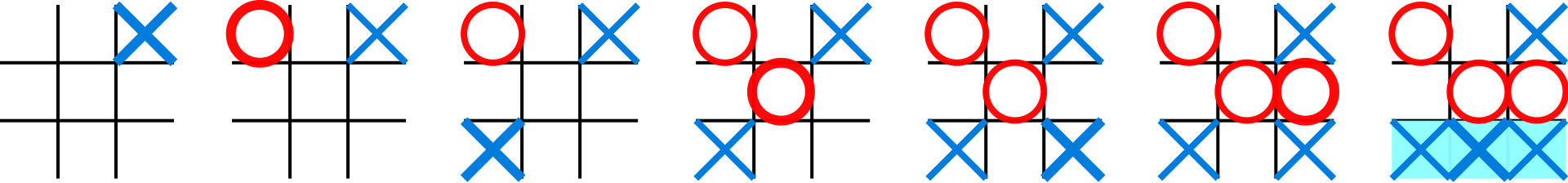
The British Museum algorithm is a general approach to find a solution by checking all possibilities one by one, beginning with the smallest.
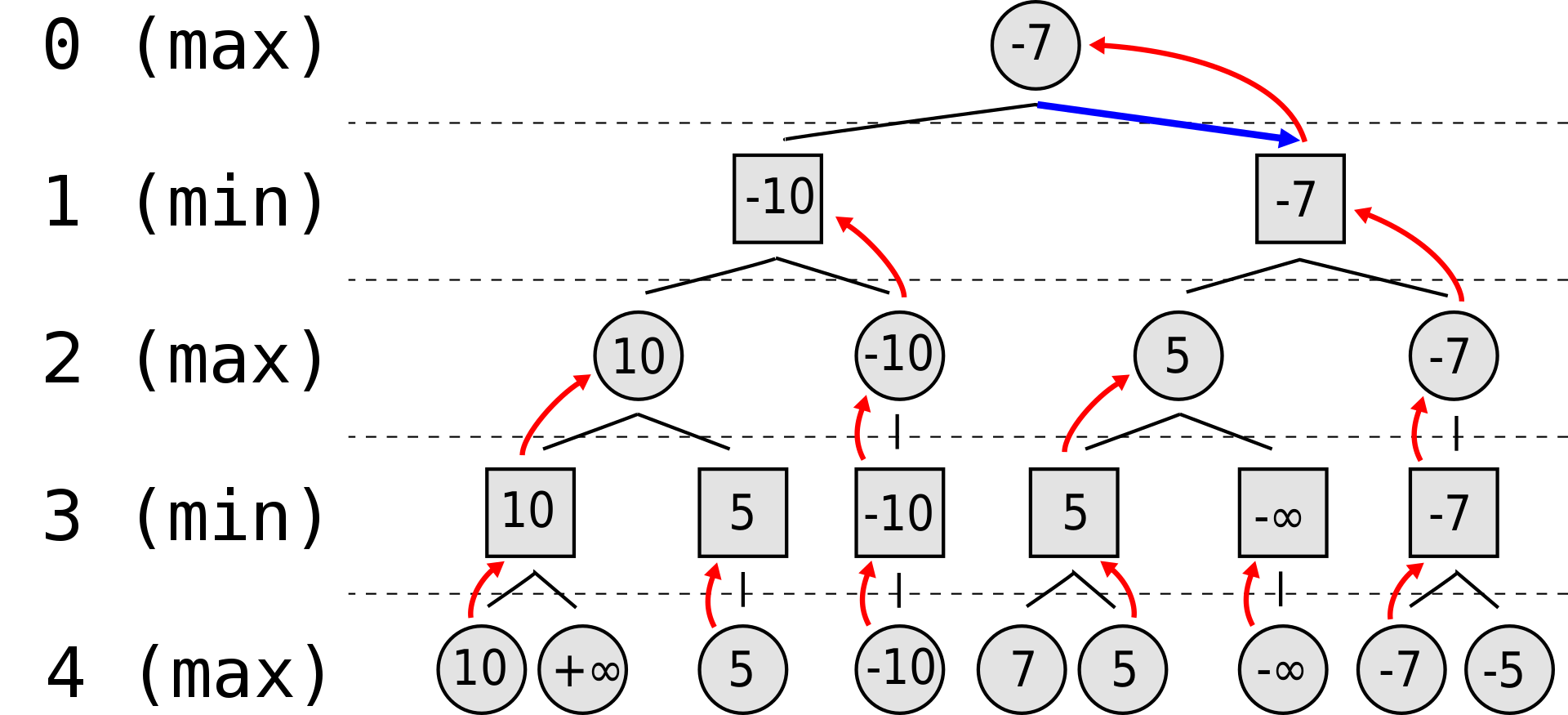
Minimax is a decision rule for minimizing the possible loss for a worst case (maximum loss) scenario. When dealing with gains, it is referred to as "maximin" — to maximize the minimum gain.
The maximin value of a player is the highest value that the player can be sure to get without knowing the actions of the other players; equivalently, it is the lowest value the other players can force the player to receive when they know the player's action.
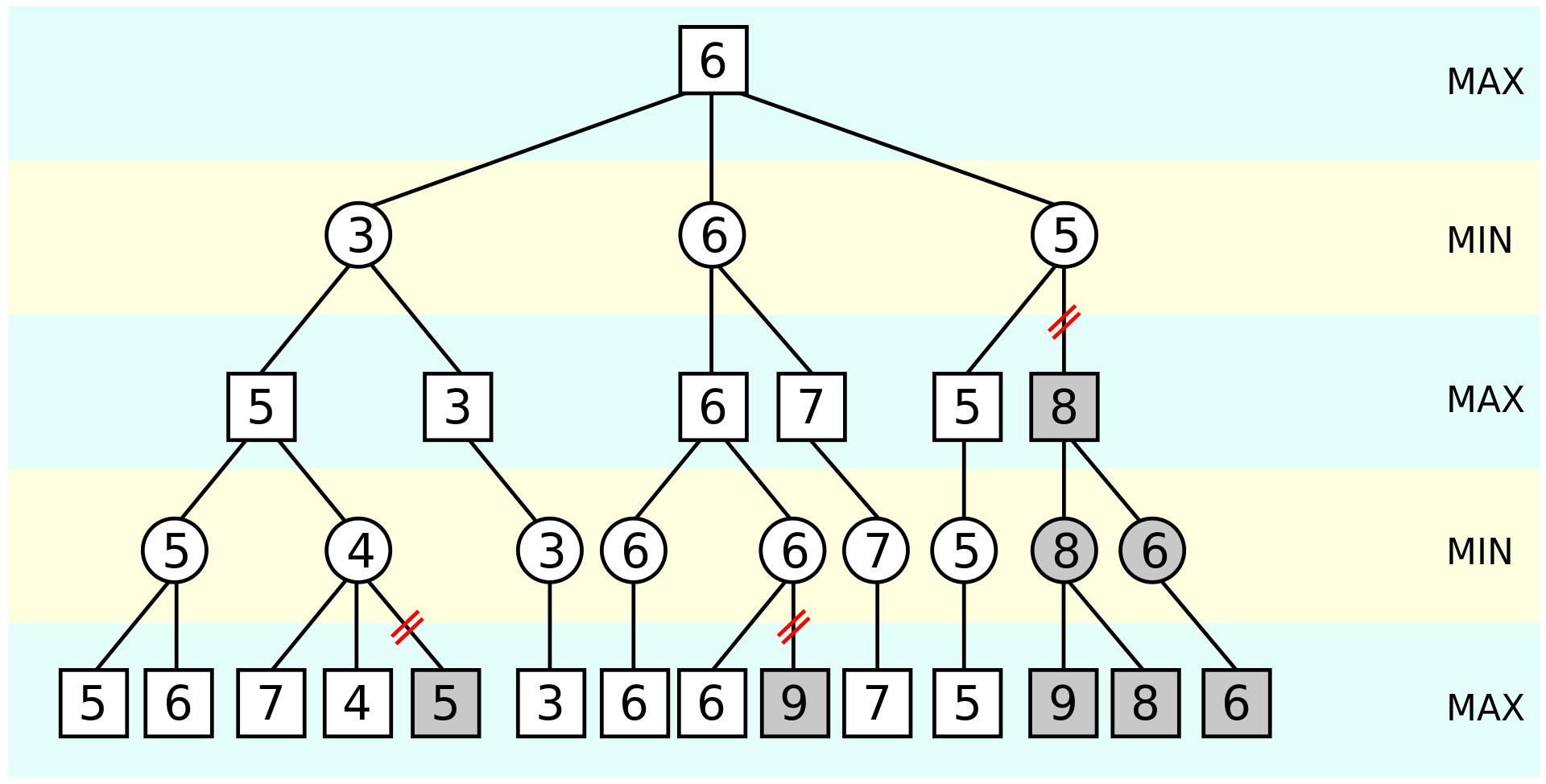
Alpha–beta pruning is a search algorithm that seeks to decrease the number of nodes that are evaluated by the minimax algorithm in its search tree.
The grayed-out subtrees don't need to be explored (when moves are evaluated from left to right), since we know the group of subtrees as a whole yields the value of an equivalent subtree or worse, and as such cannot influence the final result.
The pseudo-code for depth limited minimax with alpha-beta pruning is as follows:
function alphabeta(node, depth, α, β, maximizingPlayer) is
if depth = 0 or node is a terminal node then
return the heuristic value of node
if maximizingPlayer then
value := −∞
for each child of node do
value := max(value, alphabeta(child, depth − 1, α, β, FALSE))
α := max(α, value)
if α ≥ β then
break (* β cut-off *)
return value
else
value := +∞
for each child of node do
value := min(value, alphabeta(child, depth − 1, α, β, TRUE))
β := min(β, value)
if α ≥ β then
break (* α cut-off *)
return value