ bdh -G #Gb Format.
$ bdh -m or $ bdh -M #Mb Format.
$ bdh -k or $ bdh -K #Kb Format.
Depending to the usage and thresholds set up for each file system, a different kind of visual alarm will be displayed on the screen as follows:
White fill -> The FS usage is less to NORMAL usage according to the thresholds configurations.
Yellow fill -> The FS reached to MAJOR usage according to the threshold configurations.
Red fill -> The FS reached to CRITICAL usage according to the threshold configurations.
Flashing -> The FS reached to URGENT usage according to the threshold configurations.
The animated image above shows the result of all visual alarm possibilities when bdh was ran in manually mode.
On this mode bdh runs as daemon and monitore the FS automatically through intervall time option (in seconds) required to start the process. When one or more FS reach to CRITICAL or URGENT threshold, the user is notified through an alarm message sent to SLACK CHANNEL using incoming WebHook messages app.
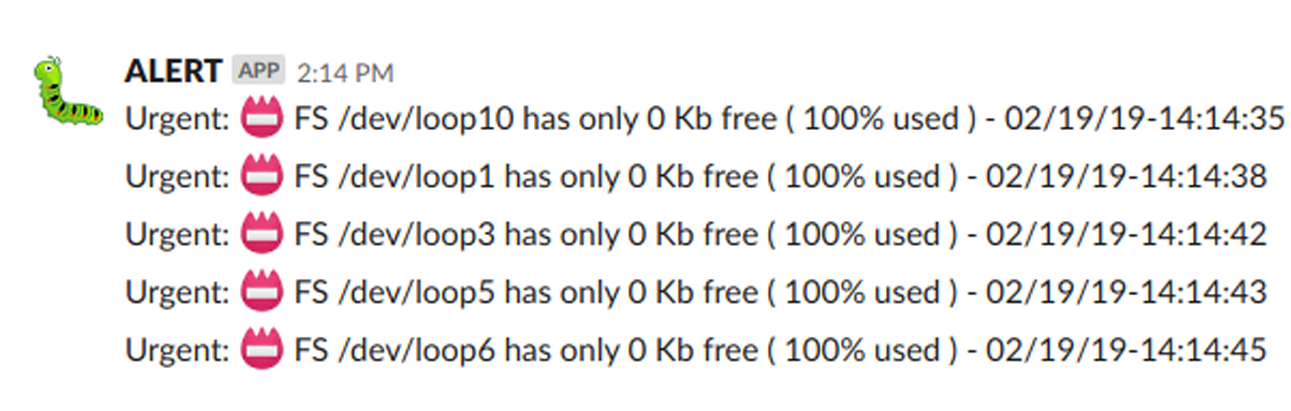
The image below shows an alert message sent to Slack by bdh.
To START bdh as deamon (automatic) mode, the user need to type the following command in the system terminal:
$ bdh -d or bdh -D (interval in seconds) #eg. bdg -d 60 -> bdh check all FS use every minute (60 seconds).
Once started in the Daemon mode, the better and safe way to STOP bdh process is typing the following command on the systen terminal:
$ bdh -s or bdh -S
Example of CRITICAL alarm message identify by a 💣 icon sent to SLACK #CHANNEL by bdh -d process:
Example of URGENT alarm message isentify by a 🔥 icon sent to SLACK #CHANNEL by bdh -d process:
When bdh starts in daemon mode (and only in this mode), a log file named bdh_.log is generated. To set up the log directory where the log will be stored, see the next session how to configure bdh of this document.
Basically the information displayed in bdh logfile are START time ( with Process ID (PID), Interval time used, and logFile path), STOP time process (and which user performed that command), and important informations about FS usage like type, time, FS name, usage in Kb at that moment, free space and percent of usage.
$cat /tmp/bdh_021819.log
START | 02/18/19-23:56:33 | Starting process in Deamon mode | PID: 9282 INTERVAL: 3600 | logFile: /tmp/bdh_021819.log
INFO | 02/19/19-13:33:56 | FS: tmpfs | Used: 32 kb | Free: 782368 kb | 1%
CRITICAL | 02/19/19-15:23:09 | FS: /dev/loop5 | Used: 80 kb | Free: 20 kb | 80%
URGENT | 02/19/19-15:23:09 | FS: /dev/loop8 | Used: 100 kb | Free: 0 kb | 100%
STOP | 02/19/19-15:23:10 | Process stopped by LEONARDO MACEDO
If Slack was set up to use Webhook APP and bdh was configured properly to sent HTTP REQUESTS to Webhook APP URL (see prerequisites topic for further information), slack will receive alarms from both thresholds: CRITICAL and URGENT sent by bdh -d process.
To customize FS usage thresholds, open bdh script using a text editor your choice and replace the lines below by the values you prefer Remember: All these values were set up using percent format. (e.g. the number "70" means "70%" of FS usage).
#set FS usage thresholds here:
Def_major="70"; #Set value for MAJOR FS usage.
Def_critical="85"; #Set value for CRITICAL FS usage.
Def_urgent="95"; #Set value for URGENT FS usage.
*PS: This setting will affect both: Manual and Automatic alerts.
To configure WebHook to allow Slack receives HTTP REQUESTS sent by bdh process, change the variable value below setting URL Webhook you got when install APP using the tutorial at prerequisites topic.
SlackWebHook="INSERT YOUR WEBHOOK URL HERE"
To change the directory where bdh will write the process log file, Open the bdh script using a text editor you prefer, locate, and change the value of variable logdir as showing below:
#Change here logdir (log will be generated only in daemon mode).
logdir="/tmp"
- Leonardo Macedo - MSc Software Engineering | Unix/Linux Sysadm, IT Consultant, DevOps Operations, Continuos Integration, Python, and Shell script
- mail|linkedin|github