By Zidu Wang, Xiangyu Zhu, Tianshuo Zhang, Baiqin Wang and Zhen Lei.
This repository is the official implementation of 3DDFA_V3 in CVPR2024 (Highlight).
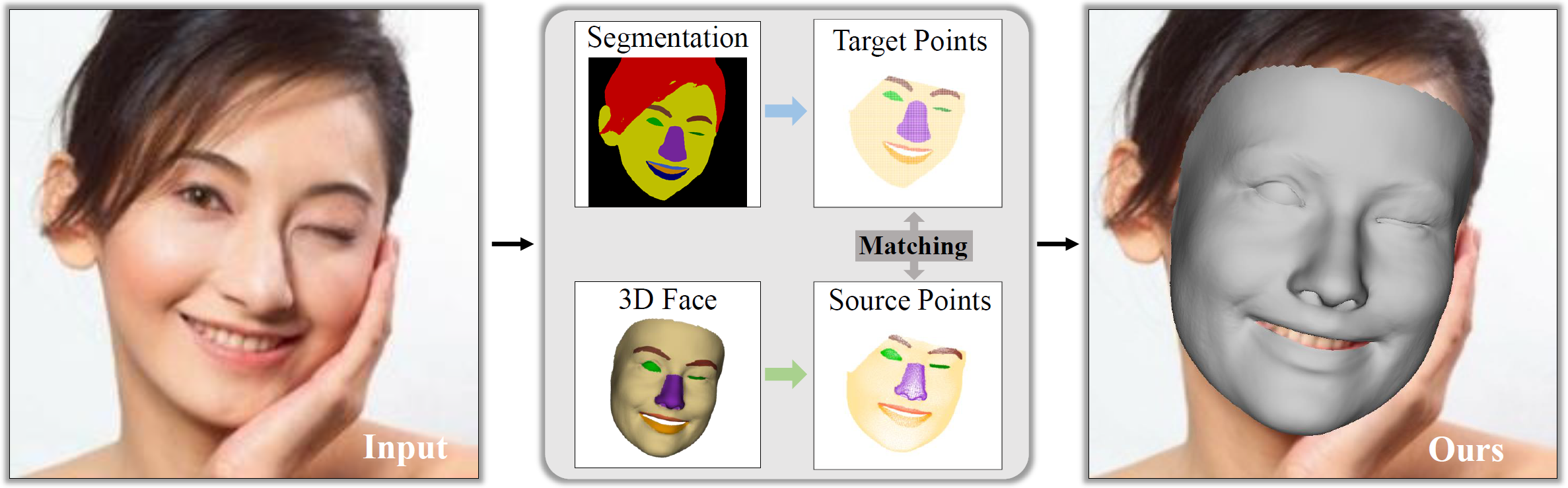
3DDFA_V3 uses the geometric guidance of facial part segmentation for face reconstruction, improving the alignment of reconstructed facial features with the original image and excelling at capturing extreme expressions. The key idea is to transform the target and prediction into semantic point sets, optimizing the distribution of point sets to ensure that the reconstructed regions and the target share the same geometry.
- [08/01/2024] We provide a fast CPU renderer based on face3d. It is capable of performing rendering inference functions similar to nvdiffrast.
- [06/14/2024] We provide a fast version based on MobileNet-V3, which achieves similar results to the ResNet-50 version at a higher speed. Please note that if your environment supports ResNet-50, we still strongly recommend using the ResNet-50 version. (The MobileNet-V3 version is still under testing, and we may update it further in the future.)
# Clone the repo:
git clone https://github.com/wang-zidu/3DDFA-V3
cd 3DDFA-V3
conda create -n TDDFAV3 python=3.8
conda activate TDDFAV3
# The pytorch version is not strictly required.
pip install torch==1.12.1+cu102 torchvision==0.13.1+cu102 torchaudio==0.12.1 --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu102
# or: conda install pytorch==1.12.1 torchvision==0.13.1 torchaudio==0.12.1 cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch
# On Windows 10, it has been verified that version 1.10 works. You can install it with the following command: pip install torch==1.10.0+cu102 torchvision==0.11.0+cu102 torchaudio==0.10.0 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Some results in the paper are rendered by pytorch3d and nvdiffrast
# This repository only uses nvdiffrast for convenience.
git clone https://github.com/NVlabs/nvdiffrast.git
cd nvdiffrast
pip install .
cd ..
# In some scenarios, nvdiffrast may not be usable. Therefore, we additionally provide a fast CPU renderer based on face3d.
# The results produced by the two renderers may have slight differences, but we consider these differences to be negligible.
# Please note that we still highly recommend using nvdiffrast.
cd util/cython_renderer/
python setup.py build_ext -i
cd ..
cd ..-
Please refer to this README to prepare assets and pretrained models.
-
Run demos.
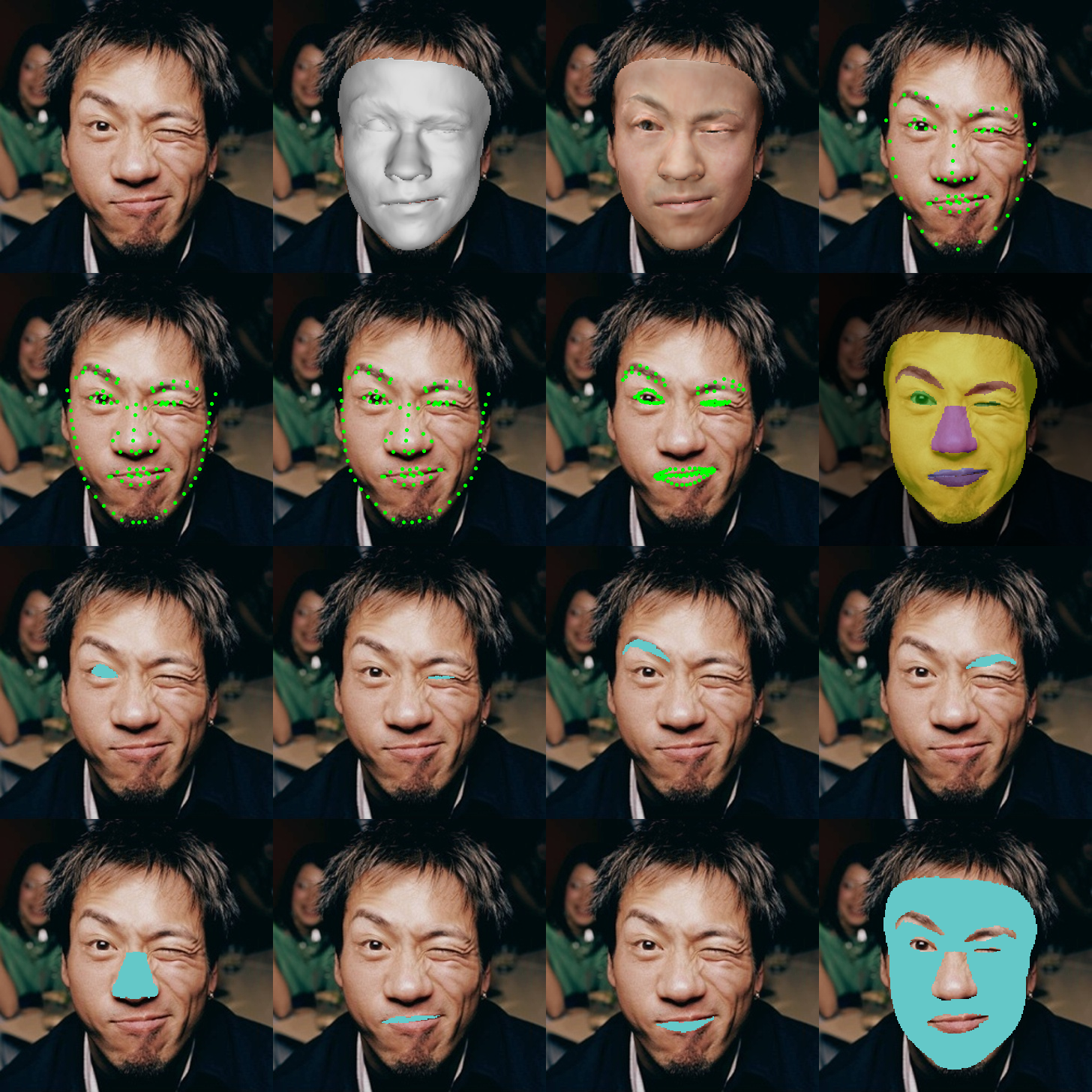
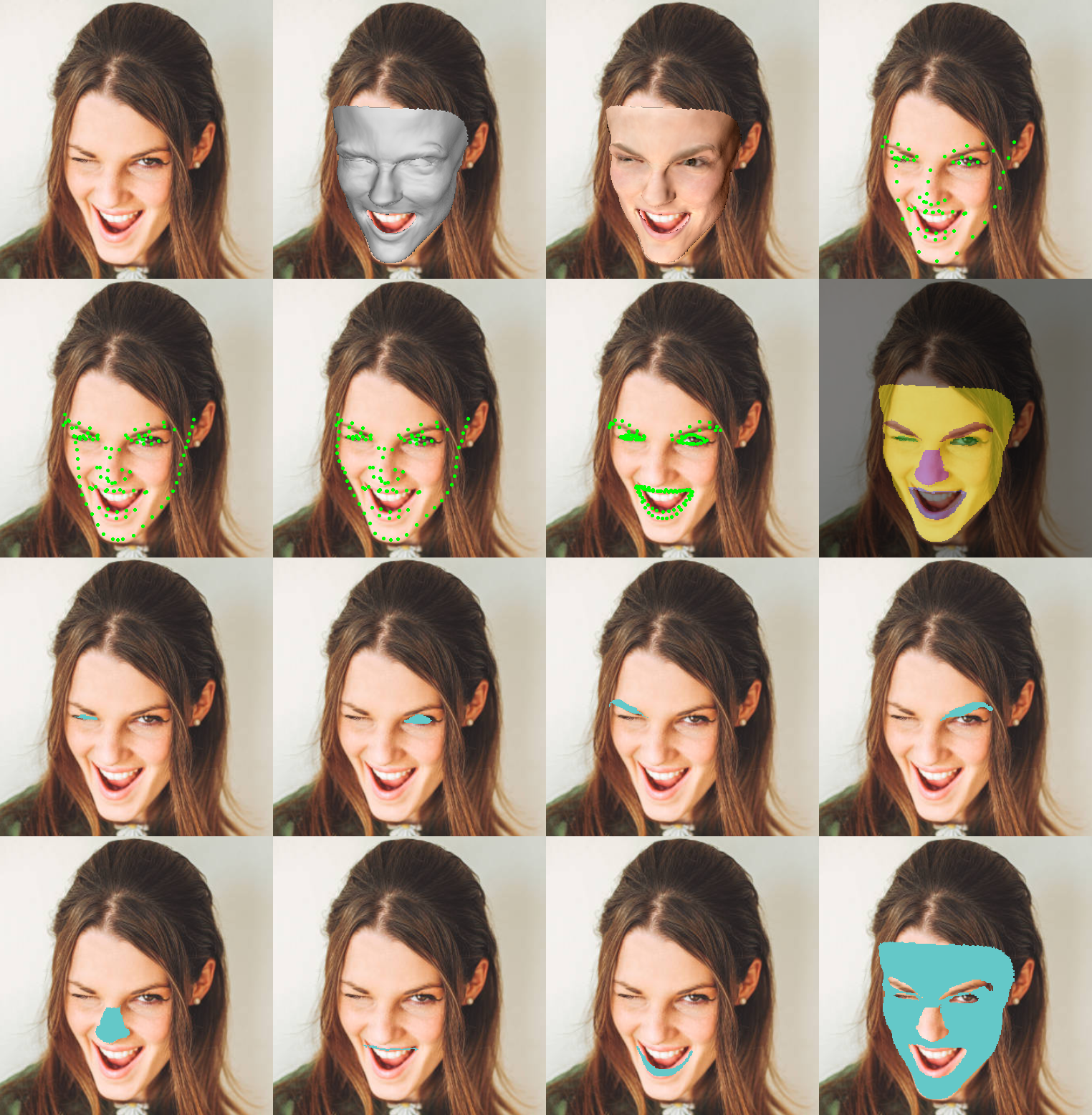
python demo.py --inputpath examples/ --savepath examples/results --device cuda --iscrop 1 --detector retinaface --ldm68 1 --ldm106 1 --ldm106_2d 1 --ldm134 1 --seg_visible 1 --seg 1 --useTex 1 --extractTex 1 --backbone resnet50-
--inputpath: path to the test data, should be a image folder. -
--savepath: path to the output directory, where results (obj, png files) will be stored. -
--iscrop: whether to crop input image, set false only when the test image are well cropped and resized into (224,224,3). -
--detector: face detector for cropping image, support for retinaface (recommended) and mtcnn. -
--ldm68,--ldm106,--ldm106_2dand--ldm134: save and show landmarks. -
--backbone: backbone for reconstruction, support for resnet50 and mbnetv3.
With the 3D mesh annotations provided by 3DDFA_V3, we can generate 2D facial segmentation results based on the 3D mesh:-
--seg_visible: save and show segmentation in 2D with visible mask. When a part becomes invisible due to pose changes, the corresponding region will not be displayed. All segmentation results of the 8 parts will be shown in a single subplot. -
--seg: save and show segmentation in 2D. When a part becomes invisible due to pose changes, the corresponding segmented region will still be displayed (obtained from 3D estimation), and the segmentation information of the 8 parts will be separately shown in 8 subplots.
We provide two types of 3D mesh files in OBJ format as output.-
--useTex: save .obj use texture from BFM model. -
--extractTex: save .obj use texture extracted from the input image. We use median-filtered-weight pca-texture for texture blending at invisible region (Poisson blending should give better-looking results).
-
-
Results.
image_name.png: the visualization results.image_name.npy: landmarks, segmentation, etc.image_name_pcaTex.obj: 3D mesh files in OBJ format using texture from the BFM model.image_name_extractTex.obj: 3D mesh files in OBJ format using texture extracted from the input image.
Please refer to this README to download our masks (annotations).
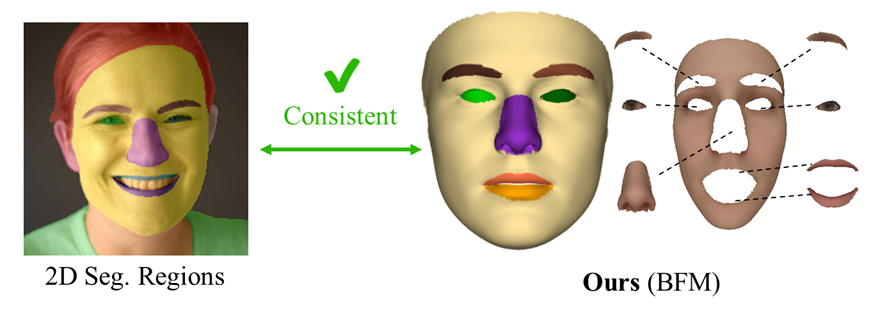
We provide a new 3D mesh part masks aligned with the semantic regions in 2D face segmentation. The current version is based on BFM (with 35,709 vertices), which shares the same topology as the face models used by Deep3D, MGCNet, HRN, etc. We also provide some other useful attributes.
Please refer to this README to download data.
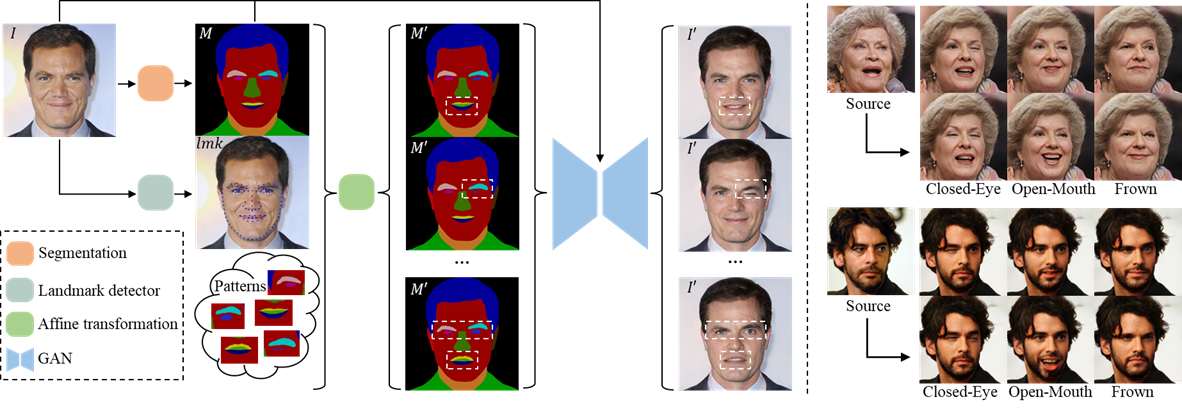
Based on MaskGan, we introduce a new synthetic face dataset including closed-eye, open-mouth, and frown expressions.
If you use our work in your research, please cite our publication:
@inproceedings{wang20243d,
title={3D Face Reconstruction with the Geometric Guidance of Facial Part Segmentation},
author={Wang, Zidu and Zhu, Xiangyu and Zhang, Tianshuo and Wang, Baiqin and Lei, Zhen},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
pages={1672--1682},
year={2024}
}
There are some functions or scripts in this implementation that are based on external sources. We thank the authors for their excellent works. Here are some great resources we benefit: Deep3D, DECA, HRN, 3DDFA-V2, Nvdiffrast, Pytorch3D, Retinaface, MTCNN, MaskGan, DML-CSR, REALY.
We plan to train 3DDFA_V3 with a larger dataset and switch to more strong backbones or face models. Additionally, we will provide a fast version based on MobileNet. If you have any suggestions or requirements, please feel free to contact us at [email protected].