E-LatentLPIPS [Project Page]
Diffusion2GAN: Distilling Diffusion Models into Conditional GANs (paper)
Minguk Kang, Richard Zhang, Connelly Barnes, Sylvain Paris, Suha Kwak, Jaesik Park, Eli Shechtman, Jun-Yan Zhu, Taesung Park. In ECCV, 2024.
This repository contains the author’s re-implementation of E-LatentLPIPS from my memory.
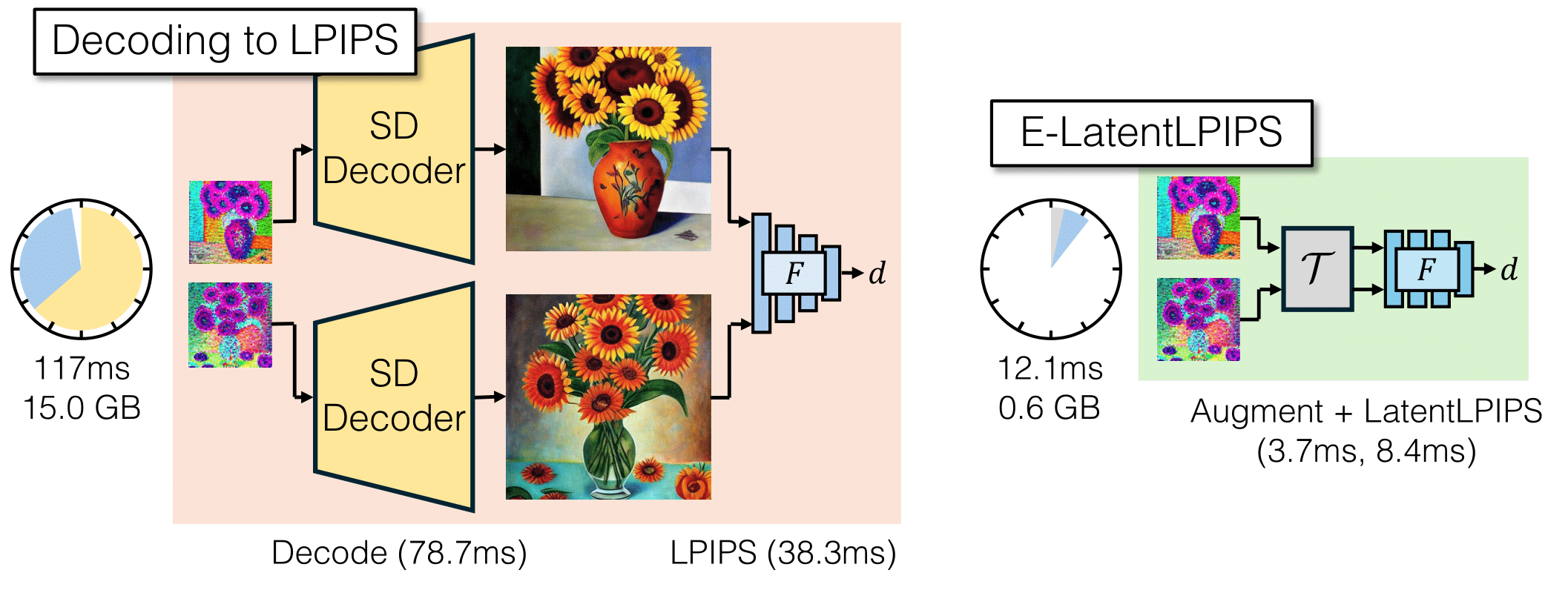
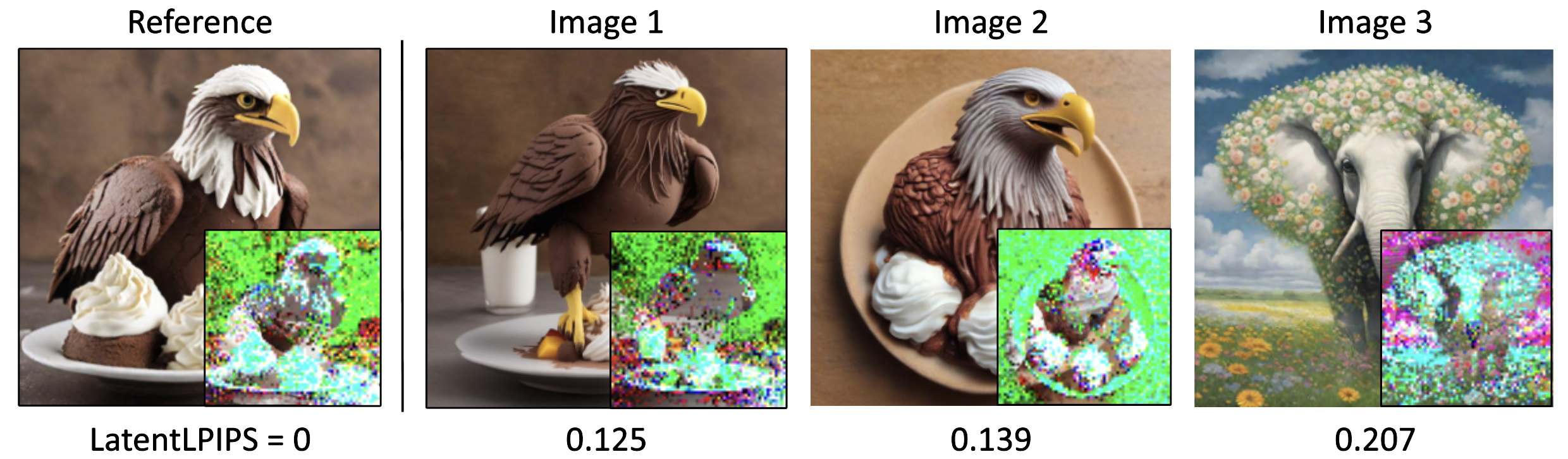
E-LatentLPIPS is a perceptual distance metric that operates directly in the latent space of a Latent Diffusion Model, allowing users to calculate perceptual distances for regression tasks without decoding the latents into pixel space. This bypasses the costly decoding process required by LPIPS, offering a 9.7× speed up and reducing memory usage.
We provide E-LatentLPIPS for five different Latent Diffusion Models: SD1.5, SD2.1, SDXL, SD3, and FLUX.
SD1.5 E-LatentLPIPSOperates in the 4-channel latent spaceSD2.1 E-LatentLPIPSOperates in the 4-channel latent space (identical to SD1.5)SDXL E-LatentLPIPSOperates in the 4-channel latent spaceSD3 E-LatentLPIPSOperates in the 16-channel latent spaceFLUX E-LatentLPIPSOperates in the 16-channel latent space
Each model supports the use of E-LatentLPIPS within its specific latent space configuration.
Option 1: Install using pip:
pip install elatentlpips
Option 2: Clone our repo and install dependencies.
git clone https://github.com/mingukkang/elatentlpips.git
cd elatentlpips
pip install -r requirements.txt
import torch
from diffusers import AutoencoderKL
from elatentlpips import ELatentLPIPS
# Load the VAE encoder and decoder from the FLUX model
# If you want to use the latest FLUX encoder, please ensure that you update your diffusers package to the latest version:
# 'pip install --upgrade diffusers[torch]'
vae = AutoencoderKL.from_pretrained("black-forest-labs/FLUX.1-dev", subfolder="vae").to("cuda")
# Initialize E-LatentLPIPS with the specified encoder model (options: sd15, sd21, sdxl, sd3, flux)
# The 'augment' parameter can be set to one of the following: b, bg, bgc, bgco
elatentlpips = ELatentLPIPS(encoder="flux", augment='bg').to("cuda").eval()
# Generate random images (ensure images are RGB and normalized to the range [-1, 1])
image0 = torch.zeros(1, 3, 512, 512).to("cuda") # First image (RGB, normalized)
image1 = torch.zeros(1, 3, 512, 512).to("cuda") # Second image (RGB, normalized)
# Encode the images into the latent space using the VAE
latent0 = vae.encode(image0).latent_dist.sample() # Encoded latent for image0
latent1 = vae.encode(image1).latent_dist.sample() # Encoded latent for image1
# Compute the perceptual distance between the two latent representations
# Note: Set `normalize=True` if the latents (latent0 and latent1) are not already normalized
# by `vae.config.scaling_factor` and `vae.config.shift_factor`.
distance = elatentlpips(latent0, latent1, normalize=True).mean()| Perceptual Metric | ImageNet Top-1 Acc. | BAPPS 2AFC Traditional | BAPPS 2AFC CNN |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPIPS | 73.36 | 73.36 | 82.20 |
| SD1.5-LatentLPIPS (paper) | 68.26 | 74.29 | 81.99 |
| SD1.5-LatentLPIPS | 69.91 | 73.68 | 81.77 |
| SD2.1-LatentLPIPS | 69.91 | 73.68 | 81.77 |
| SDXL-LatentLPIPS | 68.90 | 71.33 | 81.10 |
| SD3-LatentLPIPS | 71.10 | 76.15 | 82.63 |
| FLUX-LatentLPIPS | 66.18 | 75.00 | 82.47 |
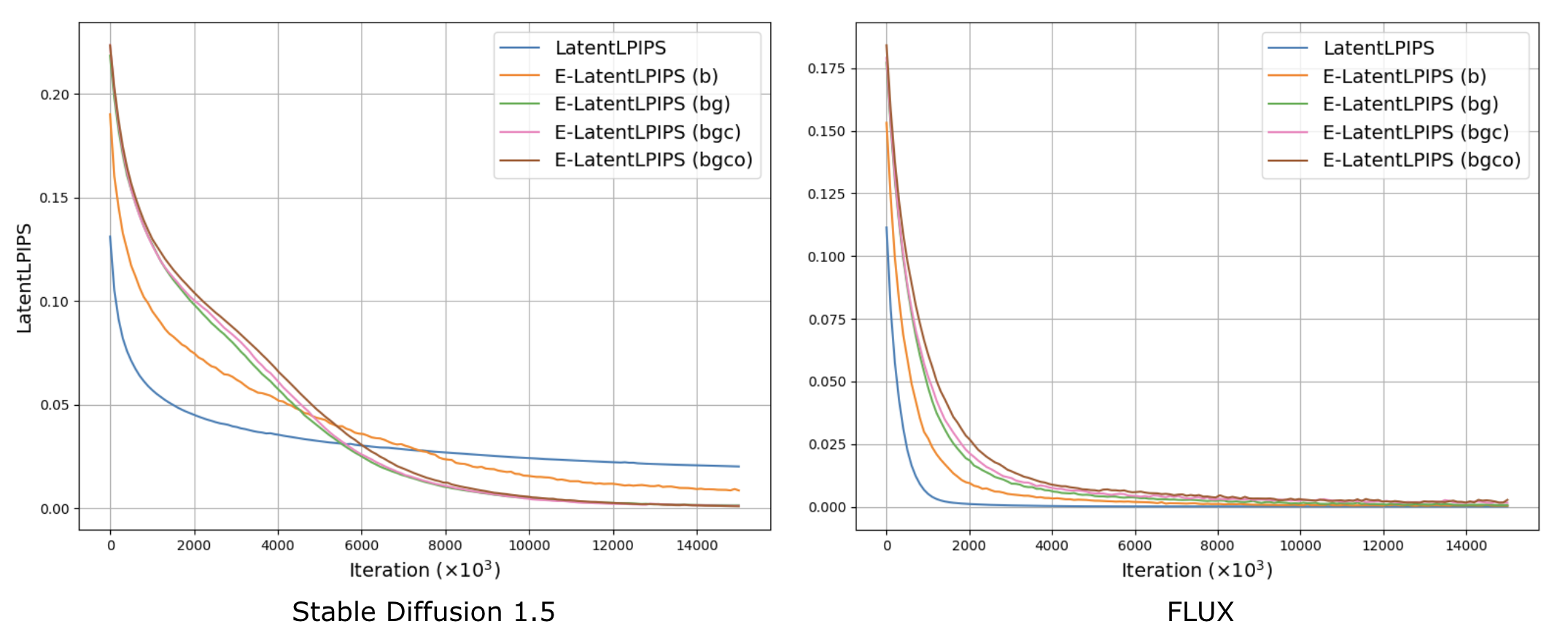
We perform overfitting experiments as outlined in Appendix B of the Diffusion2GAN paper. We observed that LatentLPIPS tends to exhibit a more favorable optimization landscape when using larger channel latent space, such as that of SD3 and FLUX.
Command: CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 overfitting_exp.py --encoder sd15 or flux
We use the following notations: b for pixel blitting, g for geometric transformations, c for color transformations, and o for cutout. Thus, E-LatentLPIPS (bg) refers to ensembled LatentLPIPS with pixel blitting and geometric transformations applied as augmentations.
LPIPS (BSD-2-Clause license): https://github.com/richzhang/PerceptualSimilarity
Differentiable Augmentation (MIT license): https://github.com/mit-han-lab/data-efficient-gans
ADA (NVIDIA source code license): https://github.com/NVlabs/stylegan2-ada-pytorch
E-LatentLPIPS is an open-source library under the CC-BY-NC license.
If you find E-LatentLPIPS useful in your research, please cite our work:
@inproceedings{kang2024diffusion2gan,
author = {Kang, Minguk and Zhang, Richard and Barnes, Connelly and Paris, Sylvain and Kwak, Suha and Park, Jaesik and Shechtman, Eli and Zhu, Jun-Yan and Park, Taesung},
title = {{Distilling Diffusion Models into Conditional GANs}},
booktitle = {European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV)},
year = {2024},
}